-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |
|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 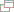
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
In 1603, after decades of civil warfare, the Tokugawa shogunate (a military-led, dynastic government) ushered in a long period of relative political stability and isolation from foreign influence. For more than two centuries this policy enabled Japan to enjoy a flowering of its indigenous culture. Japan opened its ports after signing the Treaty of Kanagawa with the US in 1854 and began to intensively modernize and industrialize. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Japan became a regional power that was able to defeat the forces of both China and Russia. It occupied Korea, Formosa (Taiwan), and southern Sakhalin Island. In 1931-32 Japan occupied Manchuria, and in 1937 it launched a full-scale invasion of China. Japan attacked US forces in 1941 - triggering America's entry into World War II - and soon occupied much of East and Southeast Asia. After its defeat in World War II, Japan recovered to become an economic power and an ally of the US. While the emperor retains his throne as a symbol of national unity, elected politicians hold actual decision-making power. Following three decades of unprecedented growth, Japan's economy experienced a major slowdown starting in the 1990s, but the country remains a major economic power. In March 2011, Japan's strongest-ever earthquake, and an accompanying tsunami, devastated the northeast part of Honshu island, killing thousands and damaging several nuclear power plants. The catastrophe hobbled the country's economy and its energy infrastructure, and tested its ability to deal with humanitarian disasters.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
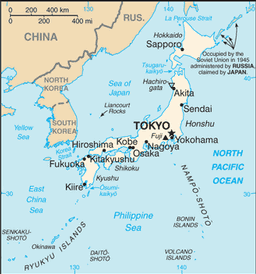
Eastern Asia, island chain between the North Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan, east of the Korean Peninsula
|
|
|
|

|
|
36 00 N, 138 00 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 377,915 sq km
country comparison to the world: 62
land:
364,485 sq km
water:
13,430 sq km
note:
includes Bonin Islands (Ogasawara-gunto), Daito-shoto, Minami-jima, Okino-tori-shima, Ryukyu Islands (Nansei-shoto), and Volcano Islands (Kazan-retto)
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than California
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
29,751 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the international straits - La Perouse or Soya, Tsugaru, Osumi, and Eastern and Western Channels of the Korea or Tsushima Strait
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|

|
|
varies from tropical in south to cool temperate in north
|
|
|
|

|
|
mostly rugged and mountainous
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Hachiro-gata -4 m
highest point:
Fujiyama 3,776 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
negligible mineral resources, fish
note:
with virtually no energy natural resources, Japan is the world's largest importer of coal and liquefied natural gas, as well as the second largest importer of oil
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 11.64%
permanent crops:
0.9%
other:
87.46% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
25,160 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
430 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 88.43 cu km/yr (20%/18%/62%)
per capita:
690 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
many dormant and some active volcanoes; about 1,500 seismic occurrences (mostly tremors but occasional severe earthquakes) every year; tsunamis; typhoons
volcanism:
both Unzen (elev. 1,500 m) and Sakura-jima (elev. 1,117 m), which lies near the densely populated city of Kagoshima, have been deemed "Decade Volcanoes" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Asama, Honshu Island's most active volcano, Aso, Bandai, Fuji, Iwo-Jima, Kikai, Kirishima, Komaga-take, Oshima, Suwanosejima, Tokachi, Yake-dake, and Usu
|
|
|
|

|
|
air pollution from power plant emissions results in acid rain; acidification of lakes and reservoirs degrading water quality and threatening aquatic life; Japan is one of the largest consumers of fish and tropical timber, contributing to the depletion of these resources in Asia and elsewhere
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
strategic location in northeast Asia
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Japan |
|
|

|
|
noun: Japanese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Japanese
|
|
|
|

|
|
Japanese 98.5%, Koreans 0.5%, Chinese 0.4%, other 0.6%
note:
up to 230,000 Brazilians of Japanese origin migrated to Japan in the 1990s to work in industries; some have returned to Brazil (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Japanese
|
|
|
|

|
|
Shintoism 83.9%, Buddhism 71.4%, Christianity 2%, other 7.8%
note:
total adherents exceeds 100% because many people belong to both Shintoism and Buddhism (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
127,368,088 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 13.5% (male 8,927,803/ female 8,268,937)
15-64 years:
62.6% (male 39,850,531/ female 39,909,944)
65 years and over:
23.9% (male 13,097,558/ female 17,313,315) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 45.4 years
male:
44.1 years
female:
46.9 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
-0.077% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.39 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 217
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.15 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 67% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
TOKYO (capital) 36.507 million; Osaka-Kobe 11.325 million; Nagoya 3.257 million; Fukuoka-Kitakyushu 2.809 million; Sapporo 2.673 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.08 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.76 male(s)/female
total population:
0.94 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 173
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2.21 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 222
male:
2.44 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
1.97 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 83.91 years
country comparison to the world: 3
male:
80.57 years
female:
87.43 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.39 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.063 physicians/1,000 population (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.75 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
less than 0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|

