Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide






CHAPTER 1. Overview of Enterprise Manager
This chapter introduces Oracle Enterprise Manager and provides an overview of its components. The following topics are included in this chapter:
Note: For an overview of the Enterprise Manager system, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts.
Introducing Enterprise Manager
Oracle Enterprise Manager combines a graphical console, agents, common services, and tools to provide an integrated, comprehensive systems management platform for managing Oracle products. From Enterprise Manager's console, you can:
- Administer, diagnose, and tune multiple databases.
- Distribute software to multiple servers and clients.
- Schedule jobs on multiple nodes at varying time intervals.
- Monitor objects and events throughout the network.
- Customize your display using multiple graphic maps and groups of network objects, such as nodes and databases.
- Integrate participating third-party tools.
Attention: See the compatability matrix in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Documentation Release Note for information on the specific Oracle7 server releases that are supported by Oracle Enterprise Manager and its components.
Enterprise Manager's Components
Enterprise Manager consists of multiple components that integrate into a powerful and easy-to-use graphical user interface.
- Database Administration (DBA) Tools and Utilities
Console
The Enterprise Manager Console is a graphical user interface that provides menus, toolbars, launch palettes, and the framework to allow access to Oracle tools, plus utilities available through other vendors.
The Console menu bar provides access to the Navigator, Map, Job, Event, and database administration applications. You can also use toolbars and tool palettes to access the tools. For information on the Console menus, see page 1 - 8.
The format of the Console screen and the applications displayed are determined by the products purchased and user preferences. See Figure 1 - 1 on for an illustration of a Console screen.
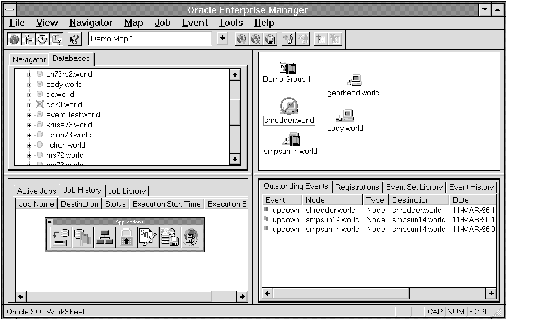 Figure 1 - 1. Enterprise Manager Console
Figure 1 - 1. Enterprise Manager Console
Navigator
The Navigator provides a tree list of all the objects in a network, providing a direct view of objects such as user-defined groups, nodes, listeners, names servers, and databases, plus the objects that they contain. While specific types of objects can be viewed in the tree lists of the DBA tools, the Navigator shows all the network objects with their relationships to other objects.
Through the Navigator, you can also launch administration tasks with various objects, such as users and tablespaces. You can also perform some administration tasks in the Navigator, such as creating, altering, or dropping a user. For information on this feature, see "Navigator"![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Map
The Map allows you to monitor your system at a glance. Using the Map system, you can create, save, modify, and recall views of the network. You simply drag and drop objects from the Navigator into the Map view to create the various groups that you want to monitor.
For information, see "Map" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Job Scheduling
Job Scheduling allows you to manage job scheduling among the databases, listeners, and nodes that you are administering. Jobs can be scheduled at various times, such as daily or weekly, and at single or multiple destinations. The Job window contains the following pages of information:
For information, see "Job Scheduling" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Event Management
Event Management allows you to track and display the status of events occurring on the databases, listeners, and nodes in your networked system. You can also create a job that you specify to be run to automatically fix the problem. The Event window contains the following pages of information:
For information, see "Event Management" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Repository
The repository is a set of tables in an Oracle database. Each administrator is associated with a specific repository in a database. Any information related to the tasks performed by the administrator is stored in that repository.
For example, the repository contains information about the jobs you submitted and the events being monitored for you. The repository also stores information about maps and groups.
The repository tables can be installed in any database accessible to the Console. An administrator can log on to the repository database from any machine. Also, the repositories for the administrators do not have to be in the same database.
