-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |
|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 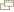
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Once the seat of Viking raiders and later a major north European power, Denmark has evolved into a modern, prosperous nation that is participating in the general political and economic integration of Europe. It joined NATO in 1949 and the EEC (now the EU) in 1973. However, the country has opted out of certain elements of the European Union's Maastricht Treaty, including the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), European defense cooperation, and issues concerning certain justice and home affairs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
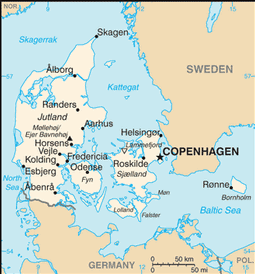
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland); also includes several major islands (Sjaelland, Fyn, and Bornholm)
|
|
|
|

|
|
56 00 N, 10 00 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 43,094 sq km
country comparison to the world: 134
land:
42,434 sq km
water:
660 sq km
note:
includes the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark (the Jutland Peninsula, and the major islands of Sjaelland and Fyn), but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly less than twice the size of Massachusetts
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 68 km
border countries:
Germany 68 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
7,314 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|

|
|
temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
|
|
|
|

|
|
low and flat to gently rolling plains
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Lammefjord -7 m
highest point:
Mollehoj/Ejer Bavnehoj 171 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone, chalk, stone, gravel and sand
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 52.59%
permanent crops:
0.19%
other:
47.22% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4,350 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.1 cu km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 0.67 cu km/yr (32%/26%/42%)
per capita:
123 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
|
|

|
|
flooding is a threat in some areas of the country (e.g., parts of Jutland, along the southern coast of the island of Lolland) that are protected from the sea by a system of dikes
|
|
|
|

|
|
air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
controls Danish Straits (Skagerrak and Kattegat) linking Baltic and North Seas; about one-quarter of the population lives in greater Copenhagen
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Denmark |
|
|

|
|
noun: Dane(s)
adjective:
Danish
|
|
|
|

|
|
Scandinavian, Inuit, Faroese, German, Turkish, Iranian, Somali
|
|
|
|

|
|
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority)
note:
English is the predominant second language
|
|
|
|

|
|
Evangelical Lutheran (official) 95%, other Christian (includes Protestant and Roman Catholic) 3%, Muslim 2%
|
|
|
|

|
|
5,543,453 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 17.4% (male 494,967/ female 469,918)
15-64 years:
65% (male 1,806,653/ female 1,796,576)
65 years and over:
17.6% (male 433,401/ female 541,938) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 41.2 years
male:
40.3 years
female:
42.1 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.239% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 173
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.22 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.19 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.36 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 87% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
COPENHAGEN (capital) 1.174 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.8 male(s)/female
total population:
0.97 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 4.19 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 196
male:
4.25 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
4.12 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 78.78 years
country comparison to the world: 48
male:
76.39 years
female:
81.31 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.74 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|

|
|
7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.419 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.57 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|

|
|
5,300 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|

|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|

|
|
11.4% (2006)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.8% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 17 years
male:
16 years
female:
18 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 11.2%
country comparison to the world: 96
male:
12.4%
female:
9.9% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Denmark
conventional short form:
Denmark
local long form:
Kongeriget Danmark
local short form:
Danmark
|
|
|
|

|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Copenhagen
geographic coordinates:
55 40 N, 12 35 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note:
applies to continental Denmark only, not to its North Atlantic components
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan Denmark - 5 regions (regioner, singular - region); Hovedstaden, Midtjylland, Nordjylland, Sjaelland, Syddanmark
note:
an extensive local government reform merged 271 municipalities into 98 and 13 counties into five regions, effective 1 January 2007
|
|
|
|

|
|
ca. 965 (unified and Christianized under HARALD I Gormson); 5 June 1849 (became a constitutional monarchy)
|
|
|
|

|
|
none designated; Constitution Day, 5 June (1849) is generally viewed as the National Day
|
|
|
|

|
|
5 June 1953; note - constitution allowed for a unicameral legislature and a female chief of state
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law; judicial review of legislative acts
|
|
|
|

|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II (since 14 January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the monarch (born on 26 May 1968)
head of government:
Prime Minister Helle THORNING-SCHMIDT (since 3 October 2011)
cabinet:
Council of State appointed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral People's Assembly or Folketing (179 seats, including 2 from Greenland and 2 from the Faroe Islands; members elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms unless the Folketing is dissolved earlier)
elections:
last held on 15 September 2011 (next to be held by September 2015)
election results:
percent of vote by party - Liberal Party 26.7%, Social Democrats 24.9%, Danish People's Party 12.3%, Social Liberal Party 9.5%, Socialist People's Party 9.2%, Unity List 6.7%, Liberal Alliance 5%, Conservative People's Party 4.9%, other 0.8%; seats by party - Liberal Party 47, Social Democrats 44, Danish People's Party 22, Social Liberal Party 17, Socialist People's Party 16, Unity List 12, Liberal Alliance 9, Conservative People's Party 8; note - does not include the two seats from Greenland and the two seats from the Faroe Islands
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed for life by the monarch)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Conservative People's Party (Det Konservative Folkeparti) [Lars BARFOED]; Danish People's Party (Dansk Folkeparti) or DF [Kristian THULESEN DAHL]; Liberal Alliance or LA [Anders SAMUELSEN]; Liberal Party (Venstre) or V [Lars LOKKE RAMUSSEN]; Red-Green Alliance (Enhedslisten) [collective leadership, spokesperson Johanne SCHMIDT-NIELSEN]; Social Democratic Party (Socialdemokratiet) or SDP [Helle THORNING-SCHMIDT]; Social Liberal Party (Det Radicale Venstre) or SLP [Margrethe VESTAGER]; Socialist People's Party (Socialistisk Folkeparti) or SF [Annette VILHELMSEN]
|
|
|
|

