-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on June 14, 2011 |
|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 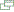
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
The territory of Northern Rhodesia was administered by the [British] South Africa Company from 1891 until it was taken over by the UK in 1923. During the 1920s and 1930s, advances in mining spurred development and immigration. The name was changed to Zambia upon independence in 1964. In the 1980s and 1990s, declining copper prices, economic mismanagement and a prolonged drought hurt the economy. Elections in 1991 brought an end to one-party rule, but the subsequent vote in 1996 saw blatant harassment of opposition parties. The election in 2001 was marked by administrative problems with three parties filing a legal petition challenging the election of ruling party candidate Levy MWANAWASA. The new president launched an anticorruption investigation in 2002 to probe high-level corruption during the previous administration. In 2006-07, this task force successfully prosecuted four cases, including a landmark civil case in the UK in which former President CHILUBA and numerous others were found liable for more than USD 41 million. MWANAWASA was reelected in 2006 in an election that was deemed free and fair. Upon his abrupt death in August 2008, he was succeeded by his Vice President Rupiah BANDA, who subsequently won a special presidential by-election in October 2008. Under President BANDA, the Task Force on Corruption was abolished, President CHILUBA and his wife were acquitted in their criminal cases, and the government declined to register the UK civil verdict.
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
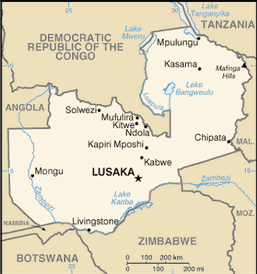
Southern Africa, east of Angola, south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
|
|
|
|

|
|
15 00 S, 30 00 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 752,618 sq km
country comparison to the world: 39
land:
743,398 sq km
water:
9,220 sq km
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly larger than Texas
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5,664 km
border countries:
Angola 1,110 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 1,930 km, Malawi 837 km, Mozambique 419 km, Namibia 233 km, Tanzania 338 km, Zimbabwe 797 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|

|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical; modified by altitude; rainy season (October to April)
|
|
|
|

|
|
mostly high plateau with some hills and mountains
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Zambezi river 329 m
highest point:
unnamed elevation in Mafinga Hills 2,301 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
copper, cobalt, zinc, lead, coal, emeralds, gold, silver, uranium, hydropower
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 6.99%
permanent crops:
0.04%
other:
92.97% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,560 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
105.2 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1.74 cu km/yr (17%/7%/76%)
per capita:
149 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
periodic drought; tropical storms (November to April)
|
|
|
|

|
|
air pollution and resulting acid rain in the mineral extraction and refining region; chemical runoff into watersheds; poaching seriously threatens rhinoceros, elephant, antelope, and large cat populations; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; lack of adequate water treatment presents human health risks
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural riverine boundary with Zimbabwe
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
13,881,336 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 46.7% (male 3,253,125/female 3,228,844)
15-64 years:
50.8% (male 3,544,640/female 3,508,344)
65 years and over:
2.5% (male 148,531/female 197,852) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 16.5 years
male:
16.5 years
female:
16.6 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.062% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|

|
|
44.08 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.61 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|

|
|
-0.84 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 36% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
3.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
LUSAKA (capital) 1.413 million (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.68 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 66.6 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 22
male:
71.27 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
61.78 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 52.36 years
country comparison to the world: 208
male:
51.13 years
female:
53.63 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.98 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|

|
|
13.5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|

|
|
980,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|

|
|
45,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria and plague are high risks in some locations
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 87% of population
rural: 46% of population
total: 60% of population
unimproved:
urban: 13% of population
rural: 54% of population
total: 40% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 59% of population
rural: 43% of population
total: 49% of population
unimproved:
urban: 41% of population
rural: 47% of population
total: 51% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
noun: Zambian(s)
adjective:
Zambian
|
|
|
|

|
|
African 99.5% (includes Bemba, Tonga, Chewa, Lozi, Nsenga, Tumbuka, Ngoni, Lala, Kaonde, Lunda, and other African groups), other 0.5% (includes Europeans, Asians, and Americans) (2000 Census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Christian 50%-75%, Muslim and Hindu 24%-49%, indigenous beliefs 1%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Bemba (official) 30.1%, Nyanja (official) 10.7%, Tonga (official) 10.6%, Lozi (official) 5.7%, Chewa 4.9%, Nsenga 3.4%, Tumbuka 2.5%, Lunda (official) 2.2%, Kaonde (official) 2%, Lala 2%, Luvale (official) 1.7%, English (official) 1.7%, other 22.5% (2000 Census)
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write English
total population:
80.6%
male:
86.8%
female:
74.8% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 7 years
male:
8 years
female:
7 years (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.3% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Zambia
conventional short form:
Zambia
former:
Northern Rhodesia
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Lusaka
geographic coordinates:
15 25 S, 28 17 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|

