-
Mission
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an independent US
Government agency responsible for providing national security
intelligence to senior US policymakers.
To learn more, visit CIA Vision, Mission & Values.
|
Central Intelligence Agency
The Work of a Nation. The Center of Intelligence
|
|
| page last updated on June 14, 2011 |
|
|
(CONTAINS DESCRIPTION)
|
|
|
Click flag or map to enlarge 
|
|
|
|
Click map to enlarge 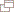
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Britain conquered Burma over a period of 62 years (1824-1886) and incorporated it into its Indian Empire. Burma was administered as a province of India until 1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony; independence from the Commonwealth was attained in 1948. Gen. NE WIN dominated the government from 1962 to 1988, first as military ruler, then as self-appointed president, and later as political kingpin. In September 1988, the military deposed NE WIN and established a new ruling junta. Despite multiparty legislative elections in 1990 that resulted in the main opposition party - the National League for Democracy (NLD) - winning a landslide victory, the junta refused to hand over power. NLD leader and Nobel Peace Prize recipient AUNG SAN SUU KYI, who was under house arrest from 1989 to 1995 and 2000 to 2002, was imprisoned in May 2003 and subsequently transferred to house arrest. She was finally released in November 2010. After the ruling junta in August 2007 unexpectedly increased fuel prices, tens of thousands of Burmese marched in protest, led by prodemocracy activists and Buddhist monks. In late September 2007, the government brutally suppressed the protests, killing at least 13 people and arresting thousands for participating in the demonstrations. Since then, the regime has continued to raid homes and monasteries and arrest persons suspected of participating in the pro-democracy protests. Burma in early May 2008 was struck by Cyclone Nargis, which claimed over 138,000 dead and tens of thousands injured and homeless. Despite this tragedy, the junta proceeded with its May constitutional referendum, the first vote in Burma since 1990. Parliamentary elections held in November 2010, considered flawed by many in the international community, saw the junta's Union Solidarity and Development Party garnering over 75% of the seats. Parliament convened in January 2011 and selected former Prime Minister THEIN SEIN as president. The vast majority of national-level appointees named by THEIN SEIN are former or current military officers.
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Bangladesh and Thailand
|
|
|
|

|
|
22 00 N, 98 00 E
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 676,578 sq km
country comparison to the world: 40
land:
653,508 sq km
water:
23,070 sq km
|
|
|
|

|
|
slightly smaller than Texas
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5,876 km
border countries:
Bangladesh 193 km, China 2,185 km, India 1,463 km, Laos 235 km, Thailand 1,800 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,930 km
|
|
|
|

|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|

|
|
tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures, lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April)
|
|
|
|

|
|
central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest point: Andaman Sea 0 m
highest point:
Hkakabo Razi 5,881 m
|
|
|
|

|
|
petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas, hydropower
|
|
|
|

|
|
arable land: 14.92%
permanent crops:
1.31%
other:
83.77% (2005)
|
|
|
|

|
|
22,500 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1,045.6 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 33.23 cu km/yr (1%/1%/98%)
per capita:
658 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|

|
|
destructive earthquakes and cyclones; flooding and landslides common during rainy season (June to September); periodic droughts
|
|
|
|

|
|
deforestation; industrial pollution of air, soil, and water; inadequate sanitation and water treatment contribute to disease
|
|
|
|

|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|

|
|
strategic location near major Indian Ocean shipping lanes
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
53,999,804 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
note:
estimates for this country take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
|
|
|
|

|
|
0-14 years: 27.5% (male 7,560,859/female 7,278,652)
15-64 years:
67.5% (male 18,099,707/female 18,342,696)
65 years and over:
5% (male 1,184,291/female 1,533,599) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 26.9 years
male:
26.3 years
female:
27.5 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
1.084% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|

|
|
19.31 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.16 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|

|
|
-0.31 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|

|
|
urban population: 34% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.9% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
RANGOON (capital) 4.259 million; Mandalay 1.009 million; Nay Pyi Taw 992,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.77 male(s)/female
total population:
0.99 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 49.23 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 49
male:
56.16 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
41.88 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total population: 64.88 years
country comparison to the world: 168
male:
62.57 years
female:
67.33 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.26 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|

|
|
0.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|

|
|
240,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|

|
|
18,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|

|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever and malaria
water contact disease:
leptospirosis
animal contact disease:
rabies
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 75% of population
rural: 69% of population
total: 71% of population
unimproved:
urban: 25% of population
rural: 31% of population
total: 29% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
improved:
urban: 86% of population
rural: 79% of population
total: 81% of population
unimproved:
urban: 14% of population
rural: 21% of population
total: 19% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
noun: Burmese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Burmese
|
|
|
|

|
|
Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Indian 2%, Mon 2%, other 5%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim 4%, animist 1%, other 2%
|
|
|
|

|
|
Burmese (official)
note:
minority ethnic groups have their own languages
|
|
|
|

