-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
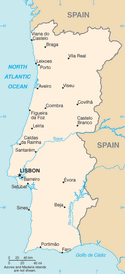
Click map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Following its heyday as a global maritime power during the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal lost much of its wealth and status with the destruction of Lisbon in a 1755 earthquake, occupation during the Napoleonic Wars, and the independence of its wealthiest colony of Brazil in 1822. A 1910 revolution deposed the monarchy; for most of the next six decades, repressive governments ran the country. In 1974, a left-wing military coup installed broad democratic reforms. The following year, Portugal granted independence to all of its African colonies. Portugal is a founding member of NATO and entered the EC (now the EU) in 1986. In January 2011, Portugal assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2011-12 term.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Southwestern Europe, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Spain
|
|
|
|

|
|
39 30 N, 8 00 W
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 92,090 sq km
country comparison to the world: 111
land:
91,470 sq km
water:
620 sq km
note:
includes Azores and Madeira Islands
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than Indiana
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1,214 km
border countries:
Spain 1,214 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,793 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|

|
|
maritime temperate; cool and rainy in north, warmer and drier in south
|
|
|
|

|
|
mountainous north of the Tagus River, rolling plains in south
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Ponta do Pico (Pico or Pico Alto) on Ilha do Pico in the Azores 2,351 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
fish, forests (cork), iron ore, copper, zinc, tin, tungsten, silver, gold, uranium, marble, clay, gypsum, salt, arable land, hydropower
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 17.29%
permanent crops:
7.84%
other:
74.87% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5,840 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
73.6 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 11.09 cu km/yr (10%/12%/78%)
per capita:
1,056 cu m/yr (1998)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Azores subject to severe earthquakes
volcanism:
limited volcanic activity in the Azores Islands; Fayal or Faial (elev. 1,043 m) last erupted in 1958; most volcanoes have not erupted in centuries; historically active volcanoes include Agua de Pau, Furnas, Pico, Picos Volcanic System, San Jorge, Sete Cidades, and Terceira
|
|
|
|

|
|
soil erosion; air pollution caused by industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution, especially in coastal areas
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Environmental Modification
|
|
|
|

|
|
Azores and Madeira Islands occupy strategic locations along western sea approaches to Strait of Gibraltar
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Portugal |
|
|

|
|
noun: Portuguese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Portuguese
|
|
|
|

|
|
homogeneous Mediterranean stock; citizens of black African descent who immigrated to mainland during decolonization number less than 100,000; since 1990 East Europeans have entered Portugal
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portuguese (official), Mirandese (official, but locally used)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Roman Catholic 84.5%, other Christian 2.2%, other 0.3%, unknown 9%, none 3.9% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
10,781,459 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 16.1% (male 906,062/ female 831,992)
15-64 years:
65.7% (male 3,548,140/ female 3,538,562)
65 years and over:
18.1% (male 800,339/ female 1,156,364) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 40.4 years
male:
38.3 years
female:
42.6 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.181% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.76 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.86 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 61% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
LISBON (capital) 2.808 million; Porto 1.344 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.09 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.69 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 4.6 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 186
male:
5.04 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
4.12 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 78.7 years
country comparison to the world: 49
male:
75.45 years
female:
82.16 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.51 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|

|
|
11.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.755 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.37 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|

|
|
42,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|

|
|
fewer than 500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|

|
|
14.2% (2005)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.4% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
95.2%
male:
96.9%
female:
93.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 16 years
male:
16 years
female:
16 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 20%
country comparison to the world: 57
male:
18.6%
female:
21.6% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Portuguese Republic
conventional short form:
Portugal
local long form:
Republica Portuguesa
local short form:
Portugal
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic; parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Lisbon
geographic coordinates:
38 43 N, 9 08 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 districts (distritos, singular - distrito) and 2 autonomous regions* (regioes autonomas, singular - regiao autonoma); Aveiro, Acores (Azores)*, Beja, Braga, Braganca, Castelo Branco, Coimbra, Evora, Faro, Guarda, Leiria, Lisboa (Lisbon), Madeira*, Portalegre, Porto, Santarem, Setubal, Viana do Castelo, Vila Real, Viseu
|
|
|
|