|
|
9 provinces; Central, Copperbelt, Eastern, Luapula, Lusaka, Northern, North-Western, Southern, Western
|
|
|
|

|
|
24 October 1964 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 24 October (1964)
|
|
|
|

|
|
24 August 1991; amended in 1996 to establish presidential term limits
|
|
|
|

|
|
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law; judicial review of legislative acts in an ad hoc constitutional council
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Rupiah BANDA (since 19 August 2008); Vice President George KUNDA (since 14 November 2008); the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Rupiah BANDA (since 19 August 2008); Vice President George KUNDA (since 14 November 2008)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president from among the members of the National Assembly
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 30 October 2008 (next to be held by October 2011); vice president appointed by the president; note - due to the death of former President Levy MWANAWASA, early elections were held to identify a replacement to serve out the remainder of his term
election results:
Rupiah BANDA elected president; percent of vote - Rupiah BANDA 40.1%, Michael SATA 38.1%, Hakainde HICHILEMA 19.7%, Godfrey MIYANDA 0.8%, other 1.3%
|
|
|
|

|
|
unicameral National Assembly (158 seats; 150 members are elected by popular vote, 8 members appointed by the president, to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 28 September 2006 (next to be held by October 2011)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - MMD 72, PF 44, UDA 27, ULP 2, NDF 1, independents 2; seats not determined 2
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court (the final court of appeal; justices are appointed by the president); High Court (has unlimited jurisdiction to hear civil and criminal cases)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Alliance for Democracy and Development or ADD [Charles MILUPI]; Forum for Democracy and Development or FDD [Edith NAWAKWI]; Heritage Party or HP [Godfrey MIYANDA]; Movement for Multiparty Democracy or MMD [Rupiah BANDA]; National Restoration Party or NAREP [Elias CHIPIMO]; Party of Unity for Democracy and Development or PUDD [Dan PULE]; Patriotic Front or PF [Michael SATA]; Reform Party [Nevers MUMBA]; United Democratic Alliance or UDA (a coalition of RP, ZADECO, PUDD, and ZRP); United Liberal Party or ULP [Sakwiba SIKOTA]; United National Independence Party or UNIP [Tilyenji KAUNDA]; United Party for National Development or UPND [Hakainde HICHILEMA]; Zambia Democratic Congress or ZADECO [Langton SICHONE]; Zambian Republican Party or ZRP [Benjamin MWILA]
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Sheila Z. SIWELA
chancery:
2419 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 265-9717 through 9719
FAX:
[1] (202) 332-0826
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mark C. STORELLA
embassy:
corner of Independence and United Nations Avenues, Lusaka
mailing address:
P. O. Box 31617, Lusaka
telephone:
[260] (211) 357-000
FAX:
[260] (211) 357-224
|
|
|
|

|
|
green field with a panel of three vertical bands of red (hoist side), black, and orange below a soaring orange eagle, on the outer edge of the flag; green stands for the country's natural resources and vegetation, red symbolizes the struggle for freedom, black the people of Zambia, and orange the country's mineral wealth; the eagle represents the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Lumbanyeni Zambia" (Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free)
lyrics/music:
multiple/Enoch Mankayi SONTONGA
note:
adopted 1964; the melody, from the popular song "God Bless Africa," is the same as that of Tanzania but with different lyrics; the melody is also incorporated into South Africa's anthem
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Zambia's economy has experienced strong growth in recent years, with real GDP growth in 2005-10 about 6% per year. Privatization of government-owned copper mines in the 1990s relieved the government from covering mammoth losses generated by the industry and greatly increased copper mining output and profitability to spur economic growth. Copper output has increased steadily since 2004, due to higher copper prices and foreign investment. In 2005, Zambia qualified for debt relief under the Highly Indebted Poor Country Initiative, consisting of approximately USD 6 billion in debt relief. Poverty remains a significant problem in Zambia, despite a stronger economy. Zambia's dependency on copper makes it vulnerable to depressed commodity prices, but record high copper prices and a bumper maize crop in 2010 helped Zambia rebound quickly from the world economic slowdown that began in 2008. A high birth rate, relatively high HIV/AIDS burden, and market distorting agricultural policies have meant that Zambia's economic growth has not dramatically decreased the stubbornly high poverty rates.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$20.04 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
$18.63 billion (2009 est.)
$17.5 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$16.19 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
6.4% (2009 est.)
5.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1,500 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
$1,400 (2009 est.)
$1,400 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 19.7%
industry:
33.7%
services:
46.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.524 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 85%
industry:
6%
services:
9% (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
14% (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
50% (2000 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
64% (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 1.2%
highest 10%:
38.8% (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
50.8 (2004)
country comparison to the world: 19
52.6 (1998)
|
|
|
|