|
|
Confederation of Danish Employers or DA [President Jorn Neergaard LARSEN]; Confederation of Danish Industries [CEO Karsten DYBVAD]; Confederation of Danish Labor Unions (Landsorganisationen) or LO [President Harald BORSTING]; Danish Bankers Association [CEO Joergen HORWITZ]; DaneAge Association [President Bjarne HASTRUP]; Danish Society for Nature Conservation [President Ella Maria BISSCHOP-LARSEN]
other:
environmental groups; humanitarian relief; development assistance; human rights NGOs
|
|
|
|

|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EITI (implementing country), ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Peter TAKSOE-JENSEN
chancery:
3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-4300
FAX:
[1] (202) 328-1470
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, New York
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Laurie S. FULTON
embassy:
Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen
mailing address:
Unit 5280, DPO, AE 09716
telephone:
[45] 33 41 71 00
FAX:
[45] 35 43 02 23
|
|
|
|

|
|
red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side; the banner is referred to as the Dannebrog (Danish flag) and is one of the oldest national flags in the world; traditions as to the origin of the flag design vary, but the best known is a legend that the banner fell from the sky during an early-13th century battle; caught up by the Danish king before it ever touched the earth, this heavenly talisman inspired the royal army to victory; in actuality, the flag may derive from a crusade banner or ensign
note:
the shifted design element was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
|
|
|
|

|
|
lion; mute swan
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Der er et yndigt land" (There is a Lovely Land); "Kong Christian" (King Christian)
lyrics/music:
Adam Gottlob OEHLENSCHLAGER/Hans Ernst KROYER; Johannes EWALD/unknown
note:
Denmark has two national anthems with equal status; "Der er et yndigt land," adopted 1844, is a national anthem, while "Kong Christian," adopted 1780, serves as both a national and royal anthem; "Kong Christian" is also known as "Kong Christian stod ved hojen mast" (King Christian Stood by the Lofty Mast) and "Kongesangen" (The King's Anthem); within Denmark, the royal anthem is played only when royalty is present and is usually followed by the national anthem; when royalty is not present, only the national anthem is performed; outside Denmark, the royal anthem is played, unless the national anthem is requested
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
This thoroughly modern market economy features a high-tech agricultural sector, state-of-the-art industry with world-leading firms in pharmaceuticals, maritime shipping and renewable energy, and a high dependence on foreign trade. Denmark is a member of the European Union (EU); Danish legislation and regulations conform to EU standards on almost all issues. Danes enjoy a high standard of living and the Danish economy is characterized by extensive government welfare measures and an equitable distribution of income. Denmark is a net exporter of food and energy and enjoys a comfortable balance of payments surplus but depends on imports of raw materials for the manufacturing sector. Within the EU, Denmark is among the strongest supporters of trade liberalization. After a long consumption-driven upswing, Denmark's economy began slowing in 2007 with the end of a housing boom. Housing prices dropped markedly in 2008-09 and, following a short respite in 2010, has since continued to decline. The global financial crisis has exacerbated this cyclical slowdown through increased borrowing costs and lower export demand, consumer confidence, and investment. The global financial crises cut Danish real GDP in 2008-09. Denmark made a modest recovery in 2010 with real GDP growth of 1.3%, in part because of increased government spending; however, the country experienced a technical recession in late 2010-early 2011. Historically low levels of unemployment rose sharply with the recession and have remained at about 6% in 2010-12, based on the national measure, about two-thirds average EU unemployment. An impending decline in the ratio of workers to retirees will be a major long-term issue. Denmark maintained a healthy budget surplus for many years up to 2008, but the budget balance swung into deficit in 2009. In spite of the deficits, the new coalition government delivered a modest stimulus to the economy in 2012. Nonetheless, Denmark's fiscal position remains among the strongest in the EU with public debt at about 45% of GDP in 2012. Despite previously meeting the criteria to join the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), so far Denmark has decided not to join, although the Danish krone remains pegged to the euro. Denmark held the EU presidency during the first half of 2012; priorities included promoting a responsible, dynamic, green, and safe Europe, while working to steer Europe out of its euro zone economic crisis.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$208.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$209.4 billion (2011 est.)
$207.8 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$309.2 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
-0.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
0.8% (2011 est.)
1.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$37,700 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$37,700 (2011 est.)
$37,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 1.3%
industry:
22.1%
services:
76.6% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.848 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 2.6%
industry:
20.3%
services:
77.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
6.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.4% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%:
28.7% (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.8 (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
24.7 (1992)
|
|
|
|