|
|
1143 (Kingdom of Portugal recognized); 5 October 1910 (republic proclaimed)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portugal Day (Dia de Portugal), 10 June (1580); note - also called Camoes Day, the day that revered national poet Luis de Camoes (1524-80) died
|
|
|
|

|
|
adopted 2 April 1976; subsequently revised
note:
the revisions placed the military under strict civilian control, trimmed the powers of the president, and laid the groundwork for a stable, pluralistic liberal democracy; they allowed for the privatization of nationalized firms and government-owned communications media
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law system; Constitutional Tribunal review of legislative acts
|
|
|
|

|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Anibal CAVACO SILVA (since 9 March 2006)
head of government:
Prime Minister Pedro Manuel Mamede PASSOS COELHO (since 21 June 2011)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
note:
there is also a Council of State that acts as a consultative body to the president
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 23 January 2011 (next to be held in January 2016); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president
election results:
Anibal CAVACO SILVA reelected president; percent of vote - Anibal CAVACO SILVA 53%, Manuel ALEGRE 19.8%, Fernando NOBRE 14.1%, Francisco LOPES 7.1%, Manuel COELHO 4.5%, Defensor MOURA 1.6%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral Assembly of the Republic or Assembleia da Republica (230 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 5 June 2011 (next to be held in 2015)
election results:
percent of vote by party - PPD/PSD 38%, PS 28%, CDS/PP 11%, PCP/PEV 7%, BE 5%; seats by party - PPD/PSD 108, PS 74, CDS/PP 24, PCP/PEV 16, BE 8
|
|
|
|

|
|
Constitutional Court (Tribunal Constitucional) consists of 13 judges (10 appointed by the Assembly and 3 are coopted by the 10 judges) for six-year terms; Supreme Court (Supremo Tribunal de Justica); Audit Court (auditoria do Tribunal); Supreme Administrative Court (Supremo Tribunal Administrativo); all judges are appointed for life by the Conselho Superior da Magistratura
|
|
|
|

|
|
Democratic and Social Center/Popular Party or CDS/PP [Paulo PORTAS]; Social Democratic Party or PSD [Pedro PASSOS COELHO]; Socialist Party or PS [Jose SEGURO]; The Left Bloc or BE [Pedro Filipe SOARES]; Unitarian Democratic Coalition or CDU [Jeronimo DE SOUSA] (includes Portuguese Communist Party or PCP and Ecologist Party ("The Greens") or PEV)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Armed Forces Officers' Association (AOFA) [Colonel Pereira CRACEL]; the Desperate Generation (youth movement protesting against low wages, precarious labor conditions, and unemployment); the General Workers Union or General Confederation of Portuguese Workers (UGT) [Joao PROENCA]; Portuguese National Workers' Conference (CGTP) [Armenio CARLOS]; TugaLeaks (a website that has become a mouthpiece for publicizing diverse protest action)
other:
the media; labor unions
|
|
|
|

|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CERN, CPLP, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club (associate), PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIT, UNSC (temporary), UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Nuno Filipe Alves Salvador e BRITO
chancery:
2012 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone:
[1] (202) 332-3007
FAX:
[1] (202) 462-3726
consulate(s) general:
Boston, New York, Newark (New Jersey), San Francisco
consulate(s):
New Bedford (Massachusetts), Providence (Rhode Island)
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Allan J. KATZ
embassy:
Avenida das Forcas Armadas, 1600-081 Lisbon
mailing address:
Apartado 43033, 1601-301 Lisboa; PSC 83, APO AE 09726
telephone:
[351] (21) 727-3300
FAX:
[351] (21) 726-9109
consulate(s):
Ponta Delgada (Azores)
|
|
|
|