Note: Only one repository should be set up for each username. If you create identical users with repositories in different databases, this can cause problems with agent notifications. The intelligent agents use the unique username when tracking jobs and events. The username is appended to the Console location when creating a return address for notifications.
When you log in to the Console, you must enter the connect information for the database that contains your repository. The Console looks up the repository associated with your username.
Note: You should not log on to the Console repository multiple times with the same username. A warning displays if you attempt this. You should only ignore the warning if the previous Console session was aborted or a machine was disconnected. When a username is logged in multiple times, agent notifications are sent to most recent login.
The information in the repository can be updated by third-party applications that integrate into the Enterprise Manager Console. Refer to the "Repository Control Interface" in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Developer's Guide.
Communication Daemon
Enterprise Manager uses a communication daemon, which runs on the Console machine, to manage Console communication activities, such as communicating with the intelligent agents running on remote nodes in the system.
The communication daemon is one of the components responsible for discovering services in the SQL*Net network that are used to populate the Navigator tree. The communication daemon locates services by reading a topology file (topology.ora) that is generated by Oracle Network Manager. You can also create the topology file manually but using Network Manager is recommended.
For information on the the communication daemon, see "Agents and Communication Daemon" ![[*]](jump.gif) . For information on using Oracle Network Manager, see the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide. For examples of configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide.
. For information on using Oracle Network Manager, see the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide. For examples of configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide.
Discovery Cache
The discovery cache is an efficient in-memory list of information about services and nodes. While you are logged into the Console, the discovery cache stores the current view of the network, including the user-defined groups and the states of nodes and services. When the you log out of the Console, the contents of the discovery cache are stored in the repository.
The next time you start the Console, the discovery cache is loaded with information from the repository and updated with any new information gathered from the topology file. The new information can include a new service or object discovered by the daemon, or a state that changed since last login.
The information in the discovery cache can be accessed by third-party applications that integrate into the Enterprise Manager Console. Refer to the "Discovery Cache Interface" in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Developer's Guide.
Intelligent Agents
The agents are intelligent processes running on remote nodes in the network. Oracle Enterprise Manager uses intelligent agents to schedule and run remote jobs, and monitor events on remote sites. The Console communication daemon communicates with the intelligent agents on the remote nodes in the system.
For information on the intelligent agents, see "Agents and Communication Daemon" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Database Administration Tools
Enterprise Manager provides easy-to-use DBA tools for administrative tasks such as:
- Managing instances and sessions
- Entering and executing DBA commands, SQL statements, and PL/SQL commands
Some of the functions of these applications can also be performed from the Navigator; however, the full set of functions is accessed through each application. For example, to run tasks on a specific group of objects, such as users, you would launch the Security application which provides complete task-oriented administration of the user objects.
Note: For an overview of the database tools, see "Overview of Database Tools" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Data Manager
Data Manager allows you to transfer data in and out of an Oracle database. The components are:
- Export Manager for exporting from an Oracle database to an Oracle binary operating system file.
- Import Manager for importing data that has been exported with the Export Manager.
- SQL*Loader for importing operating system files to an Oracle database.
Software Manager
Software Manager allows you to distribute, install, and deinstall software packages on servers and clients throughout the network. The Software Packager component allows you to creating packages consisting of non-Oracle products, or products requiring special installation processes.
Server Manager Line Mode
For the times when a command line interface is necessary or desirable, Oracle Server Manager provides a conversational line mode. In line mode, you can explicitly execute database administration (DBA) commands on a command line.
You may want to use Server Manager in line mode when a graphical device is unavailable, such as when dialing-in from a non-GUI terminal, or when performing unattended operations, such as running nightly batch jobs or batch scripts that do not require user intervention.
For more information about using Server Manager in line mode, see "Using Server Manager in Line Mode" ![[*]](jump.gif) . For information on the Server Manager DBA commands, see "DBA Commands"
. For information on the Server Manager DBA commands, see "DBA Commands" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Online Help
Enterprise Manager uses the Microsoft Windows online help system to provide you with help information for windows and dialog boxes in the Console and database tools. The Help system is context sensitive, but you can also search through help information to find a particular topic.
