-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on June 14, 2011 |
|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 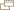
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Although ultimately a victor in World Wars I and II, France suffered extensive losses in its empire, wealth, manpower, and rank as a dominant nation-state. Nevertheless, France today is one of the most modern countries in the world and is a leader among European nations. Since 1958, it has constructed a hybrid presidential-parliamentary governing system resistant to the instabilities experienced in earlier more purely parliamentary administrations. In recent decades, its reconciliation and cooperation with Germany have proved central to the economic integration of Europe, including the introduction of a common exchange currency, the euro, in January 1999. In the early 21st century, five French overseas entities - French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion - became French regions and were made part of France proper.
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
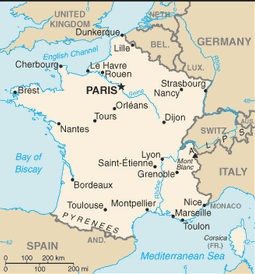
metropolitan France: Western Europe, bordering the Bay of Biscay and English Channel, between Belgium and Spain, southeast of the UK; bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Italy and Spain
French Guiana:
Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Brazil and Suriname
Guadeloupe:
Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico
Martinique:
Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Mayotte:
Southern Indian Ocean, island in the Mozambique Channel, about half way between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique
Reunion:
Southern Africa, island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: 46 00 N, 2 00 E
French Guiana:
4 00 N, 53 00 W
Guadeloupe:
16 15 N, 61 35 W
Martinique:
14 40 N, 61 00 W
Mayotte:
12 50 S, 45 10 E
Reunion:
21 06 S, 55 36 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: Europe
French Guiana:
South America
Guadeloupe:
Central America and the Caribbean
Martinique:
Central America and the Caribbean
Mayotte:
Africa
Reunion:
World
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 643,801 sq km; 551,500 sq km (metropolitan France)
country comparison to the world: 42
land:
640,427 sq km; 549,970 sq km (metropolitan France)
water:
3,374 sq km; 1,530 sq km (metropolitan France)
note:
the first numbers include the overseas regions of French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly less than the size of Texas
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France - total: 2,889 km
border countries:
Andorra 56.6 km, Belgium 620 km, Germany 451 km, Italy 488 km, Luxembourg 73 km, Monaco 4.4 km, Spain 623 km, Switzerland 573 km
French Guiana - total:
1,183 km
border countries:
Brazil 673 km, Suriname 510 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 4,853 km
metropolitan France:
3,427 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm (does not apply to the Mediterranean)
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: generally cool winters and mild summers, but mild winters and hot summers along the Mediterranean; occasional strong, cold, dry, north-to-northwesterly wind known as mistral
French Guiana:
tropical; hot, humid; little seasonal temperature variation
Guadeloupe and Martinique:
subtropical tempered by trade winds; moderately high humidity; rainy season (June to October); vulnerable to devastating cyclones (hurricanes) every eight years on average
Mayotte:
tropical; marine; hot, humid, rainy season during northeastern monsoon (November to May); dry season is cooler (May to November)
Reunion:
tropical, but temperature moderates with elevation; cool and dry (May to November), hot and rainy (November to April)
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in north and west; remainder is mountainous, especially Pyrenees in south, Alps in east
French Guiana:
low-lying coastal plains rising to hills and small mountains
Guadeloupe:
Basse-Terre is volcanic in origin with interior mountains; Grande-Terre is low limestone formation; most of the seven other islands are volcanic in origin
Martinique:
mountainous with indented coastline; dormant volcano
Mayotte:
generally undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks
Reunion:
mostly rugged and mountainous; fertile lowlands along coast
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Rhone River delta -2 m
highest point:
Mont Blanc 4,807 m
note:
in order to assess the possible effects of climate change on the ice and snow cap of Mont Blanc, its surface and peak have been extensively measured in recent years; these new peak measurements have exceeded the traditional height of 4,807 m and have varied between 4,808 m and 4,811 m; the actual rock summit is 4,792 m and is 40 m away from the ice-covered summit
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, antimony, arsenic, potash, feldspar, fluorspar, gypsum, timber, fish
French Guiana:
gold deposits, petroleum, kaolin, niobium, tantalum, clay
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 33.46%
permanent crops:
2.03%
other:
64.51%
note:
French Guiana - arable land 0.13%, permanent crops 0.04%, other 99.83% (90% forest, 10% other); Guadeloupe - arable land 11.70%, permanent crops 2.92%, other 85.38%; Martinique - arable land 9.09%, permanent crops 10.0%, other 80.91%; Reunion - arable land 13.94%, permanent crops 1.59%, other 84.47% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 26,950 sq km;
metropolitan France:
26,700 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
189 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 33.16 cu km/yr (16%/74%/10%)
per capita:
548 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: flooding; avalanches; midwinter windstorms; drought; forest fires in south near the Mediterranean
overseas departments:
hurricanes (cyclones); flooding; volcanic activity (Guadeloupe, Martinique, Reunion)
|
|
|
|

