-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Venezuela was one of three countries that emerged from the collapse of Gran Colombia in 1830 (the others being Ecuador and New Granada, which became Colombia). For most of the first half of the 20th century, Venezuela was ruled by generally benevolent military strongmen, who promoted the oil industry and allowed for some social reforms. Democratically elected governments have held sway since 1959. Hugo CHAVEZ, president since 1999, seeks to implement his "21st Century Socialism," which purports to alleviate social ills while at the same time attacking capitalist globalization and existing democratic institutions. Current concerns include: a weakening of democratic institutions, political polarization, a politicized military, rampant violent crime, overdependence on the petroleum industry with its price fluctuations, and irresponsible mining operations that are endangering the rain forest and indigenous peoples.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
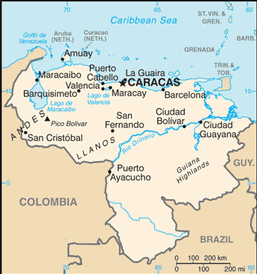
Northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, between Colombia and Guyana
|
|
|
|

|
|
8 00 N, 66 00 W
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 912,050 sq km
country comparison to the world: 33
land:
882,050 sq km
water:
30,000 sq km
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly more than twice the size of California
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 4,993 km
border countries:
Brazil 2,200 km, Colombia 2,050 km, Guyana 743 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,800 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
15 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands
|
|
|
|

|
|
Andes Mountains and Maracaibo Lowlands in northwest; central plains (llanos); Guiana Highlands in southeast
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point:
Pico Bolivar 5,007 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, bauxite, other minerals, hydropower, diamonds
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 2.85%
permanent crops:
0.88%
other:
96.27% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5,800 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,233.2 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 8.37 cu km/yr (6%/7%/47%)
per capita:
313 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
subject to floods, rockslides, mudslides; periodic droughts
|
|
|
|

|
|
sewage pollution of Lago de Valencia; oil and urban pollution of Lago de Maracaibo; deforestation; soil degradation; urban and industrial pollution, especially along the Caribbean coast; threat to the rainforest ecosystem from irresponsible mining operations
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed but not ratified::
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
on major sea and air routes linking North and South America; Angel Falls in the Guiana Highlands is the world's highest waterfall
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Venezuela |
|
|

|
|
noun: Venezuelan(s)
adjective:
Venezuelan
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Arab, German, African, indigenous people
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spanish (official), numerous indigenous dialects
|
|
|
|

|
|
nominally Roman Catholic 96%, Protestant 2%, other 2%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Although poverty in Venezuela has declined during the CHAVEZ administration, dropping from nearly 50% in 1999 to about 27% in 2011, it remains high and some experts question how much of a role social expenditures have played in this poverty reduction. Progress in lowering poverty, income inequality, and unemployment may in fact be more closely linked to the rise and fall of prices for oil, Venezuela's dominant export. In the long-run, education and healthcare spending may increase economic growth and reduce income inequality, but rising costs and the staffing of new healthcare jobs with foreigners are slowing development. In the meantime, social investment has led to better living standards, including increased school enrollment, a substantial reduction in infant and child mortality, and greater access to potable water and sanitation.
Since CHAVEZ came to power in 1999, more than a million predominantly middle- and upper-class Venezuelans are estimated to have emigrated. The brain drain is attributed to a repressive political system, lack of economic opportunities, steep inflation, a high crime rate, and corruption. Thousands of oil engineers emigrated to Canada, Colombia, and the United States following Chavez's firing of over 20,000 employees of the state-owned petroleum company during a 2002-2003 oil strike. Additionally, thousands of Venezuelans of European descent have taken up residence in their ancestral homelands. Nevertheless, Venezuela continues to attract immigrants from South America and southern Europe because of its lenient migration policy and the availability of education and healthcare. Venezuela also has been a fairly accommodating host to more than 200,000 Colombian refugees.
|
|
|
|

