-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 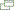
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
What is now Ecuador formed part of the northern Inca Empire until the Spanish conquest in 1533. Quito became a seat of Spanish colonial government in 1563 and part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717. The territories of the Viceroyalty - New Granada (Colombia), Venezuela, and Quito - gained their independence between 1819 and 1822 and formed a federation known as Gran Colombia. When Quito withdrew in 1830, the traditional name was changed in favor of the "Republic of the Equator." Between 1904 and 1942, Ecuador lost territories in a series of conflicts with its neighbors. A border war with Peru that flared in 1995 was resolved in 1999. Although Ecuador marked 30 years of civilian governance in 2004, the period was marred by political instability. Protests in Quito contributed to the mid-term ouster of three of Ecuador's last four democratically elected Presidents. In late 2008, voters approved a new constitution, Ecuador's 20th since gaining independence. General elections, under the new constitutional framework, were held in April 2009, and voters re-elected President Rafael CORREA.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Western South America, bordering the Pacific Ocean at the Equator, between Colombia and Peru
|
|
|
|

|
|
2 00 S, 77 30 W
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 283,561 sq km
country comparison to the world: 74
land:
276,841 sq km
water:
6,720 sq km
note:
includes Galapagos Islands
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than Nevada
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2,010 km
border countries:
Colombia 590 km, Peru 1,420 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,237 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 200 nm
continental shelf:
100 nm from 2,500-m isobath
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical along coast, becoming cooler inland at higher elevations; tropical in Amazonian jungle lowlands
|
|
|
|

|
|
coastal plain (costa), inter-Andean central highlands (sierra), and flat to rolling eastern jungle (oriente)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Chimborazo 6,267 m
note:
due to the fact that the earth is not a perfect sphere and has an equatorial bulge, the highest point on the planet furthest from its center is Mount Chimborazo not Mount Everest, which is merely the highest peak above sea-level
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, fish, timber, hydropower
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 5.71%
permanent crops:
4.81%
other:
89.48% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8,650 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
432 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 16.98 cu km/yr (12%/5%/82%)
per capita:
1,283 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
frequent earthquakes; landslides; volcanic activity; floods; periodic droughts
volcanism:
volcanic activity concentrated along the Andes Mountains; Sangay (elev. 5,230 m), which erupted in 2010, is mainland Ecuador's most active volcano; other historically active volcanoes in the Andes include Antisana, Cayambe, Chacana, Cotopaxi, Guagua Pichincha, Reventador, Sumaco, and Tungurahua; Fernandina (elev. 1,476 m), a shield volcano that last erupted in 2009, is the most active of the many Galapagos volcanoes; other historically active Galapagos volcanoes include Wolf, Sierra Negra, Cerro Azul, Pinta, Marchena, and Santiago
|
|
|
|

|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; water pollution; pollution from oil production wastes in ecologically sensitive areas of the Amazon Basin and Galapagos Islands
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
Cotopaxi in Andes is highest active volcano in world
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Ecuador |
|
|

|
|
noun: Ecuadorian(s)
adjective:
Ecuadorian
|
|
|
|

|
|
mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 65%, Amerindian 25%, Spanish and others 7%, black 3%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spanish (official), indigenous (Quechua, Shuar)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Roman Catholic 95%, other 5%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Ecuador's high poverty and income inequality most affect indigenous, mixed race, and rural populations. The government has increased its social spending to ameliorate these problems, but critics question the efficiency and implementation of its national development plan. Nevertheless, the conditional cash transfer program, which requires participants' children to attend school and have medical check-ups, has helped improve educational attainment and healthcare among poor children. Ecuador is stalled at above replacement level fertility and the population most likely will keep growing rather than stabilize.
An estimated 2 to 3 million Ecuadorians live abroad, but increased unemployment in key receiving countries - Spain, the United States, and Italy - is slowing emigration and increasing the likelihood of returnees to Ecuador. The first large-scale emigration of Ecuadorians occurred between 1980 and 2000, when an economic crisis drove Ecuadorians from southern provinces to New York City, where they had trade contacts. A second, nationwide wave of emigration in the late 1990s was caused by another economic downturn, political instability, and a currency crisis. Spain was the logical destination because of its shared language and the wide availability of low-skilled, informal jobs at a time when increased border surveillance made illegal migration to the US difficult. Ecuador has a small but growing immigrant population and is Latin America's top recipient of refugees; 98% are neighboring Colombians fleeing violence in their country.
|
|
|
|