|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
89.9%
male:
93.9%
female:
86.4% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 9 years
male:
8 years
female:
8 years (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
conventional long form: Union of Burma
conventional short form:
Burma
local long form:
Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (translated by the US Government as Union of Myanma and by the Burmese as Union of Myanmar)
local short form:
Myanma Naingngandaw
former:
Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
note:
since 1989 the military authorities in Burma have promoted the name Myanmar as a conventional name for their state; the US Government did not adopt the name, which is a derivative of the Burmese short-form name Myanma Naingngandaw
|
|
|
|

|
|
military regime (a nominally civilian government has been named, but a formal transfer of power has not yet taken place)
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: Rangoon (Yangon)
geographic coordinates:
16 48 N, 96 09 E
time difference:
UTC+6.5 (11.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note:
Nay Pyi Taw is the administrative capital
|
|
|
|

|
|
7 divisions (taing-myar, singular - taing) and 7 states* (pyi ne-myar, singular - pyi ne)
divisions:
Ayeyarwady, Bago, Magway, Mandalay, Sagaing, Tanintharyi, Yangon
states:
Chin, Kachin, Kayah, Kayin, Mon, Rakhine (Arakan), Shan
|
|
|
|

|
|
4 January 1948 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Independence Day, 4 January (1948); Union Day, 12 February (1947)
|
|
|
|

|
|
3 January 1974; suspended 18 September 1988; a new constitution was to take effect when the bicameral legislature convened 31 January 2011, but no announcement has been made
|
|
|
|

|
|
mixed legal system of English common law (as introduced in codifications designed for colonial India) and customary law
|
|
|
|

|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|

|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of state: President THEIN SEIN (since 4 February 2011); Vice President SAI MOUK KHAM (since 3 February 2011); Vice President TIN AUNG MYINT OO (since 4 February 2011)
head of government:
Prime Minister THEIN SEIN (since 24 October 2007)
cabinet:
cabinet is appointed by the president and confirmed by the parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
THEIN SEIN elected president by the parliament from among three vice presidents; the upper house, the lower house, and military members of the parliament each nominate one vice president (president serves a five-year term)
|
|
|
|

|
|
bicameral, consists of the House of Nationalities [Amyotha Hluttaw] (224 seats, 168 directly elected and 56 appointed by the military; members serve five-year terms) and the House of Representatives [Pythu Hluttaw] (440 seats, 330 directly elected and 110 appointed by the military; members serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 7 November 2010 (next to be held in December 2015)
election results:
House of Nationalities - percent of vote by party - USDP 74.8%, others (NUP, SNDP, RNDP, NDF, AMRDP) 25.2%; seats by party - USDP 129, others 39; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - USDP 79.6%, others (NUP, SNDP, RNDP, NDF, AMRDP) 20.4%; seats by party - USDP 259, others 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
remnants of the British-era legal system are in place, but there is no guarantee of a fair public trial; the judiciary is not independent of the executive; the 2011 constitution calls for a Supreme Court, a Courts-Martial, and a Constitutional Tribunal of the Union
|
|
|
|

|
|
All Mon Region Democracy Party or AMRDP [NAING NGWE THEIN]; National Democratic Force or NDF [KHIN MAUNG SWE, Dr.THAN NYEIN]; National League for Democracy or NLD [AUNG SHWE, U TIN OO, AUNG SAN SUU KYI]; note - the party was deregisted because it did not register for the 2010 election, but it is still active; National Unity Party or NUP [TUN YE]; Rakhine Nationalities Development Party or RNDP [Dr. AYE MG]; Shan Nationalities Democratic Party [SAI AIKE PAUNG]; Shan Nationalities League for Democracy or SNLD [HKUN HTUN OO]; Union Solidarity and Development Party or USDP [SHWE MANN, HTAY OO]; numerous smaller parties
|
|
|
|

|
|
Thai border: Ethnic Nationalities Council or ENC; Federation of Trade Unions-Burma or FTUB (exile trade union and labor advocates); National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma or NCGUB (self-proclaimed government in exile) ["Prime Minister" Dr. SEIN WIN] consists of individuals, some legitimately elected to the People's Assembly in 1990 (the group fled to a border area and joined insurgents in December 1990 to form a parallel government in exile); National Council-Union of Burma or NCUB (exile coalition of opposition groups)
Inside Burma:
Kachin Independence Organization or KIO; Karen National Union or KNU; Karenni National People's Party or KNPP; Union Solidarity and Development Association or USDA (pro-regime, a social and political mass-member organization) [HTAY OO, general secretary] became the Union Solidarity and Development Party in 2010; United Wa State Army or UWSA; 88 Generation Students (pro-democracy movement); several other Shan factions
note:
freedom of expression is highly restricted in Burma; political groups, other than parties approved by the government, are limited in number
|
|
|
|