|
|
8,100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|

|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.1% (2000)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.5% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2002)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 15 years
male:
15 years
female:
15 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 9.1%
country comparison to the world: 109
male:
10.1%
female:
8% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Japan
local long form:
Nihon-koku/Nippon-koku
local short form:
Nihon/Nippon
|
|
|
|

|
|
a parliamentary government with a constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Tokyo
geographic coordinates:
35 41 N, 139 45 E
time difference:
UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
47 prefectures; Aichi, Akita, Aomori, Chiba, Ehime, Fukui, Fukuoka, Fukushima, Gifu, Gunma, Hiroshima, Hokkaido, Hyogo, Ibaraki, Ishikawa, Iwate, Kagawa, Kagoshima, Kanagawa, Kochi, Kumamoto, Kyoto, Mie, Miyagi, Miyazaki, Nagano, Nagasaki, Nara, Niigata, Oita, Okayama, Okinawa, Osaka, Saga, Saitama, Shiga, Shimane, Shizuoka, Tochigi, Tokushima, Tokyo, Tottori, Toyama, Wakayama, Yamagata, Yamaguchi, Yamanashi
|
|
|
|

|
|
3 May 1947 (current constitution adopted as amendment to Meiji Constitution); notable earlier dates: 660 B.C. (traditional date of the founding of the nation by Emperor JIMMU); 29 November 1890 (Meiji Constitution provides for constitutional monarchy)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Birthday of Emperor AKIHITO, 23 December (1933)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3 May 1947
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law system based on German model; system also reflects Anglo-American influence and Japanese traditions; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court
|
|
|
|

|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
20 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: Emperor AKIHITO (since 7 January 1989)
head of government:
Prime Minister Shinzo ABE (since 26 December 2012); Deputy Prime Minister Taro ASO (since 26 December 2012)
cabinet:
Cabinet is appointed by the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
Diet designates the prime minister; constitution requires that the prime minister commands parliamentary majority; following legislative elections, the leader of majority party or leader of majority coalition in House of Representatives usually becomes prime minister; the monarchy is hereditary
|
|
|
|

|
|
bicameral Diet or Kokkai consists of the House of Councillors or Sangi-in (242 seats - members elected for fixed six-year terms; 146 members in multi-seat constituencies and 96 by proportional representation) half elected every three years; and the House of Representatives or Shugi-in (480 seats - members elected for maximum four-year terms; 300 in single-seat constituencies; 180 members by proportional representation in 11 regional blocs); the prime minister has the right to dissolve the House of Representatives at any time with the concurrence of the cabinet
elections:
House of Councillors - last held on 11 July 2010 (next to be held in July 2013); House of Representatives - last held on 16 December 2012 (next to be held by 15 December 2016)
election results:
House of Councillors - percent of vote by party - DPJ 31.6%, LDP 24.1%, YP 13.6%, NK 13.1%, JCP 6.1%, SDP 3.8%, others 7.7%; seats by party - DPJ 106, LDP 84, NK 19, YP 11, JCP 6, SDP 4, others 12
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party (by proportional representation) - LDP 31.6%, DPJ 16.6%, JRP 22.2%, New Komeito 12.2%, Your Party 7.7%, TRP 3.9%, JCP 4.4%, others 0.56%; seats by party LDP 294, DPJ 57, JRP 54, New Komeito 31, Your Party 18, TPJ 9, JCP 8, others 4, independents 5
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court (chief justice is appointed by the monarch after designation by the cabinet; all other justices are appointed by the cabinet)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Democratic Party of Japan or DPJ [Banri KAIEDA]; Japan Communist Party or JCP [Kazuo SHII]; Japan Restoration Party or JRP [Shintaro ISHIHARA]; Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Shinzo ABE]; New Komeito or NK [Natsuo YAMAGUCHI]; People's New Party or PNP; Social Democratic Party or SDP [Mizuho FUKUSHIMA]; Tomorrow Party Japan of TPJ {Yukiko KADA]; Your Party or YP [Yoshimi WATANABE]
|
|
|
|

|
|
other: business groups; trade unions
|
|
|
|

|
|
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE (observer), CERN (observer), CICA (observer), CP, EAS, EBRD, EITI (implementing country), FAO, FATF, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SELEC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Kenichiro SASAE
chancery:
2520 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 238-6700
FAX:
[1] (202) 328-2187
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Denver, Detroit, Agana (Guam), Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Portland (Oregon), San Francisco, Seattle
consulate(s):
Anchorage, Nashville
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador John V. ROOS
embassy:
1-10-5 Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo 107-8420
mailing address:
Unit 9800, Box 300, APO AP 96303-0300
telephone:
[81] (03) 3224-5000
FAX:
[81] (03) 3505-1862
consulate(s) general:
Naha (Okinawa), Osaka-Kobe, Sapporo
consulate(s):
Fukuoka, Nagoya
|
|
|
|

