-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
| Introduction ::El Salvador |
|
|

|
|
El Salvador achieved independence from Spain in 1821 and from the Central American Federation in 1839. A 12-year civil war, which cost about 75,000 lives, was brought to a close in 1992 when the government and leftist rebels signed a treaty that provided for military and political reforms.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
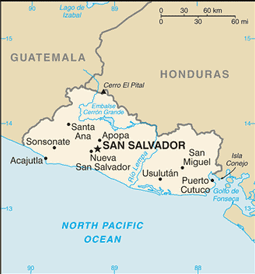
Central America, bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Guatemala and Honduras
|
|
|
|

|
|
13 50 N, 88 55 W
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 21,041 sq km
country comparison to the world: 153
land:
20,721 sq km
water:
320 sq km
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than Massachusetts
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 545 km
border countries:
Guatemala 203 km, Honduras 342 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
307 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical; rainy season (May to October); dry season (November to April); tropical on coast; temperate in uplands
|
|
|
|

|
|
mostly mountains with narrow coastal belt and central plateau
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Cerro El Pital 2,730 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
hydropower, geothermal power, petroleum, arable land
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 31.37%
permanent crops:
11.88%
other:
56.75% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
450 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|

|
|
25.2 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1.28 cu km/yr (25%/16%/59%)
per capita:
186 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
known as the Land of Volcanoes; frequent and sometimes destructive earthquakes and volcanic activity; extremely susceptible to hurricanes
volcanism:
significant volcanic activity; San Salvador (elev. 1,893 m), which last erupted in 1917, has the potential to cause major harm to the country's capital, which lies just below the volcano's slopes; San Miguel (elev. 2,130 m), which last erupted in 2002, is one of the most active volcanoes in the country; other historically active volcanoes include Conchaguita, Ilopango, Izalco, and Santa Ana
|
|
|
|

|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution; contamination of soils from disposal of toxic wastes
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|

|
|
smallest Central American country and only one without a coastline on Caribbean Sea
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::El Salvador |
|
|

|
|
noun: Salvadoran(s)
adjective:
Salvadoran
|
|
|
|

|
|
mestizo 90%, white 9%, Amerindian 1%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Spanish (official), Nahua (among some Amerindians)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Roman Catholic 57.1%, Protestant 21.2%, Jehovah's Witnesses 1.9%, Mormon 0.7%, other religions 2.3%, none 16.8% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
El Salvador is the smallest and most densely populated country in Central America. It is well into its demographic transition, experiencing slower population growth, a decline in its number of youths, and the gradual aging of its population. The increased use of family planning has substantially lowered El Salvador's fertility rate, from approximately 6 children per woman in the 1970s to replacement level today. A 2008 national family planning survey showed that female sterilization remained the most common contraception method in El Salvador - its sterilization rate is among the highest in Latin America and the Caribbean - but that the use of injectable contraceptives is growing. Fertility differences between rich and poor and urban and rural women are narrowing.
Salvadorans fled during the 1979 to 1992 civil war mainly to the United States but also to Canada and to neighboring Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. Emigration to the United States increased again in the 1990s and 2000s as a result of deteriorating economic conditions, natural disasters (Hurricane Mitch in 1998 and earthquakes in 2001), and family reunification. At least 20% of El Salvador's population lives abroad. The remittances they send home account for close to 20% of GDP, are the second largest source of external income after exports, and have helped reduce poverty.
|
|
|
|

|
|
6,090,646 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 29.7% (male 929,135/ female 882,159)
15-64 years:
63.7% (male 1,829,483/ female 2,049,977)
65 years and over:
6.6% (male 178,004/ female 221,888) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 24.7 years
male:
23.4 years
female:
26.2 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.303% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|

|
|
17.44 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.63 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 173
|
|
|
|

|
|
-8.78 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 64% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
SAN SALVADOR (capital) 1.534 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.89 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.8 male(s)/female
total population:
0.93 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
81 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 19.66 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 97
male:
21.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
17.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 73.69 years
country comparison to the world: 116
male:
70.41 years
female:
77.12 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.04 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.9% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.596 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.1 beds/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 89% of population
rural: 83% of population
total: 87% of population
unimproved:
urban: 11% of population
rural: 17% of population
total: 13% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|

|
|
34,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever
water contact disease:
leptospirosis (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.1% (2003)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.6% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
81.1%
male:
82.8%
female:
79.6% (2007 census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
12 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 11.4%
country comparison to the world: 94
male:
13%
female:
8.3% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of El Salvador
conventional short form:
El Salvador
local long form:
Republica de El Salvador
local short form:
El Salvador
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: San Salvador
geographic coordinates:
13 42 N, 89 12 W
time difference:
UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
all year for 2012
|
|
|
|

|
|
14 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Ahuachapan, Cabanas, Chalatenango, Cuscatlan, La Libertad, La Paz, La Union, Morazan, San Miguel, San Salvador, San Vicente, Santa Ana, Sonsonate, Usulutan
|
|
|
|