There are several ways of accessing the online Help system. In a main window, such as the Console window, you can access the Help system by pressing F1 or choosing Contents from the Help menu. In a dialog box, click the Help button or press F1 to access the online Help system. For information on the Help menu, see page 1 - 11.
Value Added Products
Oracle produces a number of additional administration utilities that can be purchased separately and integrated into the Enterprise Manager Console.
Monitoring and Diagnostic Utilities
Oracle provides easy-to-use tools for monitoring and diagnosing databases. These utilities include:
- Oracle Performance Monitoring
- Oracle Tablespace Manager
- Oracle TopSessions Monitor
The utilities allow you to gather and inspect specific performance statistics that are useful for tuning your database. For information on monitoring and diagnostic tools, see the Oracle Performance Monitoring User's Guide, the Oracle Expert User's Guide, and the Oracle Trace User's Guide.
Console Menus
The Console menu bar provided access to the following menus:
When using the Console menus, note that:
- Some menus include other menus as well. For example, when you select the Show Map item from the Map menu, a menu containing a list of saved maps displays.
- Menu options vary depending on the objects selected or the active window in the Console. The Tools menu items vary depending on the setup of your system.
- When a menu item is dimmed, it is not currently available. Menu items that end with an ellipsis (...) indicate that you will be asked to enter more information to complete the command.
- Context-sensitive menus can be displayed for objects in Console windows.
The File, View, Tools, and Help menus are described in this section.
- For information about the Navigator menu, see page 2 - 7.
- For information about the Map menu, see page 3 - 5.
- For information about the Job menu, see page 4 - 7.
- For information about the Event menu, see page 5 - 9.
Context-Sensitive Menus
You can click the right mouse button on objects in some windows of the Console to display a context-sensitive, or short-cut, menu. This menu usually contains a subset of the options that are available through a menu in the main menu bar.
For example, if you click the right mouse button on a registered event set in the Event Registrations window pane, a menu appears with the Event menu options.
Note: For information on context-sensitive menu options in the Navigator, see "Navigator Context-Sensitive Menus" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
File Menu
The File menu items allow you to manipulate maps, open or close database connections, and change login connections. The File menu is described below:
| Preferences... | Displays the User Preferences property sheet that contains the user credentials for services accessed through the Console. See "Console User Preferences" ![[*]](jump.gif) for information on user preferences. for information on user preferences. |
| Print Setup | Determines the print setup for the Oracle Enterprise Manager. |
| Exit | Exits Enterprise Manager. |
View Menu
The View menu allows you to determine whether toolbars, palettes, or windows are displayed or hidden.
| Show Navigator Pane | Hides or shows the Navigator window. The menu item is checked or unchecked. |
| Show Map Pane | Hides or shows the Map. The menu item is checked or unchecked. |
| Show Job Pane | Hides or shows the Job Scheduling window. The menu item is checked or unchecked. |
| Show Event Pane | Hides or shows the Event Management window. The menu item is checked or unchecked. |
Note: At least one window must be visible in the Console.
| Launch Palettes | Hides or shows the the launch palettes set up for Enterprise Manager. You can choose to hide or show all the palettes. |
| Toolbar | Hides or shows the Enterprise Manager toolbar. |
| Status Bar | Hides or shows the Status bar at the bottom of the Console. |
Tools Menu
The Tools menu allows you to execute database applications and other utilities that have been installed on your system. You can also execute the applications from a launch palette. The menu options in the Tools menu depend on your system configuration.
Note: See "Overview of the Database Tools" ![[*]](jump.gif) for a discussion of the database administration tools.
for a discussion of the database administration tools.