|
|
white with a large red disk (representing the sun without rays) in the center
|
|
|
|

|
|
red sun disc; chrysanthemum
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Kimigayo" (The Emperor"s Reign)
lyrics/music:
unknown/Hiromori HAYASHI
note:
adopted 1999; in use as unofficial national anthem since 1883; oldest anthem lyrics in the world, dating to the 10th century or earlier; there is some opposition to the anthem because of its association with militarism and worship of the emperor
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
In the years following World War II, government-industry cooperation, a strong work ethic, mastery of high technology, and a comparatively small defense allocation (1% of GDP) helped Japan develop a technologically advanced economy. Two notable characteristics of the post-war economy were the close interlocking structures of manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors, known as keiretsu, and the guarantee of lifetime employment for a substantial portion of the urban labor force. Both features are now eroding under the dual pressures of global competition and domestic demographic change. Japan's industrial sector is heavily dependent on imported raw materials and fuels. A tiny agricultural sector is highly subsidized and protected, with crop yields among the highest in the world. Usually self-sufficient in rice, Japan imports about 60% of its food on a caloric basis. Japan maintains one of the world's largest fishing fleets and accounts for nearly 15% of the global catch. For three decades, overall real economic growth had been spectacular - a 10% average in the 1960s, a 5% average in the 1970s, and a 4% average in the 1980s. Growth slowed markedly in the 1990s, averaging just 1.7%, largely because of the after effects of inefficient investment and an asset price bubble in the late 1980s that required a protracted period of time for firms to reduce excess debt, capital, and labor. Modest economic growth continued after 2000, but the economy has fallen into recession three times since 2008. A sharp downturn in business investment and global demand for Japan's exports in late 2008 pushed Japan into recession. Government stimulus spending helped the economy recover in late 2009 and 2010, but the economy contracted again in 2011 as the massive 9.0 magnitude earthquake in March disrupted manufacturing. Recovery spending helped boost GDP in early 2012, but slower global economic growth began weakening Japan's export-oriented economy by mid-year. Electricity supplies remain tight because Japan tentatively shut down almost all of its nuclear power plants after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors were crippled by the earthquake and resulting tsunami. Newly-elected Prime Minister Shinzo ABE has declared the economy his government's top priority; he has pledged to reconsider his predecessor's plan to permanently close nuclear power plants and has said he will increase stimulus spending and press the Bank of Japan to loosen monetary policy. Measured on a purchasing power parity (PPP) basis that adjusts for price differences, Japan in 2012 stood as the fourth-largest economy in the world after second-place China, which surpassed Japan in 2001, and third-place India, which edged out Japan in 2012. The new government will continue a longstanding debate on restructuring the economy and reining in Japan's huge government debt, which exceeds 200% of GDP. Persistent deflation, reliance on exports to drive growth, and an aging and shrinking population are other major long-term challenges for the economy.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.617 trillion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$4.516 trillion (2011 est.)
$4.551 trillion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.984 trillion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.2% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
-0.8% (2011 est.)
4.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$36,200 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$35,300 (2011 est.)
$35,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 1.2%
industry:
27.5%
services:
71.4% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
65.27 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 3.9%
industry:
26.2%
services:
69.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
4.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
16% (2010)
note:
Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) press release, 20 October 2009 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%:
27.5% (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
37.6 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 74
24.9 (1993)
|
|
|
|

|
|
21.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $2.025 trillion
expenditures:
$2.57 trillion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
33.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|

|
|
-9.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
|
|
|
|

|
|
218.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
205.5% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
-0.3% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.3% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 141
0.3% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
1.48% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$6.735 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
$6.637 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$14.46 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
$13.41 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$14.65 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$14.64 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$3.541 trillion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 4
$4.1 trillion (31 December 2010)
$3.378 trillion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
rice, sugar beets, vegetables, fruit; pork, poultry, dairy products, eggs; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
-3.5% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|

|
|
$84.7 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$119.1 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$792.9 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$787 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
motor vehicles 13.6%; semiconductors 6.2%; iron and steel products 5.5%; auto parts 4.6%; plastic materials 3.5%; power generating machinery 3.5%
|
|
|
|

|
|
China 19.7%, US 15.5%, South Korea 8%, Hong Kong 5.2%, Thailand 4.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$856.9 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$807.6 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum 15.5%; liquid natural gas 5.7%; clothing 3.9%; semiconductors 3.5%; coal 3.5%; audio and visual apparatus 2.7%
|
|
|
|

