-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
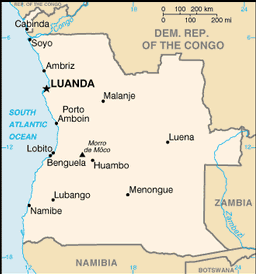
|
Click map to enlarge 
|
|

|
| |
| no photos available of Angola |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Angola is rebuilding its country after the end of a 27-year civil war in 2002. Fighting between the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS, and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), led by Jonas SAVIMBI, followed independence from Portugal in 1975. Peace seemed imminent in 1992 when Angola held national elections, but fighting picked up again by 1996. Up to 1.5 million lives may have been lost - and 4 million people displaced - in the quarter century of fighting. SAVIMBI's death in 2002 ended UNITA's insurgency and strengthened the MPLA's hold on power. President DOS SANTOS pushed through a new constitution in 2010 and held elections in 2012.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and Democratic Republic of the Congo
|
|
|
|

|
|
12 30 S, 18 30 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1,246,700 sq km
country comparison to the world: 23
land:
1,246,700 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly less than twice the size of Texas
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5,198 km
border countries:
Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,511 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province), Republic of the Congo 201 km, Namibia 1,376 km, Zambia 1,110 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,600 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|

|
|
semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April)
|
|
|
|

|
|
narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateau
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Morro de Moco 2,620 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 2.65%
permanent crops:
0.23%
other:
97.12% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
800 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
184 cu km (1987)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 0.35 cu km/yr (23%/17%/60%)
per capita:
22 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateau
|
|
|
|

|
|
overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion attributable to population pressures; desertification; deforestation of tropical rain forest, in response to both international demand for tropical timber and to domestic use as fuel, resulting in loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and siltation of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable water
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Angola |
|
|

|
|
noun: Angolan(s)
adjective:
Angolan
|
|
|
|

|
|
Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portuguese (official), Bantu and other African languages
|
|
|
|

|
|
indigenous beliefs 47%, Roman Catholic 38%, Protestant 15% (1998 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18,056,072 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 43.9% (male 4,041,055/ female 3,884,175)
15-64 years:
53.2% (male 4,845,463/ female 4,763,480)
65 years and over:
2.9% (male 241,421/ female 280,478) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 17.7 years
male:
17.5 years
female:
17.9 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.784% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|

|
|
39.36 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.06 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.55 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 59% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
LUANDA (capital) 4.511 million; Huambo 979,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.86 male(s)/female
total population:
1.02 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
450 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 83.53 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 8
male:
87.39 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
79.47 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 54.59 years
country comparison to the world: 202
male:
53.49 years
female:
55.73 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.54 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.8 beds/1,000 population (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 86% of population
rural: 18% of population
total: 57% of population
unimproved:
urban: 14% of population
rural: 82% of population
total: 43% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|

|
|
200,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|

|
|
11,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria, African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
27.5% (2001)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.6% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
70.1%
male:
82.7%
female:
58.1% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 9 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Angola
conventional short form:
Angola
local long form:
Republica de Angola
local short form:
Angola
former:
People's Republic of Angola
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic; multiparty presidential regime
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Luanda
geographic coordinates:
8 50 S, 13 13 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Bengo, Benguela, Bie, Cabinda, Kwando Kubango, Kwanza Norte, Kwanza Sul, Cunene, Huambo, Huila, Luanda, Lunda Norte, Lunda Sul, Malanje, Moxico, Namibe, Uige, Zaire
|
|
|
|

|
|
11 November 1975 (from Portugal)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 11 November (1975)
|
|
|
|

|
|
adopted by National Assembly 5 February 2010
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil legal system based on Portuguese civil law; no judicial review of legislation
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS (since 21 September 1979); Vice President Manuel Domingos VICENTE (since 26 September 2012); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS (since 21 September 1979); Vice President Manuel Domingos VICENTE (since 26 September 2012)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president indirectly elected by National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second consecutive or discontinuous term) under the 2010 constitution; President DOS SANTOS was selected by the party to take over after the death of former President Augustino NETO (1979) under a one-party system and stood for reelection in Angola's first multiparty elections on 29-30 September 1992 but the election was suspended; following the results of the 2012 legislative elections Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS was indirectly elected president(elligible for a second term)
election results:
NA; Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS was indirectly elected president by the National Assembly following legislative elections on 31 August 2012; DOS SANTOS was inaugurated on 26 September 2012 to serve the first of a possible two terms under the 2010 constitution
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Assembleia Nacional (220 seats; members elected by proportional vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 31 August 2012 (next to be held in 2016)
election results:
percent of vote by party - MPLA 71.8%, UNITA 18.7%, CASA-CE 6.0%, PRS 1.7%, FNLA 1.1%, other 0.8%; seats by party - MPLA 175, UNITA 32, CASA-CE 8, PRS 3, FNLA 2
|
|
|
|