Applications
This menu option lists the database administration tools and utilities that you can execute from the Console. The menu can includes:
| Oracle Backup Manager | Executes the Backup application.
|
| Oracle Instance Manager | Executes the Instance application.
|
| Oracle Schema Manager | Executes the Schema application.
|
| Oracle Security Manager | Executes the Security application.
|
| Oracle Storage Manager | Executes the Storage application.
|
| Oracle SQL Worksheet | Executes the SQL Worksheet application. |
| Oracle Data Manager | Executes the Data Manager application. |
| Oracle Software Manager | Executes the Software Manager application.
|
Performance Pack
This menu option lists the optional Performance Pack applications that you can execute from the Console. The menu can includes:
| Oracle Performance Manager | Executes the Performance Manager application.
|
| Oracle Tablespace | Executes the Tablespace Manager application. |
| Oracle TopSessions | Executes the TopSessions Monitor application. |
| Oracle Locks Manager | Executes the Locks Manager application. |
| Oracle Expert | Executes the Oracle Expert application. |
| Oracle Trace | Executes the Oracle Trace application. |
Daemon Manager
The Daemon Manager executes the communication daemon monitoring program. For more information, see "Daemon Monitor" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Help Menu
From the Help menu, you can access the Enterprise Manager online Help system. For more information about Enterprise Manager online Help system, see "Using Online Help" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
| Contents | Displays the overview topic of the Oracle Enterprise Manager help system. |
| Search for Help On... | Displays a dialog box containing a scrolling list of index entries and keywords that you can search for in the help system. |
| Using Help | Displays information on using the Microsoft Windows help system. |
| About Oracle Enterprise Manager | Displays a dialog box containing version information about Enterprise Manager and its components. |
Toolbars and Launch Palettes
Enterprise Manager provides toolbars and launch palettes to execute commands and run applications.
Toolbars
The Enterprise Manager provides toolbar options that allow you to:
- Perform various menu options for the Event, Job, and Map components.
- Hide or show the Navigator, Job, Event, or Map panes.
The toolbar icons represent the items in the menus. The toolbar options are enabled depending on the objects viewed or selected in a window. Move the mouse cursor over a toolbar icon to display the description of the icon's function in the status bar at the bottom of the Console.
The toolbar can be:
- Moved to the top or bottom of the Console window, or can float as a separate window.
- Displayed or hidden through the View menu.
Launch Palettes
The launch palettes contain the applications that you can launch from the Enterprise Manager Console.
- Each palette represents a portion of the Tools menu options. The palette is the same as the Tools menu except that the palette provides icons rather than text items to represent the applications.
- The launch palette items vary depending on the applications that have been installed on your system.
- The palettes can be moved to the top, bottom, or sides of the Console window, or can float as a separate window. The palettes can either be displayed or hidden through the View menu.
- Move the mouse cursor over a palette icon to display the description the icon's function in the status bar at the bottom of the Console.
Using Enterprise Manager
To use Enterprise Manager, you must install Enterprise Manager on a computer running Windows NT. During the installation you will need to run SQL scripts to create the tables necessary for the Enterprise Manager repository. You can create the repository tables in an existing database or create a new one. The database can be on any node accessible to the Enterprise Manager Console.
To use the Job and Event systems, an intelligent agent must be running on the node that you plan to run jobs or monitor events.
Note: For instructions on installing Enterprise Manager, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide.
Privileged Operations
To perform an operation or task using Enterprise Manager, you must have the appropriate privileges. To fully utilize Oracle Enterprise Manager, you should make sure you have DBA system privileges when you connect to the Console.
For example, to create a tablespace using Enterprise Manager, you must have the CREATE TABLESPACE system privilege. Because many of Enterprise Manager's windows include information selected from data dictionary tables, you need the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege. These system privilege are part of the SYSDBA/SYSOPER role.
Enterprise Manager does not enable any additional roles, so any privileges you need must be part of your default roles and privileges. For information about privileges and roles, refer to the Oracle7 Server Concepts and Oracle7 Server Administrator's Guide.
Administration of a Remote Database
Before submitting a database administration task, such as starting up or shutting down a database, through the Oracle Enterprise Manager Job system, you need to set up the database password file on the node where the database and agent are located. This can be done using the password file creation utility orapwd. Enter the following at the operating system prompt:
orapwd file = $ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapwd <$SID> password=manager
Also, you need to add the following to the init.ora database initialization file:
REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE=EXCLUSIVE
Note: When you log onto Oracle Enterprise Manager, you need to connect as SYSDBA (or SYSOPER) to have the privileges to startup and shutdown databases.