|
|
28,047,938 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 29% (male 4,147,023/ female 3,995,375)
15-64 years:
65.4% (male 9,025,781/ female 9,311,262)
65 years and over:
5.6% (male 692,321/ female 876,176) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 26.3 years
male:
25.6 years
female:
27.1 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.468% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.88 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.2 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 93% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.7% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
CARACAS (capital) 3.051 million; Maracaibo 2.153 million; Valencia 1.738 million; Barquisimeto 1.159 million; Maracay 1.04 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.79 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
92 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 20.18 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 95
male:
23.65 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
16.54 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 74.08 years
country comparison to the world: 111
male:
70.98 years
female:
77.34 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.4 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.94 physicians/1,000 population (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 93% of population
rural: 54% of population
total: 89% of population
unimproved:
urban: 7% of population
rural: 46% of population
total: 11% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA; note - no country specific models provided
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne disease:
dengue fever and malaria (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.7% (2007)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.7% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
93%
male:
93.3%
female:
92.7% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 14 years
male:
13 years
female:
15 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 13.6%
country comparison to the world: 83
male:
12.3%
female:
15.9% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
conventional short form:
Venezuela
local long form:
Republica Bolivariana de Venezuela
local short form:
Venezuela
|
|
|
|

|
|
federal republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Caracas
geographic coordinates:
10 29 N, 66 52 W
time difference:
UTC-4.5 (half an hour ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
23 states (estados, singular - estado), 1 capital district* (distrito capital), and 1 federal dependency** (dependencia federal); Amazonas, Anzoategui, Apure, Aragua, Barinas, Bolivar, Carabobo, Cojedes, Delta Amacuro, Dependencias Federales (Federal Dependencies)**, Distrito Capital (Capital District)*, Falcon, Guarico, Lara, Merida, Miranda, Monagas, Nueva Esparta, Portuguesa, Sucre, Tachira, Trujillo, Vargas, Yaracuy, Zulia
note:
the federal dependency consists of 11 federally controlled island groups with a total of 72 individual islands
|
|
|
|

|
|
5 July 1811 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 5 July (1811)
|
|
|
|

|
|
30 December 1999; amended 15 February 2009
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law system based on the Spanish civil code
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; state party to the ICCT
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Hugo CHAVEZ Frias (since 2 February 1999); Executive Vice President Nicolas MADURO Moros (since 13 October 2012); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Hugo CHAVEZ Frias (since 2 February 1999); Executive Vice President Nicolas MADURO Moros (since 13 October 2012)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a six-year term (eligible for unlimited reelection); election last held on 7 October 2012 (next election expected to be held in October 2018 pending official convocation by the country's electoral body)
note:
in 1999, a National Constituent Assembly drafted a new constitution that increased the presidential term to six years; an election was subsequently held on 30 July 2000 under the terms of this constitution; in 2009, a national referendum approved the elimination of term limits on all elected officials, including the presidency
election results:
Hugo CHAVEZ Frias reelected president; percent of vote - Hugo CHAVEZ Frias 55.07%, Henrique CAPRILES Radonski 44.31%, other 0.62%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Asamblea Nacional (165 seats; members elected by popular vote on a proportional basis to serve five-year terms; three seats reserved for the indigenous peoples of Venezuela)
elections:
last held on 26 September 2010 (next to be held in 2015)
election results:
percent of vote by party - pro-government 48.9%, opposition coalition 47.9%, other 3.2%; seats by party - pro-government 98, opposition 65, other 2
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Tribunal of Justice or Tribunal Supremo de Justicia (32 magistrates are elected by the National Assembly for a single 12-year term)
|
|
|
|