|
|
some forest damage from acid rain; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from urban wastes, agricultural runoff
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
largest West European nation
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
65,312,249 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
note:
the above figure is for metropolitan France and five overseas regions; the metropolitan France population is 62,814,233
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 18.5% (male 6,180,905/female 5,886,849)
15-64 years:
64.7% (male 21,082,175/female 21,045,867)
65 years and over:
16.8% (male 4,578,089/female 6,328,834) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 39.9 years
male:
38.4 years
female:
41.5 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.5% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.29 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.76 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.46 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 85% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
PARIS (capital) 10.41 million; Marseille-Aix-en-Provence 1.457 million; Lyon 1.456 million; Lille 1.028 million; Nice-Cannes 977,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.051 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.72 male(s)/female
total population:
0.96 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 3.29 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 214
male:
3.61 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
2.96 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 81.19 years
country comparison to the world: 13
male:
78.02 years
female:
84.54 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.96 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.4% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|

|
|
150,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
noun: Frenchman(men), Frenchwoman(women)
adjective:
French
|
|
|
|

|
|
Celtic and Latin with Teutonic, Slavic, North African, Indochinese, Basque minorities
overseas departments:
black, white, mulatto, East Indian, Chinese, Amerindian
|
|
|
|

|
|
Roman Catholic 83%-88%, Protestant 2%, Jewish 1%, Muslim 5%-10%, unaffiliated 4%
overseas departments:
Roman Catholic, Protestant, Hindu, Muslim, Buddhist, pagan
|
|
|
|

|
|
French (official) 100%, rapidly declining regional dialects and languages (Provencal, Breton, Alsatian, Corsican, Catalan, Basque, Flemish)
overseas departments:
French, Creole patois, Mahorian (a Swahili dialect)
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 16 years
male:
16 years
female:
16 years (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.6% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: French Republic
conventional short form:
France
local long form:
Republique francaise
local short form:
France
|
|
|
|

|
|
republic
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Paris
geographic coordinates:
48 52 N, 2 20 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note:
applies to metropolitan France only, not to its overseas departments, collectivities, or territories
|
|
|
|

|
|
27 regions (regions, singular - region); Alsace, Aquitaine, Auvergne, Basse-Normandie (Lower Normandy), Bourgogne (Burgundy), Bretagne (Brittany), Centre, Champagne-Ardenne, Corse (Corsica), Franche-Comte, Guadeloupe, Guyane (French Guiana), Haute-Normandie (Upper Normandy), Ile-de-France, Languedoc-Roussillon, Limousin, Lorraine, Martinique, Mayotte, Midi-Pyrenees, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, Pays de la Loire, Picardie, Poitou-Charentes, Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur, Reunion, Rhone-Alpes
note:
France is divided into 22 metropolitan regions (including the "territorial collectivity" of Corse or Corsica) and 5 overseas regions (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion) and is subdivided into 96 metropolitan departments and 5 overseas departments (which are the same as the overseas regions)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Clipperton Island, French Polynesia, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, New Caledonia, Saint Barthelemy, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna
note:
the US does not recognize claims to Antarctica; New Caledonia has been considered a "sui generis" collectivity of France since 1998, a unique status falling between that of an independent country and a French overseas department
|
|
|
|

