-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
| Introduction ::Costa Rica |
|
|

|
|
Although explored by the Spanish early in the 16th century, initial attempts at colonizing Costa Rica proved unsuccessful due to a combination of factors, including: disease from mosquito-infested swamps, brutal heat, resistance by natives, and pirate raids. It was not until 1563 that a permanent settlement of Cartago was established in the cooler, fertile central highlands. The area remained a colony for some two and a half centuries. In 1821, Costa Rica became one of several Central American provinces that jointly declared their independence from Spain. Two years later it joined the United Provinces of Central America, but this federation disintegrated in 1838, at which time Costa Rica proclaimed its sovereignty and independence. Since the late 19th century, only two brief periods of violence have marred the country's democratic development. In 1949, Costa Rica dissolved its armed forces. Although it still maintains a large agricultural sector, Costa Rica has expanded its economy to include strong technology and tourism industries. The standard of living is relatively high. Land ownership is widespread.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
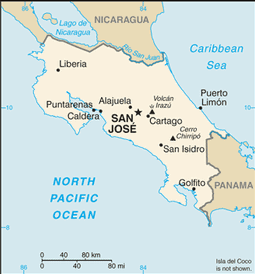
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Nicaragua and Panama
|
|
|
|

|
|
10 00 N, 84 00 W
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 51,100 sq km
country comparison to the world: 130
land:
51,060 sq km
water:
40 sq km
note:
includes Isla del Coco
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than West Virginia
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 639 km
border countries:
Nicaragua 309 km, Panama 330 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,290 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical and subtropical; dry season (December to April); rainy season (May to November); cooler in highlands
|
|
|
|

|
|
coastal plains separated by rugged mountains including over 100 volcanic cones, of which several are major volcanoes
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Cerro Chirripo 3,810 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
hydropower
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 4.4%
permanent crops:
5.87%
other:
89.73% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,080 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
112.4 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2.68 cu km/yr (29%/17%/53%)
per capita:
619 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
occasional earthquakes, hurricanes along Atlantic coast; frequent flooding of lowlands at onset of rainy season and landslides; active volcanoes
volcanism:
Arenal (elev. 1,670 m), which erupted in 2010, is the most active volcano in Costa Rica; a 1968 eruption destroyed the town of Tabacon; Irazu (elev. 3,432 m), situated just east of San Jose, has the potential to spew ash over the capital city as it did between 1963 and 1965; other historically active volcanoes include Miravalles, Poas, Rincon de la Vieja, and Turrialba
|
|
|
|

|
|
deforestation and land use change, largely a result of the clearing of land for cattle ranching and agriculture; soil erosion; coastal marine pollution; fisheries protection; solid waste management; air pollution
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|

|
|
four volcanoes, two of them active, rise near the capital of San Jose in the center of the country; one of the volcanoes, Irazu, erupted destructively in 1963-65
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Costa Rica |
|
|

|
|
noun: Costa Rican(s)
adjective:
Costa Rican
|
|
|
|

|
|
white (including mestizo) 94%, black 3%, Amerindian 1%, Chinese 1%, other 1%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spanish (official), English
|
|
|
|

|
|
Roman Catholic 76.3%, Evangelical 13.7%, Jehovah's Witnesses 1.3%, other Protestant 0.7%, other 4.8%, none 3.2%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Costa Rica's political stability, high standard of living, and well-developed social benefits system set it apart from its Central American neighbors. Through the government's sustained social spending - almost 20% of GDP annually - Costa Rica has made tremendous progress toward achieving its goal of providing universal access to education, healthcare, clean water, sanitation, and electricity. Since the 1970s, expansion of these services has led to a rapid decline in infant mortality, an increase in life expectancy at birth, and a sharp decrease in the birth rate. The average number of children born per women has fallen from about 7 in the 1960s to 3.5 in the early 1980s to below replacement level today. Costa Rica's poverty rate is lower than in most Latin American countries, but it has stalled at around 20% for almost two decades.
Costa Rica is a popular regional immigration destination because of its job opportunities and social programs. Almost 9% of the population is foreign-born, with Nicaraguans comprising nearly three-quarters of the foreign population. Many Nicaraguans who perform unskilled seasonal labor enter Costa Rica illegally or overstay their visas, which continues to be a source of tension. Less than 3% of Costa Rica's population lives abroad. The overwhelming majority of expatriates have settled in the United States after completing a university degree or in order to work in a highly skilled field.
|
|
|
|