|
|
20.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $3.2 billion
expenditures:
$3.743 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
24.1% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
25.9% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
13.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.39% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 22
14.49% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
22.06% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
19.06% (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.234 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
$983.3 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$3.573 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
$2.744 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.992 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
$2.373 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$NA (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 94
$2.346 billion (31 December 2007)
$1.186 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
corn, sorghum, rice, peanuts, sunflower seed, vegetables, flowers, tobacco, cotton, sugarcane, cassava (tapioca), coffee; cattle, goats, pigs, poultry, milk, eggs, hides
|
|
|
|

|
|
copper mining and processing, construction, foodstuffs, beverages, chemicals, textiles, fertilizer, horticulture
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.1% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.752 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.838 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|

|
|
268 million kWh (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
222 million kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
159.5 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|

|
|
16,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|

|
|
275.3 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|

|
|
14,730 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|

|
|
$-99 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
$-174 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$6.463 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
$4.203 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
copper/cobalt 64%, cobalt, electricity; tobacco, flowers, cotton
|
|
|
|

|
|
China 21.37%, Saudi Arabia 8.93%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 8.55%, South Korea 8.32%, Egypt 8.08%, South Africa 6.96%, India 5% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.949 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
$3.735 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery, transportation equipment, petroleum products, electricity, fertilizer, foodstuffs, clothing
|
|
|
|

|
|
South Africa 51.78%, UAE 7.7%, China 5.85%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 4.22% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.287 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$1.892 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$3.495 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
$3.091 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
Zambian kwacha (ZMK) per US dollar -
4,823.6 (2010)
5,046.1 (2009)
3,512.9 (2008)
3,990.2 (2007)
3,601.5 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
90,300 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.407 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: among the best in Sub-Saharan Africa
domestic:
high-capacity microwave radio relay connects most larger towns and cities; several cellular telephone services in operation and network coverage is improving; domestic satellite system being installed to improve telephone service in rural areas; Internet service is widely available; very small aperture terminal (VSAT) networks are operated by private firms
international:
country code - 260; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Atlantic Ocean), 3 owned by Zamtel
|
|
|
|

|
|
state-owned Zambia National Broadcasting Corporation (ZNBC) operates 1 TV station and is the principal local-content provider; several private TV stations are available; multi-channel subscription TV services are obtainable; ZNBC operates 3 radio networks; about 2 dozen private radio stations also broadcasting; relays of at least 2 international broadcasters are accessible in Lusaka and Kitwe (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.zm
|
|
|
|

|
|
14,771 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|

|
|
816,200 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
94 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 8
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 86
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
63
under 914 m:
18 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
oil 771 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 2,157 km
country comparison to the world: 69
narrow gauge:
2,157 km 1.067-m gauge
note:
includes 891 km of the Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (TAZARA) (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 91,440 km
country comparison to the world: 54
paved:
20,117 km
unpaved:
71,323 km (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,250 km (includes Lake Tanganyika and the Zambezi and Luapula rivers) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|

|
|
Mpulungu
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Zambian National Defense Force (ZNDF): Zambian Army, Zambian Air Force, National Service (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18-27 years of age for male and female voluntary military service (16 years of age with parental consent); no conscription; Zambian citizenship required; mandatory HIV testing upon enlistment; mandatory retirement for officers at age 65 (Army, Air Force) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 3,041,069
females age 16-49:
2,948,291 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 1,745,656
females age 16-49:
1,688,670 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 158,592
female:
158,805 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.8% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Zambia |
|

|
|
in 2004, Zimbabwe dropped objections to plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river
|
|
|
|

|
|
refugees (country of origin): 42,565 (Angola); 60,874 (Democratic Republic of the Congo); 4,100 (Rwanda) (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
transshipment point for moderate amounts of methaqualone, small amounts of heroin, and cocaine bound for southern Africa and possibly Europe; a poorly developed financial infrastructure coupled with a government commitment to combating money laundering make it an unattractive venue for money launderers; major consumer of cannabis
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