|
|
15,223,680 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 29.5% (male 2,293,743/ female 2,202,203)
15-64 years:
63.9% (male 4,797,316/ female 4,930,465)
65 years and over:
6.6% (male 479,718/ female 520,235) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 26 years
male:
25.4 years
female:
26.6 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.419% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.6 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.01 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
|
|
|
|

|
|
-0.39 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 67% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Guayaquil 2.634 million; QUITO (capital) 1.801 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.92 male(s)/female
total population:
0.99 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
110 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 19.06 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 98
male:
22.37 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
15.59 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 75.94 years
country comparison to the world: 84
male:
73 years
female:
79.04 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.38 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|

|
|
5% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.48 physicians/1,000 population (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 96% of population
rural: 84% of population
total: 92% of population
unimproved:
urban: 4% of population
rural: 16% of population
total: 8% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.4% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
37,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,200 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever and malaria
water contact disease:
leptospirosis (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.2% (2004)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
91%
male:
92.3%
female:
89.7% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 14 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 14.1%
country comparison to the world: 81
male:
11.7%
female:
18.1% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Ecuador
conventional short form:
Ecuador
local long form:
Republica del Ecuador
local short form:
Ecuador
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Quito
geographic coordinates:
0 13 S, 78 30 W
time difference:
UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
24 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Azuay, Bolivar, Canar, Carchi, Chimborazo, Cotopaxi, El Oro, Esmeraldas, Galapagos, Guayas, Imbabura, Loja, Los Rios, Manabi, Morona-Santiago, Napo, Orellana, Pastaza, Pichincha, Santa Elena, Santo Domingo de los Tsachilas, Sucumbios, Tungurahua, Zamora-Chinchipe
|
|
|
|

|
|
24 May 1822 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day (independence of Quito), 10 August (1809)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20 October 2008; this is Ecuador's 20th constitution
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law based on the Chilean civil code with modifications
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18-65 years of age, universal and compulsory; 16 and other eligible voters, optional
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Rafael CORREA Delgado (since 15 January 2007); Vice President Lenin MORENO Garces (since 15 January 2007); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Rafael CORREA Delgado (since 15 January 2007); Vice President Lenin MORENO Garces (since 15 January 2007)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a four-year term and can be re-elected for another consecutive term; election last held on 26 April 2009 (next to be held 17 February 2013)
election results:
President Rafael CORREA Delgado reelected president; percent of vote - Rafael CORREA Delgado 52%; Lucio GUTIERREZ 28.2%; Alvaro NOBOA 11.4%; other 8.4%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Asamblea Nacional (124 seats; members are elected through a party-list proportional representation system to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 26 April 2009 (next to be held 17 February 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PAIS 59, PSP 19, PSC 11, PRIAN 7, MPD 5, PRE 3, other 20; note - defections by members of National Assembly are commonplace, resulting in frequent changes in the numbers of seats held by the various parties; as of 11 December 2012, the composition legislature is as follows: seats by party - PAIS 54, PSP 15, PRIAN 7, PSC 4, MPD 5, PRE 3, other 36
|
|
|
|

|
|
National Court of Justice or Corte Nacional de Justicia (according to the Constitution, justices are elected through a procedure overseen by the Judiciary Council); Constitutional Court or Corte Constitucional (Constitutional Court justices are appointed by a commission composed of two delegates each from the Executive, Legislative, and Transparency branches of government)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Alianza PAIS movement [Rafael Vicente CORREA Delgado]; Breakaway Party [Martha ROLDOS]; Institutional Renewal and National Action Party or PRIAN [Alvaro NOBOA]; Pachakutik Plurinational Unity Movement - New Country or MUPP-NP [Rafael ANTUNI]; Patriotic Society Party or PSP [Lucio GUTIERREZ Borbua]; Popular Democratic Movement or MPD [Luis VILLACIS]; Roldosist Party or PRE [Abdala BUCARAM Pulley, director]; Social Christian Party or PSC [Pascual DEL CIOPPO]; Socialist Party; Warrior's Spirit Movement [Jaime NEBOT]
|
|
|
|