|
|
4,636,348 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 24.2% (male 572,665/ female 547,458)
15-64 years:
69.3% (male 1,614,495/ female 1,597,010)
65 years and over:
6.6% (male 141,075/ female 163,645) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 29.2 years
male:
28.7 years
female:
29.6 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.288% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|

|
|
16.4 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.38 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.86 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 64% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
SAN JOSE (capital) 1.416 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.86 male(s)/female
total population:
1.01 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
40 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 9.2 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 151
male:
10.03 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
8.32 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 77.89 years
country comparison to the world: 59
male:
75.26 years
female:
80.65 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.92 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.5% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.32 physicians/1,000 population (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.2 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 95% of population
rural: 96% of population
total: 95% of population
unimproved:
urban: 5% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 5% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|

|
|
9,800 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|

|
|
fewer than 500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
94.9%
male:
94.7%
female:
95.1% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
12 years (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 11%
country comparison to the world: 97
male:
9.6%
female:
13.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Costa Rica
conventional short form:
Costa Rica
local long form:
Republica de Costa Rica
local short form:
Costa Rica
|
|
|
|

|
|
democratic republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: San Jose
geographic coordinates:
9 56 N, 84 05 W
time difference:
UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Alajuela, Cartago, Guanacaste, Heredia, Limon, Puntarenas, San Jose
|
|
|
|

|
|
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
|
|
|
|

|
|
7 November 1949
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law system based on Spanish civil code; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court
|
|
|
|

|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (since 8 May 2010); First Vice President Alfio PIVA Mesen (since 8 May 2010); Second Vice President Luis LIBERMAN Ginsburg (since 8 May 2010); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (since 8 May 2010); First Vice President Alfio PIVA Mesen (since 8 May 2010); Second Vice President Luis LIBERMAN Ginsburg (since 8 May 2010)
cabinet:
Cabinet selected by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice presidents elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a single four-year term; election last held on 7 February 2010 (next to be held in February 2014)
election results:
Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda elected president; percent of vote - Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (PLN) 46.7%; Otton SOLIS (PAC) 25.1%, Otto GUEVARA Guth (ML) 20.8%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral Legislative Assembly or Asamblea Legislativa (57 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 7 February 2010 (next to be held in February 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PLN 24, PAC 11, ML 9, PUSC 6, PASE 4, other 3
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (22 justices are elected for renewable eight-year terms by the Legislative Assembly)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Accessibility Without Exclusion or PASE [Oscar Andres LOPEZ Arias]; Citizen Action Party or PAC [Elizabeth FONSECA]; Costa Rican Renovation Party or PRC [Gerardo Justo OROZCO Alvarez]; Broad Front (Frente Amplio) or PFA [Jose MERINO del Rio]; Libertarian Movement Party or PML [Otto GUEVARA Guth]; National Integration Party or PIN [Walter MUNOZ Cespedes]; National Liberation Party or PLN [Bernal JIMENEZ]; National Restoration Party or PRN; Patriotic Alliance [Mariano FIGUERES Olsen]; Popular Vanguard [Trino BARRANTES Araya]; Social Christian Unity Party or PUSC [Gerardo VARGAS]
|
|
|
|

