-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on January 29, 2013 |

|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
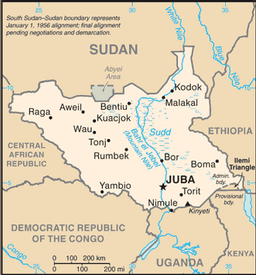
Click map to enlarge 
|
|

|
| |
| no photos available of South Sudan |
|
|
|
| Introduction ::South Sudan |
|
|

|
|
Egypt attempted to colonize the region of southern Sudan by establishing the province of Equatoria in the 1870s. Islamic Mahdist revolutionaries overran the region in 1885, but in 1898 a British force was able to overthrow the Mahdist regime. An Anglo-Egyptian Sudan was established the following year with Equatoria being the southernmost of its eight provinces. The isolated region was largely left to itself over the following decades, but Christian missionaries converted much of the population and facilitated the spread of English. When Sudan gained its independence in 1956, it was with the understanding that the southerners would be able to participate fully in the political system. When the Arab Khartoum government reneged on its promises, a mutiny began that led to two prolonged periods of conflict (1955-1972 and 1983-2005) in which perhaps 2.5 million people died - mostly civilians - due to starvation and drought. Ongoing peace talks finally resulted in a Comprehensive Peace Agreement, signed in January 2005. As part of this agreement the south was granted a six-year period of autonomy to be followed by a referendum on final status. The result of this referendum, held in January 2011, was a vote of 98% in favor of secession. Independence was attained on 9 July 2011. Since independence South Sudan has struggled with good governance and nation building and has attempted to control rebel militia groups operating in its territory. Economic conditions have deteriorated since January 2012 when the government decided to shut down oil production following bilateral disagreements with Sudan.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
East-Central Africa; south of Sudan, north of Uganda and Kenya, west of Ethiopia
|
|
|
|

|
|
8 00 N, 30 00 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 644,329 sq km
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than Texas
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5,413 km
border countries:
Central African Republic 989 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 639 km, Ethiopia 934 km, Kenya 232 km, Sudan 2,184 km, Uganda 435 km
note:
South Sudan-Sudan boundary represents 1 January 1956 alignment; final alignment pending negotiations and demarcation; final sovereignty status of Abyei Area pending negotiations between South Sudan and Sudan
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|

|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|

|
|
hot with seasonal rainfall influenced by the annual shift of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone; rainfall is heaviest in the upland areas of the south and diminishes to the north
|
|
|
|

|
|
the terrain gradually rises from plains in the north and center to southern highlands along the border with Uganda and Kenya; the White Nile, flowing north out of the uplands of Central Africa, is the major geographic feature of the country supporting agriculture and extensive wild animal populations; The Sudd (a name derived from floating vegetation that hinders navigation) is a large swampy area of more than 100,000 sq km fed by the waters of the White Nile that dominates the center of the country
|
|
|
|

|
|
Lowest point: NA
highest point:
Kinyeti 3,187 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
hydropower, fertile agricultural land, gold, diamonds, petroleum, hardwoods, limestone, iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc, tungsten, mica, silver
|
|
|
|

|
|
The Sudd is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile, comprising more than 15% of the total area; it is one of the world's largest wetlands
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::South Sudan |
|
|

|
|
noun: South Sudanese (singular and plural)
adjective:
South Sudanese
|
|
|
|

|
|
Dinka, Kakwa, Bari, Azande, Shilluk, Kuku, Murle, Mandari, Didinga, Ndogo, Bviri, Lndi, Anuak, Bongo, Lango, Dungotona, Acholi
|
|
|
|

|
|
English (official), Arabic (includes Juba and Sudanese variants) (official), regional languages include Dinka, Nuer, Bari, Zande, Shilluk
|
|
|
|

|
|
animist, Christian
|
|
|
|

|
|
10,625,176 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 46.5% (male 2,526,970/ female 2,414,245)
15-64 years:
51.3% (male 2,738,478/ female 2,716,671)
65 years and over:
2.2% (male 130,001/ female 98,811) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 22% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
JUBA (capital) 250,000 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 71.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.66 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 67% of population
rural: 53% of population
total: 55% of population
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne disease:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria, dengue fever, African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis
animal contact disease:
rabies
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
27%
male:
40%
female:
16%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of South Sudan
conventional short form:
South Sudan
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Juba
geographic coordinates:
04 51 N 31 37 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
10 states; Central Equatoria, Eastern Equatoria, Jonglei, Lakes, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, Unity, Upper Nile, Warrap, Western Bahr el Ghazal, Western Equatoria
|
|
|
|