|
|
Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional; Supreme Court or Tribunal Supremo; Court of Auditions or Tribunal de Contas; Supreme Military Court or Supremo Tribunal Militar; judges for all courts appointed by the president
|
|
|
|

|
|
Broad Convergence for Salvation of Angola Electoral Coalition or CASA-CE [Abel CHIVUKUVUKU]; National Front for the Liberation of Angola or FNLA [Lucas NGONDA]; National Union for the Total Independence of Angola or UNITA [Isaias SAMAKUVA] (largest opposition party); New Democracy Electoral Union or ND [Quintino de MOREIRA]; Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola or MPLA [Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS] (ruling party in power since 1975); Social Renewal Party or PRS [Eduardo KUANGANA]
note:
21 other parties registered to participate in the national election in August 2012
|
|
|
|

|
|
Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda or FLEC [N'zita Henriques TIAGO, Antonio Bento BEMBE]
note:
FLEC's small-scale armed struggle for the independence of Cabinda Province persists despite the signing of a peace accord with the government in August 2006
|
|
|
|

|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, CPLP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OPEC, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Alberto do Carmo BENTO RIBEIRO
chancery:
2108 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 785-1156
FAX:
[1] (202) 785-1258
consulate(s) general:
Houston, New York
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Christopher J. MCMULLEN
embassy:
number 32 Rua Houari Boumedienne (in the Miramar area of Luanda), Luanda
mailing address:
international mail: Caixa Postal 6468, Luanda; pouch: US Embassy Luanda, US Department of State, 2550 Luanda Place, Washington, DC 20521-2550
telephone:
[244] (222) 64-1000
FAX:
[244] (222) 64-1232
|
|
|
|

|
|
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and black with a centered yellow emblem consisting of a five-pointed star within half a cogwheel crossed by a machete (in the style of a hammer and sickle); red represents liberty, black the African continent, the symbols characterize workers and peasants
|
|
|
|

|
|
sable antelope
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Angola Avante" (Forward Angola)
lyrics/music:
Manuel Rui Alves MONTEIRO/Rui Alberto Vieira Dias MINGAO
note:
adopted 1975
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Angola's high growth rate in recent years was driven by high international prices for its oil. Angola became a member of OPEC in late 2006 and its current assigned a production quota of 1.65 million barrels a day (bbl/day). Oil production and its supporting activities contribute about 85% of GDP. Diamond exports contribute an additional 5%. Subsistence agriculture provides the main livelihood for most of the people, but half of the country's food is still imported. Increased oil production supported growth averaging more than 17% per year from 2004 to 2008. A postwar reconstruction boom and resettlement of displaced persons has led to high rates of growth in construction and agriculture as well. Much of the country's infrastructure is still damaged or undeveloped from the 27-year-long civil war. Land mines left from the war still mar the countryside, even though peace was established after the death of rebel leader Jonas SAVIMBI in February 2002. Since 2005, the government has used billions of dollars in credit lines from China, Brazil, Portugal, Germany, Spain, and the EU to rebuild Angola's public infrastructure. The global recession that started in 2008 temporarily stalled economic growth. Lower prices for oil and diamonds during the global recession slowed GDP growth to 2.4% in 2009, and many construction projects stopped because Luanda accrued $9 billion in arrears to foreign construction companies when government revenue fell in 2008 and 2009. Angola abandoned its currency peg in 2009, and in November 2009 signed onto an IMF Stand-By Arrangement loan of $1.4 billion to rebuild international reserves. Consumer inflation declined from 325% in 2000 to about 10% in 2012. Higher oil prices have helped Angola turn a budget deficit of 8.6% of GDP in 2009 into an surplus of 12% of GDP in 2012. Corruption, especially in the extractive sectors, also is a major challenge.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$126.2 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
$118.1 billion (2011 est.)
$113.7 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$114.8 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
3.9% (2011 est.)
3.4% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$6,200 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
$6,000 (2011 est.)
$6,000 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 9.6%
industry:
65.8%
services:
24.6% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.468 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 85%
industry and services:
15% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
40.5% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 0.6%
highest 10%:
44.7% (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $56.07 billion
expenditures:
$42.26 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
48.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|