|
|
Authentic Confederation of Democratic Workers or CATD (Communist Party affiliate); Chamber of Coffee Growers; Confederated Union of Workers or CUT (Communist Party affiliate); Costa Rican Confederation of Democratic Workers or CCTD (Liberation Party affiliate); Costa Rican Exporter's Chamber or CADEXCO; Costa Rican Solidarity Movement; Costa Rican Union of Private Sector Enterprises or UCCAEP; Federation of Public Service Workers or FTSP; National Association for Economic Development or ANFE; National Association of Educators or ANDE; National Association of Public and Private Employees or ANEP; Rerum Novarum or CTRN (PLN affiliate)
|
|
|
|

|
|
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NAM (observer), OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Shanon Muni FIGUERES Boggs
chancery:
2114 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 480-2200
FAX:
[1] (202) 265-4795
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Francisco, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Anne Slaughter ANDREW
embassy:
Calle 120 Avenida O, Pavas, San Jose
mailing address:
APO AA 34020
telephone:
[506] 2519-2000
FAX:
[506] 2519-2305
|
|
|
|

|
|
five horizontal bands of blue (top), white, red (double width), white, and blue, with the coat of arms in a white elliptical disk toward the hoist side of the red band; Costa Rica retained the earlier blue-white-blue flag of Central America until 1848 when, in response to revolutionary activity in Europe, it was decided to incorporate the French colors into the national flag and a central red stripe was added; today the blue color is said to stand for the sky, opportunity, and perseverance, white denotes peace, happiness, and wisdom, while red represents the blood shed for freedom, as well as the generosity and vibrancy of the people
note:
somewhat resembles the flag of North Korea; similar to the flag of Thailand but with the blue and red colors reversed
|
|
|
|

|
|
clay-colored robin known as Yiguirro
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Himno Nacional de Costa Rica" (National Anthem of Costa Rica)
lyrics/music:
Jose Maria ZELEDON Brenes/Manuel Maria GUTIERREZ
note:
adopted 1949; the anthem's music was originally written for an 1853 welcome ceremony for diplomatic missions from the United States and United Kingdom; the lyrics were added in 1903
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Prior to the global economic crisis, Costa Rica enjoyed stable economic growth. The economy contracted 1.3% in 2009 but resumed growth at about 4.5% per year in 2010-12. While the traditional agricultural exports of bananas, coffee, sugar, and beef are still the backbone of commodity export trade, a variety of industrial and specialized agricultural products have broadened export trade in recent years. High value added goods and services, including microchips, have further bolstered exports. Tourism continues to bring in foreign exchange, as Costa Rica's impressive biodiversity makes it a key destination for ecotourism. Foreign investors remain attracted by the country's political stability and relatively high education levels, as well as the incentives offered in the free-trade zones; and Costa Rica has attracted one of the highest levels of foreign direct investment per capita in Latin America. However, many business impediments remain such as high levels of bureaucracy, legal uncertainty due to overlapping and at times conflicting responsibilities between agencies, difficulty of enforcing contracts, and weak investor protection. Poverty has remained around 15-20% for nearly 20 years, and the strong social safety net that had been put into place by the government has eroded due to increased financial constraints on government expenditures. Unlike the rest of Central America, Costa Rica is not highly dependent on remittances as they only represent about 2% of GDP. Immigration from Nicaragua has increasingly become a concern for the government. The estimated 300,000-500,000 Nicaraguans in Costa Rica legally and illegally are an important source of mostly unskilled labor but also place heavy demands on the social welfare system. The US-Central American-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) entered into force on 1 January 2009 after significant delays within the Costa Rican legislature. CAFTA-DR has increased foreign direct investment in key sectors of the economy, including the insurance and telecommunications sectors recently opened to private investors. President CHINCHILLA was not able to gain legislative approval for fiscal reform, her top priority, though she continued to pursue fiscal reform in 2012. President CHINCHILLA and the PLN were successful in passing a tax on corporations to fund an increase for security services.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$58.6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
$55.92 billion (2011 est.)
$53.68 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$44.88 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
4.2% (2011 est.)
4.7% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$12,600 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$12,100 (2011 est.)
$11,800 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 6.2%
industry:
21.1%
services:
72.7% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.196 million
country comparison to the world: 118
note:
this official estimate excludes Nicaraguans living in Costa Rica (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 14%
industry:
22%
services:
64% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
6.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.2%
highest 10%:
39.5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
50.3 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 22
45.9 (1997)
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $6.949 billion
expenditures:
$8.937 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
15.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
|
|
|
|