|
|
China 21.5%, US 8.9%, Australia 6.6%, Saudi Arabia 5.9%, UAE 5%, South Korea 4.7% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.351 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
$1.296 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.719 trillion (30 June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 6
$2.441 trillion (30 September 2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$144.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$144.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.025 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$911.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
yen (JPY) per US dollar -
79.42 (2012 est.)
79.81 (2011 est.)
87.78 (2010 est.)
93.57 (2009)
103.58 (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1 April - 31 March
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
937.6 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|

|
|
859.7 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|

|
|
284.5 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|

|
|
63.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|

|
|
17.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|

|
|
17,480 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.384 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|

|
|
44.12 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.861 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.464 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|

|
|
366,800 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|

|
|
949,800 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.298 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
112.6 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|

|
|
109.9 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|

|
|
20.9 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.164 billion Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
64.668 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|

|
|
132.76 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: excellent domestic and international service
domestic:
high level of modern technology and excellent service of every kind
international:
country code - 81; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 7 Intelsat (Pacific and Indian Oceans), 1 Intersputnik (Indian Ocean region), 3 Inmarsat (Pacific and Indian Ocean regions), and 8 SkyPerfect JSAT (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
a mixture of public and commercial broadcast TV and radio stations; 5 national terrestrial TV networks including 1 public broadcaster; the large number of radio and TV stations available provide a wide range of choices; satellite and cable services provide access to international channels (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.jp
|
|
|
|

|
|
64.453 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|

|
|
99.182 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
175 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 143
over 3,047 m:
6
2,438 to 3,047 m:
45
1,524 to 2,437 m:
38
914 to 1,523 m:
29
under 914 m:
25 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 32
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
28 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
15 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 4,135 km; oil 171 km; oil/gas/water 53 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 27,182 km
country comparison to the world: 11
standard gauge:
4,251 km 1.435-m gauge (4,251 km electrified)
dual gauge:
486 km 1.435-1.067-m gauge (486 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
96 km 1.372-m gauge (96 km electrified); 22,301 km 1.067-m gauge (15,222 km electrified); 48 km 0.762-m gauge (48 km electrified) (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1,210,251 km
country comparison to the world: 5
paved:
973,234 km (includes 7,803 km of expressways)
unpaved:
237,017 km (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,770 km (seagoing vessels use inland seas) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 684
country comparison to the world: 16
by type:
bulk carrier 168, cargo 34, carrier 3, chemical tanker 29, container 2, liquefied gas 58, passenger 11, passenger/cargo 117, petroleum tanker 152, refrigerated cargo 4, roll on/roll off 52, vehicle carrier 54
registered in other countries:
3,122 (Bahamas 88, Bermuda 2, Burma 1, Cambodia 1, Cayman Islands 23, China 2, Cyprus 16, Honduras 4, Hong Kong 79, Indonesia 8, Isle of Man 19, Liberia 110, Luxembourg 3, Malaysia 2, Malta 5, Marshall Islands 59, Mongolia 2, Netherlands 1, Panama 2372, Philippines 77, Portugal 9, Saint Kitts and Nevis 2, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 3, Sierra Leone 4, Singapore 164, South Korea 14, Tanzania 1, UK 5, Vanuatu 39, unknown 7) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Chiba, Kawasaki, Kobe, Mizushima, Moji, Nagoya, Osaka, Tokyo, Tomakomai, Yokohama
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Japanese Ministry of Defense (MOD): Ground Self-Defense Force (Rikujou Jieitai, GSDF), Maritime Self-Defense Force (Kaijou Jieitai, MSDF), Air Self-Defense Force (Koukuu Jieitai, ASDF) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; Maritime Self-Defense Force mandatory retirement at age 54 (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 27,301,443
females age 16-49:
26,307,003 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 22,390,431
females age 16-49:
21,540,322 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 623,365
female:
591,253 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.8% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Japan |
|
|

|
|
the sovereignty dispute over the islands of Etorofu, Kunashiri, and Shikotan, and the Habomai group, known in Japan as the "Northern Territories" and in Russia as the "Southern Kuril Islands," occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945, now administered by Russia and claimed by Japan, remains the primary sticking point to signing a peace treaty formally ending World War II hostilities; Japan and South Korea claim Liancourt Rocks (Take-shima/Tok-do) occupied by South Korea since 1954; China and Taiwan dispute both Japan's claims to the uninhabited islands of the Senkaku-shoto (Diaoyu Tai) and Japan's unilaterally declared exclusive economic zone in the East China Sea, the site of intensive hydrocarbon prospecting
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