Starting Enterprise Manager
To start Enterprise Manager, double-click on the Enterprise Manager icon in the Oracle program group. For additional methods of starting Enterprise Manager, see "Starting Enterprise Manager" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Note: Only one instance of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console can be run on a machine. However, you can run multiple instances of the DBA tools.
Note: You should not log on to the Console repository multiple times with the same username. A warning displays if you attempt this and you are using the same repository. You should only ignore the warning if the previous Console session was aborted or a machine was disconnected. The intelligent agents use the unique username when tracking jobs and events. The username is appended to the Console location when creating a return address for notifications. When a username is logged in multiple times, agent notifications are sent to most recent login.
When you start Enterprise Manager, the copyright window and the Login Information dialog box appears. Use the login box to connect to the Oracle database instance where your repository for Enterprise Manager is stored. For information on connecting to an Oracle database, See "Connecting to an Instance" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Launching Tools
You can launch the Enterprise Manager tools as separate applications or through the Console.
To launch a tool separately, double-click on the application icon in the Oracle program group. Enter the connect information in the Login Information dialog box.
Note: For information on connecting to an Oracle database, See "Connecting to an Instance" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
To launch a tool through the Console, you can:
- Select the database you want to administer in the Navigator tree or in the Map window, then choose the application in the Console Tools menu or in the launch palette.
- Select the database you want to administer in the Navigator tree, then choose the application from the Related Tools menu of the context-sensitive menu.
- Choose the application in the Console Tools menu or in the launch palette, then enter connect information in the Login Information dialog box.
Note: When you select a database before launching a tool, you are connected to the database according to the preferred credentials that have been set up for the database or the credentials you used to log on to the Console. If connection to the database fails for any reason, the Login Information dialog box displays. See "Console User Preferences" ![[*]](jump.gif) for more information on connecting to a database.
for more information on connecting to a database.
Connecting to an Instance
You can connect to any Oracle database instance using the Login Information connect dialog box. See Figure 1 - 2 ![[*]](jump.gif) for an illustration of the Login Information dialog box.
for an illustration of the Login Information dialog box.
You can display the Login Information connect dialog box by selecting a database in the Navigator window and choosing Connect from the Navigator menu. You can also select a database in the Navigator window with the right-mouse to access the Connect menu option.
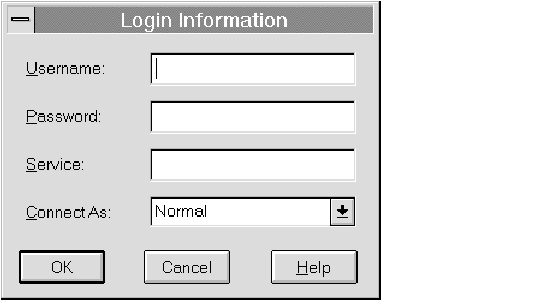 Figure 1 - 2. Login Information Dialog Box
Figure 1 - 2. Login Information Dialog Box
The elements of the Connect dialog box are described below:
| Username | Your Oracle username for the database to which you are connecting. |
| Password | Your Oracle password for the database to which you are connecting. |
| Service Name | SQL*Net service name for the database to which you are connecting. You should use SQL*Net Version 2 service names, such as NY_FINANCE, when connecting. |
| | The connect strings for the service names in the snmp.ora, topology.ora, and tnsnames.ora files must match. If not, the agents used by the Job and Event systems will not be able to locate the database. For information on configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide. |
| Connect As | Pop-up menu containing NORMAL, SYSOPER, and SYSDBA for Oracle7 release 7.1 or later. Only Normal is allowed for release 7.0. |
| | SYSOPER and SYSDBA roles allow you the maximum database administration privileges. For more information, see the Oracle7 Server Administrator's Guide. |
Note: You will need SYSDBA or SYSOPER privileges to run job tasks such as shutdown or startup on the database.
| OK | Initiates connection. |
| Cancel | Exits dialog box without connecting. |
| Help | Displays help information. |
Note: See "Console User Preferences" ![[*]](jump.gif) for more information on connecting to a database.
for more information on connecting to a database.