|
|
-4.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|

|
|
47.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
44.9% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
4.9% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
21.5% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
23% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
16% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
16.15% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.209 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
$3.693 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$20.09 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$18.68 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$23.33 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
$19.21 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.443 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 101
$1.445 billion (31 December 2010)
$1.452 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bananas, pineapples, coffee, melons, ornamental plants, sugar, corn, rice, beans, potatoes; beef, poultry, dairy; timber
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.8% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|

|
|
-$2.556 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
-$2.2 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$11.47 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$10.38 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bananas, pineapples, coffee, melons, ornamental plants, sugar; beef; seafood; electronic components, medical equipment
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 30.4%, China 11.3%, Netherlands 10.9%, UK 9.6%, Mexico 8.5% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$16.79 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
$15.53 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
raw materials, consumer goods, capital equipment, petroleum, construction materials
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 43%, Mexico 7%, China 6.2%, Japan 6% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.461 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$4.756 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$12.04 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$10.75 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$18.59 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
$16.34 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$729.3 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
$704.3 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Costa Rican colones (CRC) per US dollar -
504.5 (2012 est.)
505.66 (2011 est.)
525.83 (2010 est.)
573.29 (2009)
530.41 (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.113 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.144 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|

|
|
38 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|

|
|
62 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.49 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|

|
|
61.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|

|
|
7,361 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|

|
|
12,090 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|

|
|
50,200 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|

|
|
737 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|

|
|
39,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.411 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Costa Rica |
|
|

|
|
1.234 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.358 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: good domestic telephone service in terms of breadth of coverage; under the terms of CAFTA-DR, the state-run telecommunications monopoly is scheduled to be opened to competition from domestic and international firms, but has been slow to open to competition
domestic:
point-to-point and point-to-multi-point microwave, fiber-optic, and coaxial cable link rural areas; Internet service is available
international:
country code - 506; landing points for the Americas Region Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1), MAYA-1, and the Pan American Crossing submarine cables that provide links to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; connected to Central American Microwave System; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
multiple privately-owned TV stations and 1 publicly-owned TV station; cable network services are widely available; more than 100 privately-owned radio stations and a public radio network (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.cr
|
|
|
|

|
|
147,258 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.485 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Costa Rica |
|
|

|
|
153 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 41
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
23
under 914 m:
14 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 112
914 to 1,523 m:
19
under 914 m:
93 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
refined products 662 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 278 km
country comparison to the world: 122
narrow gauge:
278 km 1.067-m gauge
note:
none of the railway network is in use (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 38,049 km
country comparison to the world: 92
paved:
9,619 km
unpaved:
28,430 km (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
730 km (seasonally navigable by small craft) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1
country comparison to the world: 149
by type:
passenger/cargo 1 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Caldera, Puerto Limon
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
no regular military forces; Ministry of Public Security, Government, and Police (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,255,798
females age 16-49:
1,230,202 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,058,419
females age 16-49:
1,037,053 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 42,201
female:
40,444 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.6% of GDP
country comparison to the world: 154
note:
includes public security and police expenditures (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Costa Rica |
|
|

|
|
the ICJ had given Costa Rica until January 2008 to reply and Nicaragua until July 2008 to rejoin before rendering its decision on the navigation, security, and commercial rights of Costa Rican vessels on the Rio San Juan over which Nicaragua retains sovereignty
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 10,297 (Colombia) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
transshipment country for cocaine and heroin from South America; illicit production of cannabis in remote areas; domestic cocaine consumption, particularly crack cocaine, is rising; significant consumption of amphetamines; seizures of smuggled cash in Costa Rica and at the main border crossing to enter Costa Rica from Nicaragua have risen in recent years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