|
|
A New Time or UNT [Omar BARBOZA]; Brave People's Alliance or ABP [Antonio LEDEZMA]; Christian Democrats or COPEI [Roberto ENRIQUEZ]; Communist Party of Venezuela or PCV [Oscar FIGUERA]; Democratic Action or AD [Henry RAMOS ALLUP]; Fatherland for All or PPT [Rafael UZCATEGUI]; For Social Democracy or PODEMOS [Ismael GARCIA]; Justice First [Julio BORGES]; Movement Toward Socialism or MAS [Nicolas SOSA]; Popular Will or VP [Leopoldo LOPEZ]; Progressive Wave or AP [Henri FALCON]; The Democratic Unity Table or MUD [Ramon Guillermo AVELEDO]; The Radical Cause [Daniel SANTOLO]; United Socialist Party of Venezuela or PSUV [Hugo CHAVEZ]; Venezuelan Progressive Movement or MPV [Simon CALZADILLA]; Venezuela Project or PV [Henrique SALAS ROMER]
|
|
|
|

|
|
Bolivarian and Socialist Workers' Union (a ruling party labor union); Confederacion Venezolana de Industriales or Coindustria (a conservative business group); Consejos Comunales (pro-Chavez local cooperatives); FEDECAMARAS (a conservative business group); Union of Oil Workers of Venezuela or FUTPV; Venezuelan Confederation of Workers or CTV (opposition-oriented labor organization); various civil society groups and human rights organizations
|
|
|
|

|
|
Caricom (observer), CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, LAS (observer), Mercosur, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Angelo RIVERO Santos
chancery:
1099 30th Street NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 342-2214
FAX:
[1] (202) 342-6820
consulate(s) general:
Boston, Chicago, Houston, Miami (administratively closed), New Orleans, New York, San Francisco, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires James M. DERHAM
embassy:
Calle F con Calle Suapure, Urbanizacion Colinas de Valle Arriba, Caracas 1080
mailing address:
P. O. Box 62291, Caracas 1060-A; APO AA 34037
telephone:
[58] (212) 975-6411, 907-8400 (after hours)
FAX:
[58] (212) 907-8199
|
|
|
|

|
|
three equal horizontal bands of yellow (top), blue, and red with the coat of arms on the hoist side of the yellow band and an arc of eight white five-pointed stars centered in the blue band; the flag retains the three equal horizontal bands and three main colors of the banner of Gran Colombia, the South American republic that broke up in 1830; yellow is interpreted as standing for the riches of the land, blue for the courage of its people, and red for the blood shed in attaining independence; the seven stars on the original flag represented the seven provinces in Venezuela that united in the war of independence; in 2006, President Hugo CHAVEZ ordered an eighth star added to the star arc - a decision that sparked much controversy - to conform with the flag proclaimed by Simon Bolivar in 1827 and to represent the province of Guayana
|
|
|
|

|
|
troupial (bird)
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Gloria al bravo pueblo" (Glory to the Brave People)
lyrics/music:
Vicente SALIAS/Juan Jose LANDAETA
note:
adopted 1881; the lyrics were written in 1810, the music some years later; both SALIAS and LANDAETA were executed in 1814 during Venezuela's struggle for independence
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Venezuela remains highly dependent on oil revenues, which account for roughly 95% of export earnings, about 45% of federal budget revenues, and around 12% of GDP. Fueled by high oil prices, record government spending helped to boost GDP growth by 4.2% in 2011, after a sharp drop in oil prices caused an economic contraction in 2009-10. Government spending, minimum wage hikes, and improved access to domestic credit created an increase in consumption which combined with supply problems to cause higher inflation - roughly 26% in 2011 and 21% in 2012. President Hugo CHAVEZ's efforts to increase the government's control of the economy by nationalizing firms in the agribusiness, financial, construction, oil, and steel sectors have hurt the private investment environment, reduced productive capacity, and slowed non-petroleum exports. In the first half of 2010 Venezuela faced the prospect of lengthy nationwide blackouts when its main hydroelectric power plant - which provides more than 35% of the country's electricity - nearly shut down. In May 2010, CHAVEZ closed the unofficial foreign exchange market - the "parallel market" - in an effort to stem inflation and slow the currency's depreciation. In June 2010, the government created the "Transaction System for Foreign Currency Denominated Securities" to replace the "parallel" market. In December 2010, CHAVEZ eliminated the dual exchange rate system and unified the exchange rate at 4.3 bolivars per dollar. In January 2011, CHAVEZ announced the second devaluation of the bolivar within twelve months. In December 2010, the National Assembly passed a package of five organic laws designed to complete the transformation of the Venezuelan economy in line with CHAVEZ's vision of 21st century socialism. In 2012, Venezuela continued to wrestle with a housing crisis, high inflation, an electricity crisis, and rolling food and goods shortages - all of which were fallout from the government's unorthodox economic policies. The budget deficit for the entire government reached 17% of GDP in 2012, and public debt as a percent of GDP climbed steeply to 49%, despite record oil prices.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$402.1 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$380.2 billion (2011 est.)
$364.9 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$338 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.7% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
4.2% (2011 est.)
-1.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$13,200 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
$12,800 (2011 est.)
$12,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 3.7%
industry:
35.3%
services:
61.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.7 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 7.3%
industry:
21.8%
services:
70.9% (4th quarter, 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
8.2% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
31.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.7%
highest 10%:
32.7% (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
39 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 68
49.5 (1998)
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $116.3 billion
expenditures:
$175.3 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
34.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|