|
|
9 July 2011 (from Sudan)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, (9 July 2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Transitional Constitution of the Republic of South Sudan 2011, effective 9 July 2011
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); Vice President Riek MACHAR (since 10 July 2011); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011); Vice President Riek MACHAR (since 10 July 2011)
cabinet:
National Council of Ministers; appointed by the president and approved by a resolution from the Legislative Assembly
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a four year term; election last held on 11-15 April 2010 (next to be held in 2015)
election results:
Salva KIIR Mayardit elected president; percent of vote - Salva KIIR Mayardit 93%, Lam AKOL 7%
|
|
|
|

|
|
bicameral National Legislature consists of the National Legislative Assembly (332 seats) and the Council of States (50 seats); members serve four-year terms
elections:
National Legislative Assembly - last held 11-15 April 2010 (next to be held in 2015); Council of States - established and members appointed 1 August 2011
election results:
National Legislative Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - SPLM 251, SPLM-DC 6, NCP 3, independent 6, unknown 66; Council of States - seats by party - SPLM 20, unknown 30
note:
a presidential decree of 1 August 2011 reconstituted the National Legislative Assembly, as permitted under Article 94 of the Transitional Constitution, to include the 170 members elected 11-15 April 2010, 96 former members of the National Assembly of the Republic of Sudan, and 66 newly appointed members for a total of 332; a presidential decree also established a Council of States, initially with 50 members - the 20 former members of the Council of States of the Republic of Sudan plus an additional 30 appointed representatives
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court, Courts of Appeal, High Courts, County Courts
|
|
|
|

|
|
Sudan People's Liberation Movement or SPLM [Salva KIIR Mayardit]; National Congress Party or NCP; Sudan People's Liberation Movement for Democratic Change or SPLM-DC [Sisto OLUR Erista]
|
|
|
|

|
|
AU, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOM, ITU, MIGA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Akec KHOC Aciew Khoc
chancery:
1233 20th St. NW, Suite 602, Washington, DC 20036
telephone:
[1] (202) 293-7943
FAX:
[1] (202) 293-7941
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Susan D. PAGE
embassy:
Juba
|
|
|
|

|
|
three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and green; the red band is edged in white; a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side contains a gold, five-pointed star; black represents the people of South Sudan, red the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green the verdant land, and blue the waters of the Nile; the gold star represents the unity of the states making up South Sudan
note:
resembles the flag of Kenya; one of only two national flags to display six colors as part of its primary design, the other is South Africa's
|
|
|
|

|
|
African fish eagle
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: South Sudan Oyee! (Hooray!)
lyrics/music:
collective of 49 poets/Juba University students and teachers
note:
adopted 2011; the anthem was selected in a national contest
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Industry and infrastructure in landlocked South Sudan are severely underdeveloped and poverty is widespread, following several decades of civil war with Sudan. Subsistence agriculture provides a living for the vast majority of the population. Property rights are tentative and price signals are missing because markets are not well organized. South Sudan has little infrastructure - just 60 km of paved roads. Electricity is produced mostly by costly diesel generators and running water is scarce. The government spends large sums of money to maintain a big army; delays in paying salaries have periodically resulted in riots by unruly soldiers. Ethnic conflicts have resulted in a large number of civilian deaths and displacement. South Sudan depends largely on imports of goods, services, and capital from the north. Despite these disadvantages, South Sudan does have abundant natural resources. South Sudan produces nearly three-fourths of the former Sudan's total oil output of nearly a half million barrels per day. The government of South Sudan derives nearly 98% of its budget revenues from oil. Oil is exported through two pipelines that run to refineries and shipping facilities at Port Sudan on the Red Sea, and the 2005 oil sharing agreement with Khartoum called for a 50-50 sharing of oil revenues between the two entities. That deal expired on 9 July 2011, however, when South Sudan became an independent country. The economy of South Sudan undoubtedly will remain linked to Sudan for some time, given the long lead time and great expense required to build another pipeline. In early 2012 South Sudan suspended production of oil because of its dispute with Sudan over transshipment fees. This had a devastating impact on GDP, which declined by at least 55% in 2012. South Sudan holds one of the richest agricultural areas in Africa with fertile soils and abundant water supplies. Currently the region supports 10-20 million head of cattle. South Sudan does not have large external debt or structural trade deficits and has received more than $4 billion in foreign aid since 2005, largely from the UK, US, Norway, and Netherlands. Following independence, South Sudan's central bank issued a new currency, the South Sudanese Pound, allowing a short grace period for turning in the old currency. Annual inflation peaked at 79% in May 2012. Long term problems include alleviating poverty, maintaining macroeconomic stability, improving tax collection and financial management, focusing resources on speeding growth, and improving the business environment.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$9.664 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
$21.47 billion (2011 est.)
$21.16 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$11.45 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
-55% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 217
1.4% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$900 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
$2,200 (2011 est.)
$2,500 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
50.6% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
79% (May 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 224
|
|
|
|