|
|
Confederation of Indigenous Nationalities of Ecuador or CONAIE [Humberto CHOLANGO]; Federation of Indigenous Evangelists of Ecuador or FEINE [Manuel CHUGCHILAN, president]; National Federation of Indigenous Afro-Ecuatorianos and Peasants or FENOCIN [Luis Alberto ANDRANGO Cadena, president]; National Teacher's Union or UNE [Mariana PALLASCO]
|
|
|
|

|
|
CAN, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Saskia Nathalie CELY Suarez
chancery:
2535 15th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-7200
FAX:
[1] (202) 667-3482
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Miami, Minneapolis, New Haven, New Orleans, New York, Newark (New Jersey), Phoenix, San Francisco, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Adam NAMM
embassy:
Avenida Avigiras E12-170 y Avenida Eloy Alfaro, Quito
mailing address:
Avenida Guayacanes N52-205 y Avenida Avigiras
telephone:
[593] (2) 398-5000
FAX:
[593] (2) 398-5100
consulate(s) general:
Guayaquil
|
|
|
|

|
|
three horizontal bands of yellow (top, double width), blue, and red with the coat of arms superimposed at the center of the flag; the flag retains the three main colors of the banner of Gran Columbia, the South American republic that broke up in 1830; the yellow color represents sunshine, grain, and mineral wealth, blue the sky, sea, and rivers, and red the blood of patriots spilled in the struggle for freedom and justice
note:
similar to the flag of Colombia, which is shorter and does not bear a coat of arms
|
|
|
|

|
|
Andean condor
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Salve, Oh Patria!" (We Salute You Our Homeland)
lyrics/music:
Juan Leon MERA/Antonio NEUMANE
note:
adopted 1948; Juan Leon MERA wrote the lyrics in 1865; only the chorus and second verse are sung
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Ecuador is substantially dependent on its petroleum resources, which have accounted for more than half of the country's export earnings and approximately two-fifths of public sector revenues in recent years. In 1999/2000, Ecuador's economy suffered from a banking crisis, with GDP contracting by 5.3% and poverty increasing significantly. In March 2000, the Congress approved a series of structural reforms that also provided for the adoption of the US dollar as legal tender. Dollarization stabilized the economy, and positive growth returned in the years that followed, helped by high oil prices, remittances, and increased non-traditional exports. From 2002-06 the economy grew an average of 5.2% per year, the highest five-year average in 25 years. After moderate growth in 2007, the economy reached a growth rate of 7.2% in 2008, buoyed by high global petroleum prices and increased public sector investment. President Rafael CORREA, who took office in January 2007, defaulted in December 2008 on Ecuador's sovereign debt, which, with a total face value of approximately US$3.2 billion, represented about 30% of Ecuador's public external debt. In May 2009, Ecuador bought back 91% of its "defaulted" bonds via an international reverse auction. Economic policies under the CORREA administration - for example, an announcement in late 2009 of its intention to terminate 13 bilateral investment treaties, including one with the United States - have generated economic uncertainty and discouraged private investment. The Ecuadorian economy slowed to 0.4% growth in 2009 due to the global financial crisis and to the sharp decline in world oil prices and remittance flows. Growth picked up to a 3.6% rate in 2010 and 7.8% in 2011, before falling to 4% in 2012. China has become Ecuador's largest foreign bilateral lender since Quito defaulted in 2008, allowing the government to maintain a high rate of social spending; Quito owes the Chinese government more than $9 billion in oil for cash loans as of December 2012.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$134.7 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
$129.5 billion (2011 est.)
$120.1 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$70.84 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
7.8% (2011 est.)
3.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$8,800 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
$8,600 (2011 est.)
$8,100 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 6.4%
industry:
36.1%
services:
57.5% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.769 million (2012 est.) (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 27.6%
industry:
18.8%
services:
53.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
28.6% (December 2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.4%
highest 10%:
38.3%
note:
data for urban households only (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
47.3 (June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 30
50.5 (2006)
note:
data are for urban households
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $31.5 billion
expenditures:
$32.8 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
44.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|