|
|
17.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $176.5 billion
expenditures:
$188.9 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
57.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|

|
|
-4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|

|
|
45.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
46.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
2.8% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.75% (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
0.75% (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.6% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
4.5% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$134.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$134.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$230.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$266.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$664.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$640.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$179.5 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 32
$231.7 billion (31 December 2010)
$186.9 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
barley, wheat, potatoes, sugar beets; pork, dairy products; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.9% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|

|
|
$18.6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$22.08 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$110.8 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$111.8 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery and instruments, meat and meat products, dairy products, fish, pharmaceuticals, furniture, windmills
|
|
|
|

|
|
Germany 16.9%, Sweden 13.2%, UK 9.9%, Norway 5.7%, US 5.5%, Netherlands 4.9%, France 4.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$97.91 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$102.2 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery and equipment, raw materials and semimanufactures for industry, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, consumer goods
|
|
|
|

|
|
Germany 20.8%, Sweden 13.5%, Netherlands 7.2%, UK 6.3%, China 6.2%, Norway 5.8% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$85.05 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$76.52 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$626.9 billion (30 June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 21
$559.5 billion (30 June 2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$120.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$110.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$222.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$207.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar -
5.847 (2012 est.)
5.3687 (2011 est.)
5.6241 (2010 est.)
5.361 (2009)
5.0236 (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
36.39 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|

|
|
32.42 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|

|
|
11.73 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.6 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.42 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|

|
|
65.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|

|
|
34.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|

|
|
221,100 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|

|
|
171,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
70,220 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
900 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|

|
|
158,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|

|
|
160,200 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
93,890 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|

|
|
177,700 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.069 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.179 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.126 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|

|
|
369 million cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|

|
|
51.99 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
45.96 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.515 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.159 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: excellent telephone and telegraph services
domestic:
buried and submarine cables and microwave radio relay form trunk network, multiple cellular mobile communications systems
international:
country code - 45; a series of fiber-optic submarine cables link Denmark with Canada, Faroe Islands, Germany, Iceland, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and UK; satellite earth stations - 18 (6 Intelsat, 10 Eutelsat, 1 Orion, 1 Inmarsat (Blaavand-Atlantic-East)); note - the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden) share the Danish earth station and the Eik, Norway, station for worldwide Inmarsat access (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
strong public-sector TV presence with state-owned Danmarks Radio (DR) operating 4 channels and publicly-owned TV2 operating roughly a half dozen channels; broadcasts of privately-owned stations are available via satellite and cable feed; DR operates 4 nationwide FM radio stations, 15 digital audio broadcasting stations, and about 15 web-based radio stations; approximately 250 commercial and community radio stations (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.dk
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.297 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.75 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
89 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 28
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
7
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
12
under 914 m:
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 61
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
59 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 2,858 km; oil 107 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2,667 km
country comparison to the world: 61
standard gauge:
2,667 km 1.435-m gauge (640 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 73,197 km
country comparison to the world: 62
paved:
73,197 km (includes 1,111 km of expressways) (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
400 km (2010)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 367
country comparison to the world: 27
by type:
bulk carrier 4, cargo 48, carrier 1, chemical tanker 125, container 94, liquefied gas 4, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 40, petroleum tanker 36, refrigerated cargo 3, roll on/roll off 8, specialized tanker 3
foreign-owned:
27 (Germany 9, Greenland 1, Norway 2, Sweden 15)
registered in other countries:
582 (Antigua and Barbuda 20, Bahamas 69, Belgium 4, Brazil 3, Curacao 1, Cyprus 6, Egypt 1, France 11, Gibraltar 7, Hong Kong 42, Isle of Man 30, Italy 4, Jamaica 1, Liberia 8, Lithuania 8, Luxembourg 1, Malaysia 1, Malta 34, Marshall Islands 7, Moldova 1, Netherlands 27, Norway 7, Panama 41, Philippines 2, Portugal 4, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 9, Singapore 149, Sweden 4, UK 43, Uruguay 1, US 31, Venezuela 1, unknown 4) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Aalborg, Aarhus, Copenhagen, Ensted, Esbjerg, Fredericia, Kalundborg
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Defense Command: Army Operational Command, Admiral Danish Fleet, Arctic Command, Tactical Air Command, Home Guard (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; conscripts serve an initial training period that varies from 4 to 12 months according to specialization; reservists are assigned to mobilization units following completion of their conscript service; women eligible to volunteer for military service (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,236,337
females age 16-49:
1,224,182 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,014,560
females age 16-49:
1,003,921 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 37,913
female:
35,865 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.3% of GDP (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Denmark |
|
|

|
|
Iceland, the UK, and Ireland dispute Denmark's claim that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm; Faroese continue to study proposals for full independence; sovereignty dispute with Canada over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Ellesmere Island and Greenland; Denmark (Greenland) and Norway have made submissions to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) and Russia is collecting additional data to augment its 2001 CLCS submission
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