|
|
no official date of independence: 486 (Frankish tribes unified under Merovingian kingship); 10 August 843 (Western Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire); 14 July 1789 (French monarchy overthrown); 22 September 1792 (First French Republic founded); 4 October 1958 (Fifth French Republic established)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790); note - although often incorrectly referred to as Bastille Day, the celebration actually commemorates the holiday held on the first anniversary of the storming of the Bastille (on 14 July 1789) and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy; other names for the holiday are Fete Nationale (National Holiday) and quatorze juillet (14th of July)
|
|
|
|

|
|
adopted by referendum 28 September 1958; effective 4 October 1958; amended many times
note:
amended in 1962 concerning election of president; amended to comply with provisions of 1992 EC Maastricht Treaty, 1997 Amsterdam Treaty, 2003 Treaty of Nice; amended in 1993 to tighten immigration laws; amended in 2000 to change the seven-year presidential term to a five-year term; amended in 2005 to make the EU constitutional treaty compatible with the Constitution of France and to ensure that the decision to ratify EU accession treaties would be made by referendum
|
|
|
|

|
|
civil law; review of administrative but not legislative acts
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President Nicolas SARKOZY (since 16 May 2007)
head of government:
Prime Minister Francois FILLON (since 17 May 2007)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president at the suggestion of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 April and 6 May 2007 (next to be held in the spring of 2012); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Nicolas SARKOZY elected; first round: percent of vote - Nicolas SARKOZY 31.2%, Segolene ROYAL 25.9%, Francois BAYROU 18.6%, Jean-Marie LE PEN 10.4%, others 13.9%; second round: SARKOZY 53.1%, ROYAL 46.9%
|
|
|
|

|
|
bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (343 seats; 323 for metropolitan France and overseas departments, 2 for New Caledonia, 2 for French Polynesia, 1 for Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, 1 for Saint-Barthelemy, 1 for Saint-Martin, 1 for Wallis and Futuna, and 12 for French nationals abroad; members indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve six-year terms; one third elected every three years); note - between 2006 and 2011, 15 new seats will be added to the Senate for a total of 348 seats - 328 for metropolitan France and overseas departments, 2 for New Caledonia, 2 for French Polynesia, 1 for Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, 1 for Saint-Barthelemy, 1 for Saint-Martin, 1 for Wallis and Futuna, and 12 for French nationals abroad; Mayotte's previously held 2 seats as an overseas collectivity are now included in the total as an overseas department; starting in 2008, members will be indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve six-year terms with one-half elected every three years; and the National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (577 seats; 555 for metropolitan France, 15 for overseas departments, 7 for overseas dependencies; members elected by popular vote under a single-member majority system to serve five-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 21 September 2008 (next to be held in September 2011); National Assembly - last held on 10 and 17 June 2007 (next to be held in June 2012)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - UMP 151, PS 102, PCF 22, MoDem 11, NC 11, Greens 5, PG 2, other 39; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - UMP 46.4%, PS 42.2%, miscellaneous left wing parties 2.5%, PCF 2.3%, NC 2.1%, PRG 1.6%, miscellaneous right wing parties 1.2%, the Greens 0.4%, other 1.2%; seats by party - UMP 313, PS 186, NC 22, miscellaneous left wing parties 15, PCF 16, miscellaneous right wing parties 9, PRG 7, the Greens 3, other 6
|
|
|
|

|
|
Supreme Court of Appeals or Cour de Cassation (judges are appointed by the president from nominations of the High Council of the Judiciary); Constitutional Council or Conseil Constitutionnel (three members appointed by the president, three appointed by the president of the National Assembly, and three appointed by the president of the Senate); Council of State or Conseil d'Etat
|
|
|
|