|
|
-1.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|

|
|
23.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
21.7% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
4.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.17% (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 32
8.68% (31 December 2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.7% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
8.35% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$7.701 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$6.943 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$26.55 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
$22.18 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$22.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
$20.05 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.779 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 81
$5.263 billion (31 December 2010)
$4.248 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bananas, coffee, cocoa, rice, potatoes, manioc (tapioca), plantains, sugarcane; cattle, sheep, pigs, beef, pork, dairy products; fish, shrimp; balsa wood
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.1% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|

|
|
-$1.387 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
-$221 million (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$23.77 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
$23.08 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, bananas, cut flowers, shrimp, cacao, coffee, wood, fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 37.8%, Panama 9.9%, Peru 6.2%, Venezuela 5.2%, Chile 4.9%, Russia 4.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$24.67 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
$23.24 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
industrial materials, fuels and lubricants, nondurable consumer goods
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 27.6%, China 10.1%, Colombia 9%, Panama 4.6%, Peru 4.5%, Brazil 4.3%, South Korea 4% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$3.248 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
$2.958 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$20.03 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
$18.62 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$13.11 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
$12.39 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$6.33 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
$6.33 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
16.88 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
14.92 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
14.1 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.3 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.939 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
56.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|

|
|
41.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|

|
|
500,700 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|

|
|
341,900 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.573 billion bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|

|
|
174,900 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|

|
|
201,600 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|

|
|
42,230 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
76,560 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|

|
|
330 million cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
330 million cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.985 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.43 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.211 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|

|
|
15.333 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: elementary fixed-line service, but increasingly sophisticated mobile-cellular network
domestic:
fixed-line services provided by multiple telecommunications operators; fixed-line teledensity stands at about 15 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular use has surged and subscribership has reached 100 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 593; landing points for the PAN-AM and South America-1 submarine cables that provide links to the west coast of South America, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, and extending onward to Aruba and the US Virgin Islands in the Caribbean; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Ecuador has multiple TV networks and many local channels, as well as more than 300 radio stations; many TV and radio stations are privately-owned; the government owns or controls 5 national TV stations and multiple radio stations; broadcast media required by law to give the government free air time to broadcast programs produced by the state (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.ec
|
|
|
|

|
|
170,538 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.352 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
431 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 101
over 3,047 m:
3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
18
914 to 1,523 m:
23
under 914 m:
52 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 330
914 to 1,523 m:
40
under 914 m:
290 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
extra heavy crude 434 km; gas 5 km; oil 1,378 km; refined products 1,262 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 965 km
country comparison to the world: 90
narrow gauge:
965 km 1.067-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 43,670 km
country comparison to the world: 84
paved:
6,472 km
unpaved:
37,198 km (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,500 km (most inaccessible) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 44
country comparison to the world: 72
by type:
cargo 1, chemical tanker 4, liquefied gas 1, passenger 9, petroleum tanker 28, refrigerated cargo 1
registered in other countries:
4 (Panama 3, Peru 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Esmeraldas, Guayaquil, Manta, Puerto Bolivar
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Ecuadorian Armed Forces: Ecuadorian Land Force (Fuerza Terrestre Ecuatoriana, FTE), Ecuadorian Navy (Fuerza Naval del Ecuador (FNE), includes Naval Infantry, Naval Aviation, Coast Guard), Ecuadorian Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Ecuatoriana, FAE) (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20 years of age for selective conscript military service; Air Force 18-22 years of age, Ecadorian birth requirement; 12-month service obligation (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 3,728,906
females age 16-49:
3,844,918 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 2,834,213
females age 16-49:
3,269,535 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 152,593
female:
147,143 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.9% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Ecuador |
|
|

|
|
organized illegal narcotics operations in Colombia penetrate across Ecuador's shared border, which thousands of Colombians also cross to escape the violence in their home country
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 122,587 (Colombia) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
significant transit country for cocaine originating in Colombia and Peru, with much of the US-bound cocaine passing through Ecuadorian Pacific waters; importer of precursor chemicals used in production of illicit narcotics; attractive location for cash-placement by drug traffickers laundering money because of dollarization and weak anti-money-laundering regime; increased activity on the northern frontier by trafficking groups and Colombian insurgents
(2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