|
|
-17.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
|
|
|
|

|
|
49% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
29% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
data cover central government debt, as well as the debt of state-owned oil company PDVSA; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include some debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; some debt instruments for the social funds are sold at public auctions.
|
|
|
|

|
|
20.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 217
26.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
29.5% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 4
29.5% (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
16.5% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
17.15% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$175.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$110.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$188.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
$115.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$176.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
$92.82 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.143 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 87
$3.991 billion (31 December 2010)
$8.86 billion (31 December 2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
corn, sorghum, sugarcane, rice, bananas, vegetables, coffee; beef, pork, milk, eggs; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.4% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|

|
|
$20.6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$27.21 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$96.9 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$92.6 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, bauxite and aluminum, minerals, chemicals, agricultural products, basic manufactures
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 40.2%, China 10.5%, India 5.5%, Cuba 4% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$56.69 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$46.44 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
agricultural products, livestock, raw materials, machinery and equipment, transport equipment, construction materials, medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, iron and steel products
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 28.6%, China 15.1%, Brazil 10.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$25.23 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$29.89 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$63.74 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$89.6 billion (30 September 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$49.6 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$45.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$21.95 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
$19.81 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bolivars (VEB) per US dollar -
4.289 (2012 est.)
4.289 (2011 est.)
2.5821 (2010 est.)
2.147 (2009)
2.147 (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
123.1 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|

|
|
85.85 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|

|
|
633 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|

|
|
260 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.85 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|

|
|
41.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198
|
|
|
|

|
|
58.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.453 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.691 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|

|
|
209.4 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.176 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|

|
|
755,400 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|

|
|
627,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|

|
|
116,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|

|
|
31.2 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|

|
|
33.1 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.446 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.524 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
158.4 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Venezuela |
|
|

|
|
7.332 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|

|
|
28.782 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: modern and expanding
domestic:
domestic satellite system with 3 earth stations; recent substantial improvement in telephone service in rural areas; substantial increase in digitalization of exchanges and trunk lines; installation of a national interurban fiber-optic network capable of digital multimedia services; combined fixed and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership 130 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 58; submarine cable systems provide connectivity to the Caribbean, Central and South America, and US; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) and 1 PanAmSat; participating with Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia in the construction of an international fiber-optic network; constructing submarine cable to provide connectivity to Cuba with an estimated date of completion in late 2011 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
government supervises a mixture of state-run and private broadcast media; 1 state-run TV network, 4 privately-owned TV networks, a privately-owned news channel with limited national coverage, and a government-backed pan-American channel; state-run radio network includes 65 news stations and roughly another 30 stations targeted at specific audiences; state-sponsored community broadcasters include 244 radio stations and 36 TV stations; the number of private broadcast radio stations has been declining, but many still remain in operation (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.ve
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.016 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.918 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Venezuela |
|
|