|
|
Democratic Movement or MoDem [Francois BAYROU] (previously Union for French Democracy or UDF); French Communist Party or PCF [Pierre LAURENT]; Greens [Cecile DUFLOT]; Left Party or PG [Jean-Luc MELENCHON]; Left Radical Party or PRG [Jean-Michel BAYLET] (previously Radical Socialist Party or PRS and the Left Radical Movement or MRG); Movement for France or MPF [Philippe DE VILLIERS]; National Front or FN [Jean-Marie LE PEN]; New Anticapitalist Party or NPA [Olivier BESANCENOT]; New Center or NC [Herve MORIN]; Radical Party [Jean-Louis BORLOO]; Rally for France or RPF [Charles PASQUA]; Republican and Citizen Movement or MRC [Jean Pierre CHEVENEMENT]; Socialist Party or PS [Martine AUBRY]; Union for a Popular Movement or UMP [Jean-Francois COPE]; Worker's Struggle or LO [Nathalie ARTHAUD]
|
|
|
|

|
|
Confederation francaise democratique du travail or CFDT, left-leaning labor union with approximately 803,000 members; Confederation francaise de l'encadrement - Confederation generale des cadres or CFE-CGC, independent white-collar union with 196,000 members; Confederation francaise des travailleurs chretiens of CFTC, independent labor union founded by Catholic workers that claims 132,000 members; Confederation generale du travail or CGT, historically communist labor union with approximately 700,000 members; Confederation generale du travail - Force ouvriere or FO, independent labor union with an estimated 300,000 members; Mouvement des entreprises de France or MEDEF, employers' union with 750,000 companies as members (claimed)
French Guiana:
conservationists; gold mining pressure groups; hunting pressure groups
Guadeloupe:
Christian Movement for the Liberation of Guadeloupe or KLPG; General Federation of Guadeloupe Workers or CGT-G; General Union of Guadeloupe Workers or UGTG; Movement for an Independent Guadeloupe or MPGI; The Socialist Renewal Movement
Martinique:
Caribbean Revolutionary Alliance or ARC; Central Union for Martinique Workers or CSTM; Frantz Fanon Circle; League of Workers and Peasants; Proletarian Action Group or GAP
Reunion:
NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BDEAC, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, FZ, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, InOC, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), SPC, UN, UN Security Council, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Francois M. DELATTRE
chancery:
4101 Reservoir Road NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 944-6000
FAX:
[1] (202) 944-6166
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Charles H. RIVKIN
embassy:
2 Avenue Gabriel, 75382 Paris Cedex 08
mailing address:
PSC 116, APO AE 09777
telephone:
[33] (1) 43-12-22-22
FAX:
[33] (1) 42 66 97 83
consulate(s) general:
Marseille, Strasbourg
|
|
|
|