Multiple Connections
In Enterprise Manager you can have multiple database connections open simultaneously. For example, you can launch several database applications on different databases. The service name you specify when you connect becomes part of the title for each window associated with that connection.
Note: The number of connections you can have open simultaneously depends on the system and network you are using.
Console User Preferences
This feature allows you to set up specific usernames, passwords, and roles for different services in your network. You determine the preferences for accessing a database, node, or listener with the information you enter in the this property sheet. These preferences are used when you access a database, listener, or node in the Navigator or Map.
The User Preferences property sheet displays a list of databases, listeners, and nodes in the network, along with the service type and the username for accessing the service. The property sheet is accessed with the Preferences option of the Console File menu. Each row in the list of the property sheet includes:
You can click on a column heading to sort on that column. See Figure 1 - 3 ![[*]](jump.gif) for an illustration of the property sheet.
for an illustration of the property sheet.
If you have not set up preferences for a database, listener, or node, the login information that you entered to access the Console will be used. If that information is not valid for a database, you will have to enter login information each time you access the object.
Setting User Preferences
Select any row to access and update the preferences fields for the object identified in the row.
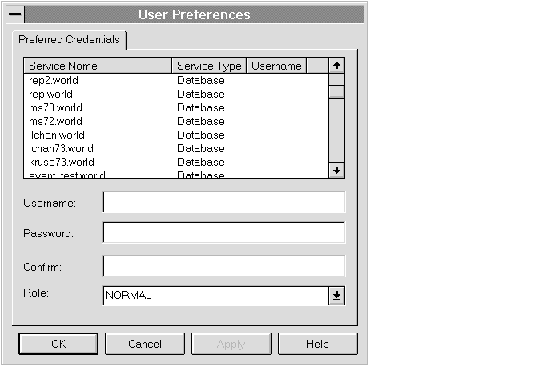 Figure 1 - 3. User Preferences Property Sheet
Figure 1 - 3. User Preferences Property Sheet
Enter the preferences for the connection to the service.
| Username | Enter the username. |
| Password | Enter the password. |
| Confirm | Confirm the password. |
| Role | Select the role from the pull-down list. |
Note: You need to login with the SYSDBA or SYSOPER role to start up or shut down a database.
Click the OK button at the bottom of the property sheet to save your updates. For more information about dialog boxes and property sheets, see "Dialog Boxes" ![[*]](jump.gif) and "Property Sheets"
and "Property Sheets" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.





<Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts GuideOracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide











 Figure 1 - 1. Enterprise Manager Console
Figure 1 - 1. Enterprise Manager Console![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) . For information on using Oracle Network Manager, see the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide. For examples of configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide.
. For information on using Oracle Network Manager, see the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide. For examples of configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Installation Guide.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) . For information on the Server Manager DBA commands, see "DBA Commands"
. For information on the Server Manager DBA commands, see "DBA Commands" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) for a discussion of the database administration tools.
for a discussion of the database administration tools.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
. ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
. ![[*]](jump.gif) for more information on connecting to a database.
for more information on connecting to a database.![[*]](jump.gif) for an illustration of the Login Information dialog box.
for an illustration of the Login Information dialog box.  Figure 1 - 2. Login Information Dialog Box
Figure 1 - 2. Login Information Dialog Box![[*]](jump.gif) for more information on connecting to a database.
for more information on connecting to a database.![[*]](jump.gif) for an illustration of the property sheet.
for an illustration of the property sheet. Figure 1 - 3. User Preferences Property Sheet
Figure 1 - 3. User Preferences Property Sheet![[*]](jump.gif) and "Property Sheets"
and "Property Sheets" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.