|
|
492 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 128
over 3,047 m:
6
2,438 to 3,047 m:
9
1,524 to 2,437 m:
35
914 to 1,523 m:
61
under 914 m:
17 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 364
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
55
914 to 1,523 m:
113
under 914 m:
193 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
extra heavy crude 980 km; gas 5,347 km; oil 6,694 km; refined products 1,620 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 806 km
country comparison to the world: 98
standard gauge:
806 km 1.435-m gauge (41 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 96,155 km
country comparison to the world: 44
paved:
32,308 km
unpaved:
63,847 km (2002)
|
|
|
|

|
|
7,100 km (the Orinoco River (400 km) and Lake de Maracaibo are navigable by oceangoing vessels) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 53
country comparison to the world: 69
by type:
bulk carrier 4, cargo 12, chemical tanker 1, liquefied gas 5, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 14, petroleum tanker 16
foreign-owned:
9 (Denmark 1, Estonia 1, Germany 1, Greece 4, Mexico 1, Spain 1)
registered in other countries:
14 (Panama 13, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
La Guaira, Maracaibo, Puerto Cabello, Punta Cardon
oil terminals:
Jose terminal
|
|
|
|

|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Caribbean Sea as a significant risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous vessels, including commercial shipping and pleasure craft, have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; crews have been robbed and stores or cargoes stolen
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Bolivarian National Armed Forces (Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana, FANB): Bolivarian National Army (Ejercito Nacional Bolivariano, ENB), Bolivarian Navy (Armada Bolivariana, AB; includes Naval Infantry, Coast Guard, Naval Aviation), Bolivarian Military Aviation (Aviacion Militar Bolivariana, AMB), Bolivarian National Guard (Guardia Nacional Bolivaria, GNB) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18-30 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; 30-month conscript service obligation; Navy requires 6th-grade education for enlisted personnel; all citizens of military service age (18-60 years old) are obligated to register for military service (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 7,013,854
females age 16-49:
7,165,661 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 5,614,743
females age 16-49:
6,074,834 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 277,210
female:
273,353 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.2% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Venezuela |
|
|

|
|
claims all of the area west of the Essequibo River in Guyana, preventing any discussion of a maritime boundary; Guyana has expressed its intention to join Barbados in asserting claims before the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea that Trinidad and Tobago's maritime boundary with Venezuela extends into their waters; dispute with Colombia over maritime boundary and Venezuelan administered Los Monjes islands near the Gulf of Venezuela; Colombian organized illegal narcotics and paramilitary activities penetrate Venezuela's shared border region; in 2006, an estimated 139,000 Colombians sought protection in 150 communities along the border in Venezuela; US, France, and the Netherlands recognize Venezuela's granting full effect to Aves Island, thereby claiming a Venezuelan Economic Exclusion Zone/continental shelf extending over a large portion of the eastern Caribbean Sea; Dominica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines protest Venezuela's full effect claim
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 201,941 (Colombia) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
current situation: Venezuela is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of commercial sexual exploitation and forced labor; Venezuelan women and girls are trafficked within the country for sexual exploitation, lured from the nation's interior to urban and tourist areas; to a lesser extent, Brazilian women and Colombian women are subjected to forced prostitution; some Venezuelan women are transported to Caribbean islands, particularly Aruba, Curacao, and Trinidad & Tobago, where they are subjected to forced prostitution
tier rating:
Tier 3 - the government investigated potential cases of suspected human trafficking and arrested at least 12 people for trafficking crimes during the reporting period; however, there was no further publicly available information regarding those cases; Venezuela is not making significant efforts to comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
small-scale illicit producer of opium and coca for the processing of opiates and coca derivatives; however, large quantities of cocaine, heroin, and marijuana transit the country from Colombia bound for US and Europe; significant narcotics-related money-laundering activity, especially along the border with Colombia and on Margarita Island; active eradication program primarily targeting opium; increasing signs of drug-related activities by Colombian insurgents on border
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