|
|
three equal vertical bands of blue (hoist side), white, and red; known as the "Le drapeau tricolore" (French Tricolor), the origin of the flag dates to 1790 and the French Revolution when the "ancient French color" of white was combined with the blue and red colors of the Parisian militia; the official flag for all French dependent areas
note:
the design and/or colors are similar to a number of other flags, including those of Belgium, Chad, Cote d'Ivoire, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, and Netherlands
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "La Marseillaise" (The Song of Marseille)
lyrics/music:
Claude-Joseph ROUGET de Lisle
note:
adopted 1795, restored 1870; originally known as "Chant de Guerre pour l'Armee du Rhin" (War Song for the Army of the Rhine), the National Guard of Marseille made the song famous by singing it while marching into Paris in 1792 during the French Revolutionary Wars
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
France is in the midst of transition from a well-to-do modern economy that has featured extensive government ownership and intervention to one that relies more on market mechanisms. The government has partially or fully privatized many large companies, banks, and insurers, and has ceded stakes in such leading firms as Air France, France Telecom, Renault, and Thales. It maintains a strong presence in some sectors, particularly power, public transport, and defense industries. With at least 75 million foreign tourists per year, France is the most visited country in the world and maintains the third largest income in the world from tourism. France's leaders remain committed to a capitalism in which they maintain social equity by means of laws, tax policies, and social spending that reduce income disparity and the impact of free markets on public health and welfare. France has weathered the global economic crisis better than most other big EU economies because of the relative resilience of domestic consumer spending, a large public sector, and less exposure to the downturn in global demand than in some other countries. Nonetheless, France's real GDP contracted 2.5% in 2009, but recovered somewhat in 2010, while the unemployment rate increased from 7.4% in 2008 to 9.5% in 2010. The government pursuit of aggressive stimulus and investment measures in response to the economic crisis, however, are contributing to a deterioration of France's public finances. The government budget deficit rose sharply from 3.4% of GDP in 2008 to 7.8% of GDP in 2010, while France's public debt rose from 68% of GDP to 84% over the same period. Paris is terminating stimulus measures, eliminating tax credits, and freezing most government spending to bring the budget deficit under the 3% euro-zone ceiling by 2013, and to highlight France's commitment to fiscal discipline at a time of intense financial market scrutiny of euro zone debt levels. President SARKOZY - who secured passage of pension reform in 2010 - is expected to seek passage of some tax reforms in 2011, but he may delay additional, more costly, reforms until after the 2012 election.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.145 trillion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
$2.114 trillion (2009 est.)
$2.169 trillion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.583 trillion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
-2.5% (2009 est.)
0.1% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$33,100 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
$32,800 (2009 est.)
$33,900 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 1.8%
industry:
19.2%
services:
79% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
28.21 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 3.8%
industry:
24.3%
services:
71.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
9.1% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.2% (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 3%
highest 10%:
24.8% (2004)
|
|
|
|

|
|
32.7 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 98
32.7 (1995)
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.9% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $1.241 trillion
expenditures:
$1.441 trillion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
83.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
77.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
0.1% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.75% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 125
1.75% (31 December 2009)
note:
this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.46% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
8.13% (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$858.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$862.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|

|
|
$2.292 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$2.306 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.319 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$4.121 trillion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.972 trillion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 7
$1.492 trillion (31 December 2008)
$2.771 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
wheat, cereals, sugar beets, potatoes, wine grapes; beef, dairy products; fish
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery, chemicals, automobiles, metallurgy, aircraft, electronics; textiles, food processing; tourism
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|

|
|
535.7 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
447.2 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
58.69 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
10.68 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
70,820 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.875 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|

|
|
597,800 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.386 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|

|
|
101.2 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|

|
|
877 million cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|

|
|
44.84 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.931 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|

|
|
45.85 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|

|
|
7.079 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|

|
|
$-53.29 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
$-51.86 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$508.7 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$473.9 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery and transportation equipment, aircraft, plastics, chemicals, pharmaceutical products, iron and steel, beverages
|
|
|
|

|
|
Germany 15.88%, Italy 8.16%, Spain 7.8%, Belgium 7.44%, UK 7.04%, US 5.65%, Netherlands 3.99% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$577.7 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$535.8 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
machinery and equipment, vehicles, crude oil, aircraft, plastics, chemicals
|
|
|
|

|
|
Germany 19.41%, Belgium 11.61%, Italy 7.97%, Netherlands 7.15%, Spain 6.68%, UK 4.9%, US 4.72%, China 4.44% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$NA (31 December 2010 est.)
$133.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.698 trillion (30 June 2010)
country comparison to the world: 5
$4.935 trillion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.207 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
$1.151 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1.837 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
$1.711 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.755 (2010)
0.7198 (2009)
0.6827 (2008)
0.7345 (2007)
0.7964 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
36.441 million; 35.5 million (metropolitan France) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|

|
|
60.95 million; 59.543 million (metropolitan France) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: highly developed
domestic:
extensive cable and microwave radio relay; extensive use of fiber-optic cable; domestic satellite system
international:
country code - 33; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Europe, Asia, Australia, the Middle East, and US; satellite earth stations - more than 3 (2 Intelsat (with total of 5 antennas - 2 for Indian Ocean and 3 for Atlantic Ocean), NA Eutelsat, 1 Inmarsat - Atlantic Ocean region); HF radiotelephone communications with more than 20 countries
overseas departments:
country codes: French Guiana - 594; Guadeloupe - 590; Martinique - 596; Mayotte - 262; Reunion - 262
|
|
|
|