|
|
two vertical bands of green (hoist side, two-fifths) and red (three-fifths) with the national coat of arms (armillary sphere and Portuguese shield) centered on the dividing line; explanations for the color meanings are ambiguous, but a popular interpretation has green symbolizing hope and red the blood of those defending the nation
|
|
|
|

|
|
armillary sphere (a spherical astrolabe modeling objects in the sky)
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "A Portugesa" (The Song of the Portuguese)
lyrics/music:
Henrique LOPES DE MENDOCA/Alfredo KEIL
note:
adopted 1910; "A Portuguesa" was originally written to protest the Portuguese monarchy's acquiescence to the 1890 British ultimatum forcing Portugal to give up areas of Africa; the lyrics refer to the "insult" that resulted from the event
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portugal has become a diversified and increasingly service-based economy since joining the European Community - the EU's predecessor - in 1986. Over the following two decades, successive governments privatized many state-controlled firms and liberalized key areas of the economy, including the financial and telecommunications sectors. The country qualified for the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) in 1998 and began circulating the euro on 1 January 2002 along with 11 other EU members. The economy grew by more than the EU average for much of the 1990s, but the rate of growth slowed in 2001-08. The economy contracted 2.5% in 2009, before growing 1.4% in 2010, but GDP fell again in 2011 and 2012, as the government began implementing spending cuts and tax increases to comply with conditions of an EU-IMF financial rescue package, agreed to in May 2011. GDP per capita stands at roughly two-thirds of the EU-27 average. Portugal also has been increasingly overshadowed by lower-cost producers in Central Europe and Asia as a destination for foreign direct investment, in part because its rigid labor market hindered greater productivity and growth. However, the government of Pedro PASSOS COELHO has enacted several measures to introduce more flexibility into the labor market, and, this, along with steps to reduce high levels of public debt, could make Portugal more attractive to foreign investors. The government reduced the budget deficit from 10.1% of GDP in 2009 to 4.5% in 2011, an achievement made possible only by the extraordinary revenues obtained from the one-time transfer of bank pension funds to the social security system. The budget deficit worsened in 2012 as a sharp reduction in domestic consumption took a bigger bite out of value-added tax revenues while rising unemployment benefits increased expenditures more than anticipated. Poor growth prospects over the next year have reinforced investors' concerns about the government's ability to achieve its budget deficit targets and regain full access to bond market financing when the EU-IMF financing program expires in 2013.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$245 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
$252.5 billion (2011 est.)
$256.8 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$210.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
-3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
-1.7% (2011 est.)
1.4% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$23,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
$23,700 (2011 est.)
$24,100 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 2.6%
industry:
22.6%
services:
74.8% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.48 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 11.7%
industry:
28.5%
services:
59.8% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
15.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
12.7% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18% (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 3.1%
highest 10%:
28.4% (1995 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
38.5 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 70
35.6 (1995)
|
|
|
|

|
|
16.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $94.67 billion
expenditures:
$107.4 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
44.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
-6.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|

|
|
119.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
107.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
3.7% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5% (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 125
1.75% (31 December 2010)
note:
this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.6% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
5.71% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$86.55 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$89.42 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|

|
|
$298.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$322.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$390.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$451.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$61.69 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 46
$82 billion (31 December 2010)
$98.65 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
grain, potatoes, tomatoes, olives, grapes; sheep, cattle, goats, pigs, poultry, dairy products; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
-2% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|

|
|
-$6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
-$15.44 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$57.8 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$59.22 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
agricultural products, food products, wine, oil products, chemical products, plastics and rubber, hides, leather, wood and cork, wood pulp and paper, textile materials, clothing, footwear, machinery and tools, base metals
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spain 25.1%, Germany 13.6%, France 12.1%, Angola 5.5%, UK 5.1% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$67.03 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$77.62 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
agricultural products, chemical products, vehicles and other transport material, and optical and precision instruments, computer accessories and parts, semi-conductors and related devices, oil products, base metals, food products, textile materials
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spain 31.8%, Germany 12.4%, France 6.9%, Italy 5.4%, Netherlands 4.8% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$21.34 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
$21 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$548.3 billion (30 June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 24
$497.8 billion (30 June 2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$128.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$120.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$64.25 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$64.25 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7838 (2012 est.)
0.7185 (2011 est.)
755 (2010 est.)
0.7198 (2009 est.)
0.6827 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
50.3 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|