|
|
sorghum, maize, rice, millet, wheat, gum arabic, sugarcane, mangoes, papayas, bananas, sweet potatoes, sunflower, cotton, sesame, cassava (manioc), beans, peanuts; cattle, sheep
|
|
|
|

|
|
South Sudanese pounds (SSP) per US dollar -
0.7838 (2012 est.)
South Sudanese pounds (SSP) per US dollar - 0.7185 (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::South Sudan |
|
|

|
|
international: country code - 211
|
|
|
|

|
|
TV is controlled by the government; several private FM stations are operational in South Sudan; some foreign radio broadcasts are available
|
|
|
|

|
|
.ss
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::South Sudan |
|
|

|
|
84
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 81
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
12
914 to 1,523 m:
34
under 914 m:
34
|
|
|
|

|
|
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|

|
|
est. 236 km; note - rail system reported to be in disrepair (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
est. 7,000 km; note - very little of the road network is paved and much of it is in disrepair (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
see entry for Sudan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA)
|
|
|
|

|
|
the Government of South Sudan announced in August 2010 that anyone younger than 18 years of age would be mustered out of the army, but 900 children were estimated to still be active at the end of that year; in April 2011, a conscription program was being implemented to thwart recruitment of military-aged males into other armed groups (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::South Sudan |
|
|

|
|
South Sudan-Sudan boundary represents 1 January 1956 alignment, final alignment pending negotiations and demarcation; final sovereignty status of Abyei Area pending negotiations between South Sudan and Sudan; periodic violent skirmishes with South Sudanese residents over water and grazing rights persist among related pastoral populations along the border with the Central African Republic; the boundary that separates Kenya and South Sudan's sovereignty is unclear in the "Ilemi Triangle," which Kenya has administered since colonial times
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 183,169 (Sudan); 18,400 (Democratic Republic of the Congo); 5,889 (Ethiopia); 1,589 (Central African Republic) (2013)
IDPs:
350,000 newly displaced in 2011 (information is lacking on those displaced in earlier years; displacement caused by: fighting in Abyei between the Sudan Armed Forces and the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) in May 2011; clashes between the SPLA and dissident militia groups in South Sudan; inter-tribal conflicts over resources and cattle; attacks from the Lord's Resistance Army; floods and drought)
|
|
|
|

|
|
current situation: South Sudan is a source and destination country for men, women, and children who are subjected to forced labor and sextrafficking; South Sudanese women and girls, particularly those who are internally displaced from rural areas, are vulnerable to forced labor and sexual exploitation in urban centers; the rising number of street children and child laborers are also exploited for forced labor and prostitution; women and girls from Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, and Congo are trafficked to South Sudan with promises of legitimate jobs and are forced into the sex trade; inter-ethnic abductions continue between some communities in South Sudan
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - the government of South Sudan does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government continued to take some steps to eliminate the use of child soldiers in its armed forces, but it did not demonstrate evidence of increasing efforts to address other forms of trafficking; pulbic officials' awareness of human trafficking remained extremely low and the government lacked sufficient human and physical capital to adequately enforce its laws, the government indisriminately arrested individuals in prostitution, including child sex trrafficking victims, and sentenced them to prison (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