|
|
a mix of both publicly-operated and privately-owned TV stations; state-owned France Televisions operates 4 networks, one of which is a network of regional stations, and has part-interest in several thematic cable/satellite channels and international channels; a large number of privately-owned regional and local TV stations; multi-channel satellite and cable services provide a large number of channels; public broadcaster Radio France operates 7 national networks, a series of regional networks, and operates services for overseas territories and foreign audiences; Radio France Internationale (RFI), under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, is a leading international broadcaster; a large number of commercial FM stations, with many of them consolidating into commercial networks (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France - .fr; French Guiana - .gf; Guadeloupe - .gp; Martinique - .mq; Mayotte - .yt; Reunion - .re
|
|
|
|

|
|
15,182,001; 15.161 million (metropolitan France) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|

|
|
45.262 million; 44.625 million (metropolitan France) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
475 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 297
over 3,047 m:
14
2,438 to 3,047 m:
27
1,524 to 2,437 m:
98
914 to 1,523 m:
83
under 914 m:
76 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 177
914 to 1,523 m:
69
under 914 m:
108 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 15,276 km; oil 2,939 km; refined products 5,084 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 29,640 km
country comparison to the world: 9
standard gauge:
29,473 km 1.435-m gauge (15,361 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
167 km 1.000-m gauge (63 km electrified) (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 1,027,183 km (metropolitan France; includes 10,958 km of expressways)
country comparison to the world: 7
note:
there are another 5,100 km of roadways in overseas departments (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: 8,501 km (1,621 km accessible to craft of 3,000 metric tons) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 167
country comparison to the world: 38
by type:
bulk carrier 2, cargo 8, chemical tanker 36, container 25, liquefied gas 12, passenger 11, passenger/cargo 44, petroleum tanker 17, refrigerated cargo 1, roll on/roll off 11
foreign-owned:
57 (Belgium 7, China 5, Denmark 12, French Polynesia 12, Germany 1, New Caledonia 3, Norway 1, NZ 1, Singapore 3, Spain 1, Sweden 6, Switzerland 5)
registered in other countries:
146 (Bahamas 19, Belgium 5, Bermuda 1, Canada 1, Cyprus 16, Egypt 1, Hong Kong 3, Indonesia 1, Italy 2, Luxembourg 16, Malta 13, Morocco 4, Netherlands 2, Norway 4, Panama 13, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2, Singapore 3, South Korea 1, Taiwan 1, UK 33, US 4, unknown 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Calais, Dunkerque, Le Havre, Marseille, Nantes, Paris, Rouen
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Army (Armee de Terre; includes Marines, Foreign Legion, Army Light Aviation), Navy (Marine Nationale, includes Naval Air, Maritime Gendarmerie (Coast Guard)), Air Force (Armee de l'Air (AdlA), includes Air Defense), National Gendarmerie (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
17-40 years of age for male and female voluntary military service (with parental consent); no conscription; 12-month service obligation; women serve in noncombat posts (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 14,563,662
females age 16-49:
14,238,434 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 12,025,341
females age 16-49:
11,721,827 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 396,050
female:
377,839 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.6% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::France |
|

|
|
Madagascar claims the French territories of Bassas da India, Europa Island, Glorioso Islands, and Juan de Nova Island; Comoros claims Mayotte; Mauritius claims Tromelin Island; territorial dispute between Suriname and the French overseas department of French Guiana; France asserts a territorial claim in Antarctica (Adelie Land); France and Vanuatu claim Matthew and Hunter Islands, east of New Caledonia
|
|
|
|

|
|
metropolitan France: transshipment point for South American cocaine, Southwest Asian heroin, and European synthetics
French Guiana:
small amount of marijuana grown for local consumption; minor transshipment point to Europe
Martinique:
transshipment point for cocaine and marijuana bound for the US and Europe
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