|
|
47.81 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.191 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.814 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|

|
|
17.39 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|

|
|
48.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|

|
|
23.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|

|
|
22.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,926 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|

|
|
205,400 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA bbl
|
|
|
|

|
|
237,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|

|
|
259,700 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|

|
|
49,650 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|

|
|
83,520 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.212 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.181 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
|
|
|
|

|
|
51.43 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Portugal |
|
|

|
|
4.53 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.335 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: Portugal's telephone system has a state-of-the-art network with broadband, high-speed capabilities
domestic:
integrated network of coaxial cables, open-wire, microwave radio relay, and domestic satellite earth stations
international:
country code - 351; a combination of submarine cables provide connectivity to Europe, North and East Africa, South Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and the US; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (2 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean), NA Eutelsat; tropospheric scatter to Azores
|
|
|
|

|
|
Radio e Televisao de Portugal (RTP),the publicly-owned TV broadcaster, operates 2 domestic channels and external service channels to Africa; overall, roughly 40 domestic TV stations; viewers have widespread access to international broadcasters with more than half of all households connected to multi-channel cable or satellite TV systems; publicly-owned radio operates 3 national networks and provides regional and external services; several privately-owned national radio stations and some 300 regional and local commercial radio stations (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.pt
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.748 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.168 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Portugal |
|
|

|
|
65 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 43
over 3,047 m:
5
2,438 to 3,047 m:
7
1,524 to 2,437 m:
8
914 to 1,523 m:
13
under 914 m:
10 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 22
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
21 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 1,307 km; oil 11 km; refined products 188 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 3,319 km
country comparison to the world: 53
broad gauge:
2,700 km 1.668-m gauge (1,436 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
192 km 1.000-m gauge; 427 km 0.760-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 82,900 km
country comparison to the world: 54
paved:
71,294 km (includes 2,613 km of expressways)
unpaved:
11,606 km (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
210 km (on Douro River from Porto) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 109
country comparison to the world: 48
by type:
bulk carrier 8, cargo 35, carrier 1, chemical tanker 21, container 7, liquefied gas 6, passenger 13, passenger/cargo 5, petroleum tanker 3, roll on/roll off 1, vehicle carrier 9
foreign-owned:
81 (Belgium 8, Colombia 1, Denmark 4, Germany 14, Greece 2, Italy 12, Japan 9, Mexico 1, Norway 2, Spain 18, Sweden 3, Switzerland 3, US 4)
registered in other countries:
15 (Cyprus 2, Malta 3, Panama 10) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Leixoes, Lisbon, Setubal, Sines
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Portuguese Army (Exercito Portuguesa), Portuguese Navy (Marinha Portuguesa; includes Marine Corps), Portuguese Air Force (Forca Aerea Portuguesa, FAP) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no compulsory military service; women serve in the armed forces, on naval ships since 1993, but are prohibited from serving in some combatant specialties; reserve obligation to age 35 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 2,566,264
females age 16-49:
2,458,297 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 2,103,080
females age 16-49:
2,018,004 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 62,208
female:
54,786 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.3% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Portugal |
|
|

|
|
Portugal does not recognize Spanish sovereignty over the territory of Olivenza based on a difference of interpretation of the 1815 Congress of Vienna and the 1801 Treaty of Badajoz
|
|
|
|

|
|
seizing record amounts of Latin American cocaine destined for Europe; a European gateway for Southwest Asian heroin; transshipment point for hashish from North Africa to Europe; consumer of Southwest Asian heroin
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