|
|
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20 December 1983
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law system with minor common law influence; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Carlos Mauricio FUNES Cartagena (since 1 June 2009); Vice President Salvador SANCHEZ CEREN (since 1 June 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Carlos Mauricio FUNES Cartagena (since 1 June 2009); Vice President Salvador SANCHEZ CEREN (since 1 June 2009)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers selected by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a single five-year term; election last held on 15 March 2009 (next to be held in February 2014)
election results:
Mauricio FUNES Cartagena elected president; percent of vote - Mauricio FUNES Cartagena 51.3%, Rodrigo AVILA 48.7%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral Legislative Assembly or Asamblea Legislativa (84 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve three-year terms)
elections:
last held on 11 March 2012 (next to be held in 2015)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ARENA 33, FMLN 31, GANA 11, CN 7, PES 1, PCD 1
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (15 judges are selected by the Legislative Assembly; the 15 judges are assigned to four Supreme Court chambers - constitutional, civil, penal, and administrative conflict)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Democratic Change (Cambio Democratico) or CD [Tomas CHEVEZ] (formerly United Democratic Center or CDU); Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front or FMLN [Medardo GONZALEZ]; Great Alliance for National Unity or GANA [Andres ROVIRA]; National Coalition (Concertation Nacional) or CN [Ciro CRUZ ZEPEDA] (formerly the National Conciliation Party or PCN); Nationalist Republican Alliance or ARENA [Alfredo CRISTIANI]; Party of Hope or PES [Rodolfo Antonio PARKER Soto] (formerly the Christian Democratic Party or PDC)
|
|
|
|

|
|
labor organizations - Electrical Industry Union of El Salvador or SIES; Federation of the Construction Industry, Similar Transport and other activities, or FESINCONTRANS; National Confederation of Salvadoran Workers or CNTS; National Union of Salvadoran Workers or UNTS; Port Industry Union of El Salvador or SIPES; Salvadoran Union of Ex-Petrolleros and Peasant Workers or USEPOC; Salvadoran Workers Central or CTS; Workers Union of Electrical Corporation or STCEL; business organizations - National Association of Small Enterprise or ANEP; Salvadoran Assembly Industry Association or ASIC; Salvadoran Industrial Association or ASI
|
|
|
|

|
|
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, NAM (observer), OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Francisco Robert ALTSCHUL Fuentes
chancery:
Suite 100, 1400 16th Street, Washington, DC 20036
telephone:
[1] (202) 265-9671
FAX:
[1] (202) 234-3763
consulate(s) general:
Brentwood (New York), Boston, Chicago, Coral Gables (Florida), Dallas, Duluth (Georgia), Elizabeth (New Jersey), Houston, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Nogales (Arizona), Santa Ana (California), San Francisco, Woodbridge (Virginia)
consulate(s):
Boston, Elizabeth (New Jersey)
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mari Carmen APONTE
embassy:
Final Boulevard Santa Elena Sur, Antiguo Cuscatlan, La Libertad, San Salvador
mailing address:
Unit 3450, APO AA 34023; 3450 San Salvador Place, Washington, DC 20521-3450
telephone:
[503] 2501-2999
FAX:
[503] 2501-2150
|
|
|
|

|
|
three equal horizontal bands of blue (top), white, and blue with the national coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms features a round emblem encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE EL SALVADOR EN LA AMERICA CENTRAL; the banner is based on the former blue-white-blue flag of the Federal Republic of Central America; the blue bands symbolize the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, while the white band represents the land between the two bodies of water, as well as peace and prosperity
note:
similar to the flag of Nicaragua, which has a different coat of arms centered in the white band - it features a triangle encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE NICARAGUA on top and AMERICA CENTRAL on the bottom; also similar to the flag of Honduras, which has five blue stars arranged in an X pattern centered in the white band
|
|
|
|

|
|
turquoise-browed motmot (bird)
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Himno Nacional de El Salvador" (National Anthem of El Salvador)
lyrics/music:
Juan Jose CANAS/Juan ABERLE
note:
officially adopted 1953, in use since 1879; the anthem of El Salvador is one of the world's longest
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
The smallest country in Central America geographically, El Salvador has the third largest economy in the region. With the global recession in 2009, real GDP contracted by 3.1%. The economy slowed even further during 2010-12. Remittances accounted for 17% of GDP in 2011 and were received by about a third of all households. In 2006, El Salvador was the first country to ratify the Dominican Republic-Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR), which has bolstered the export of processed foods, sugar, and ethanol, and supported investment in the apparel sector amid increased Asian competition. El Salvador has promoted an open trade and investment environment and has embarked on a wave of privatizations extending to telecom, electricity distribution, banking, and pension funds. The Salvadoran Government maintained fiscal discipline during post-war reconstruction and reconstruction following earthquakes in 2001 and hurricanes in 1998 and 2005. Taxes levied by the government include a value added tax (VAT) of 13%, income tax of 30%, excise taxes on alcohol and cigarettes, and import duties. The VAT accounted for about 51.7% of total tax revenues in 2011. El Salvador's external debt amounts to about one-fourth of GDP. In 2012, El Salvador successfully completed a $461 million compact with the Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) - a United States Government agency aimed at stimulating economic growth and reducing poverty in the country's northern region, the primary conflict zone during the civil war, through investments in education, public services, enterprise development, and transportation infrastructure. In December 2011, the MCC approved El Salvador's eligibility to develop a proposal for a program for consideration.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$45.98 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
$45.3 billion (2011 est.)
$44.67 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$23.99 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
1.4% (2011 est.)
1.4% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$7,700 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
$7,700 (2011 est.)
$7,600 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 10.5%
industry:
30%
services:
59.4% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.593 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 21%
industry:
20%
services:
58% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
7% (2011 est.)
note:
data are official rates; but the economy has much underemployment
|
|
|
|