|
|
12% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|

|
|
17.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
18.1% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
13.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
25% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
30% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
16% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
18.76% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$12.93 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
$11.58 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$44.65 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
$36.55 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$27.12 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
$22.18 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bananas, sugarcane, coffee, sisal, corn, cotton, cassava (manioc), tobacco, vegetables, plantains; livestock; forest products; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
$17.09 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$15.92 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$71.95 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
$65.8 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
crude oil, diamonds, refined petroleum products, coffee, sisal, fish and fish products, timber, cotton
|
|
|
|

|
|
China 38.1%, US 21.2%, India 9.2%, Canada 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$22.32 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
$19.75 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery and electrical equipment, vehicles and spare parts; medicines, food, textiles, military goods
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portugal 20.5%, China 17.8%, US 9.6%, Brazil 6.9%, South Africa 5.7%, France 5.1% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$34.63 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
$27.01 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$19.65 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
$18.78 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$115.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$101.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$8.196 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$6.346 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
kwanza (AOA) per US dollar -
95.54 (2012 est.)
93.741 (2011 est.)
91.906 (2010 est.)
79.33 (2009)
75.023 (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.08 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.659 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.155 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|

|
|
56.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|

|
|
43.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.84 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.757 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|

|
|
15 billion bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|

|
|
37,310 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|

|
|
79,430 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|

|
|
31,050 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|

|
|
41,480 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|

|
|
734 million cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
|
|
|
|

|
|
733 million cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|

|
|
310 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.2 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
303,200 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.491 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: limited system; state-owned telecom had monopoly for fixed-lines until 2005; demand outstripped capacity, prices were high, and services poor; Telecom Namibia, through an Angolan company, became the first private licensed operator in Angola's fixed-line telephone network; by 2010, the number of fixed-line providers had expanded to 5; Angola Telecom established mobile-cellular service in Luanda in 1993 and the network has been extended to larger towns; a privately-owned, mobile-cellular service provider began operations in 2001
domestic:
only about two fixed-lines per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity about 50 telephones per 100 persons in 2011
international:
country code - 244; landing point for the SAT-3/WASC fiber-optic submarine cable that provides connectivity to Europe and Asia; satellite earth stations - 29 (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
state controls all broadcast media with nationwide reach; state-owned Televisao Popular de Angola (TPA) provides terrestrial TV service on 2 channels; a third TPA channel is available via cable and satellite; TV subscription services are available; state-owned Radio Nacional de Angola (RNA) broadcasts on 5 stations; about a half dozen private radio stations broadcast locally (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.ao
|
|
|
|

|
|
20,703 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|

|
|
606,700 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
176 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 30
over 3,047 m:
6
2,438 to 3,047 m:
8
1,524 to 2,437 m:
12
914 to 1,523 m:
4 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 146
over 3,047 m:
3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
31
914 to 1,523 m:
66
under 914 m:
43 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 2 km; oil 87 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2,764 km
country comparison to the world: 59
narrow gauge:
2,641 km 1.067-m gauge; 123 km 0.600-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 51,429 km
country comparison to the world: 78
paved:
5,349 km
unpaved:
46,080 km (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,300 km (2011)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 7
country comparison to the world: 123
by type:
cargo 1, chemical tanker 1, passenger/cargo 2, petroleum tanker 2, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
1 (Spain 1)
registered in other countries:
17 (Bahamas 6, Curacao 2, Cyprus 1, Liberia 1, Malta 7) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Cabinda, Lobito, Luanda, Namibe
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Angolan Armed Forces (Forcas Armadas Angolanas, FAA): Army, Navy (Marinha de Guerra Angola, MGA), Angolan National Air Force (Forca Aerea Nacional Angolana, FANA; under operational control of the Army) (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20-45 years of age for compulsory male and 18-45 years for voluntary male military service (registration at age 18 is mandatory); conscript service obligation - 2 years; 20-45 years of age for voluntary female service; Angolan citizenship required; the Navy (MGA) is entirely staffed with volunteers (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 3,062,438
females age 16-49:
2,964,262 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,546,781
females age 16-49:
1,492,308 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 155,476
female:
152,054 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Angola |
|
|

|
|
Democratic Republic of Congo accuses Angola of shifting monuments
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 13,648 (Democratic Republic of Congo) (2011)
IDPs:
19,500 (27-year civil war ending in 2002) (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
used as a transshipment point for cocaine destined for Western Europe and other African states, particularly South Africa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