|
|
36.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1%
highest 10%:
37% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
46.9 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 31
52.5 (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
14.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $4.835 billion
expenditures:
$5.534 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|

|
|
-2.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|

|
|
57.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
57.5% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
El Salvador's total public debt includes non-financial public sector debt, financial public sector debt, and central bank debt.
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
5.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.2% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
5.99% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.942 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
$2.561 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$9.527 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
$9.213 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$11.11 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
$10.69 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.474 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 84
$4.227 billion (31 December 2010)
$4.432 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
coffee, sugar, corn, rice, beans, oilseed, cotton, sorghum; beef, dairy products
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.8% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|

|
|
-$1.035 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
-$1.223 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$5.804 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
$5.402 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
offshore assembly exports, coffee, sugar, textiles and apparel, gold, ethanol, chemicals, electricity, iron and steel manufactures
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 45.1%, Guatemala 13.3%, Honduras 8.6%, Nicaragua 5.2%, Germany 4.1% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$10.44 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
$9.801 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
raw materials, consumer goods, capital goods, fuels, foodstuffs, petroleum, electricity
|
|
|
|

|
|
US 39%, Guatemala 9.8%, Mexico 7.7%, China 5.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.623 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
$2.504 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$12.84 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$12.18 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$8.747 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
$8.097 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$12.4 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
$12.4 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
note: the US dollar is used as a medium of exchange and circulates freely in the economy, 1 (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.728 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.756 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|

|
|
101.6 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|

|
|
215.8 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.501 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|

|
|
53% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|

|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|

|
|
31.4% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|

|
|
15.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|

|
|
13,160 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|

|
|
16,750 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|

|
|
44,040 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,158 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|

|
|
26,860 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.484 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::El Salvador |
|
|

|
|
1.03 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.316 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: multiple mobile-cellular providers are expanding services rapidly and in 2011 teledensity exceeded 135 per 100 persons; growth in fixed-line services has slowed in the face of mobile-cellular competition
domestic:
nationwide microwave radio relay system
international:
country code - 503; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean); connected to Central American Microwave System (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
multiple privately-owned national terrestrial TV networks, supplemented by cable TV networks that carry international channels; hundreds of commercial radio broadcast stations and 1 government-owned radio broadcast station (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.sv
|
|
|
|

|
|
24,070 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|

|
|
746,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::El Salvador |
|
|

|
|
65 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5
over 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 60
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
11
under 914 m:
48 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 283 km
country comparison to the world: 121
narrow gauge:
283 km 0.600-m gauge
note:
railways have been inoperable since 2005 because of disuse and high costs that led to a lack of maintenance (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 10,886 km
country comparison to the world: 134
paved:
2,827 km (includes 327 km of expressways)
unpaved:
8,059 km (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
(Rio Lempa is partially navigable for small craft) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Puerto Cutuco
oil terminals:
Acajutla offshore terminal
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Salvadoran Armed Forces (FAES): Salvadoran Army (ES), Salvadoran Navy (FNES), Salvadoran Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Salvadorena, FAS) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age for selective compulsory military service; 16-22 years of age for voluntary male or female service; service obligation - 12 months, with 11 months for officers and NCOs (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,449,214
females age 16-49:
1,611,248 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,079,038
females age 16-49:
1,373,368 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 71,530
female:
68,971 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::El Salvador |
|
|

|
|
International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled on the delimitation of "bolsones" (disputed areas) along the El Salvador-Honduras boundary, in 1992, with final agreement by the parties in 2006 after an Organization of American States survey and a further ICJ ruling in 2003; the 1992 ICJ ruling advised a tripartite resolution to a maritime boundary in the Gulf of Fonseca advocating Honduran access to the Pacific; El Salvador continues to claim tiny Conejo Island, not identified in the ICJ decision, off Honduras in the Gulf of Fonseca
|
|
|
|

|
|
transshipment point for cocaine; small amounts of marijuana produced for local consumption; significant use of cocaine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