|
|
ADB, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITU, NAM, OPCW (signatory), SAARC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires HAN THU; note - Burma does not have an ambassador to the United States
chancery:
2300 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 332-3344
FAX:
[1] (202) 332-4351
consulate(s) general:
none; Burma has a Mission to the UN in New York
|
|
|
|

|
|
chief of mission: Charge d'Affaires Larry M. DINGER; note - The United States does not have an ambassador to Burma
embassy:
110 University Avenue, Kamayut Township, Rangoon
mailing address:
Box B, APO AP 96546
telephone:
[95] (1) 536-509, 535-756, 538-038
FAX:
[95] (1) 650-306
|
|
|
|

|
|
design consists of three equal horizontal stripes of yellow (top), green, and red; centered on the green band is a large white five-pointed star that partially overlaps onto the adjacent colored stripes; the design revives the triband colors used by Burma from 1943-45, during the Japanese occupation
|
|
|
|

|
|
name: "Kaba Ma Kyei" (Till the End of the World, Myanmar)
lyrics/music:
SAYA TIN
note:
adopted 1948; Burma is among a handful of non-European nations that have anthems rooted in indigenous traditions; the beginning portion of the anthem is a traditional Burmese anthem before transitioning into a Western-style orchestrated work
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Burma, a resource-rich country, suffers from pervasive government controls, inefficient economic policies, corruption, and rural poverty. Despite Burma's emergence as a natural gas exporter, socio-economic conditions have deteriorated under the regime's mismanagement, leaving most of the public in poverty, while military leaders and their business cronies exploit the country's ample natural resources. The transfer of state assets, especially real estate, to cronies and military families in 2010 under the guise of a privatization policy further widened the gap between the economic elite and the public. The economy suffers from serious macroeconomic imbalances - including unpredictable inflation, fiscal deficits, multiple official exchange rates that overvalue the Burmese kyat, a distorted interest rate regime, unreliable statistics, and an inability to reconcile national accounts. Burma's poor investment climate hampers the inflow of foreign investment; in recent years, foreign investors have shied away from nearly every sector except for natural gas, power generation, timber, and mining. The exploitation of natural resources does not benefit the population at large. The business climate is widely perceived as opaque, corrupt, and highly inefficient. Over 60% of the FY 2009-10 budget was allocated to state owned enterprises - most operating at a deficit. The most productive sectors will continue to be in extractive industries - especially oil and gas, mining, and timber - with the latter two causing significant environmental degradation. Other areas, such as manufacturing, tourism and services, struggle in the face of inadequate infrastructure, unpredictable trade policies, neglected health and education systems, and endemic corruption. A major banking crisis in 2003 caused 20 private banks to close; private banks still operate under tight restrictions, limiting the private sector's access to credit. The United States, the European Union, and Canada have imposed financial and economic sanctions on Burma. US sanctions, prohibiting most financial transactions with Burmese entities, impose travel bans on senior Burmese military and civilian leaders and others connected to the ruling regime, and ban imports of Burmese products. These sanctions affected the country's fledgling garment industry, isolated the struggling banking sector, and raised the costs of doing business with Burmese companies, particularly firms tied to Burmese regime leaders. The global crisis of 2008-09 caused exports and domestic consumer demand to drop. Remittances from overseas Burmese workers - who had provided significant financial support for their families - slowed or dried up as jobs were lost and migrant workers returned home. Although the Burmese government has good economic relations with its neighbors, significant improvements in economic governance, the business climate, and the political situation are needed to promote serious foreign investment.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$76.47 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
$72.65 billion (2009 est.)
$69.1 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
$42.95 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
5.1% (2009 est.)
3.6% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$1,400 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
$1,400 (2009 est.)
$1,300 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 43.2%
industry:
20%
services:
36.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
31.68 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|

|
|
agriculture: 70%
industry:
7%
services:
23% (2001)
|
|
|
|

|
|
5.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
4.9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
32.7% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
lowest 10%: 2.8%
highest 10%:
32.4% (1998)
|
|
|
|

|
|
15.1% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|

|
|
revenues: $1.369 billion
expenditures:
$2.951 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
9.6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
1.5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
12% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 29
12% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|

|
|
17% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
17% (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.907 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
$4.038 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
note:
this number reflects the vastly overvalued official exchange rate of 5.38 kyat per dollar in 2007; at the unofficial black market rate of 1,305 kyat per dollar for 2007, the stock of kyats would equal only US$2.465 billion and Burma's velocity of money (the number of times money turns over in the course of a year) would be six, in line with the velocity of money for other countries in the region; in January-February 2011, the unofficial black market rate averaged 890 kyat per dollar.
|
|
|
|

|
|
$7.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
$6.231 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$8.552 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$6.858 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|

|
|
rice, pulses, beans, sesame, groundnuts, sugarcane; hardwood; fish and fish products
|
|
|
|

|
|
agricultural processing; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; cement, construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer; oil and natural gas; garments, jade and gems
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|

|
|
6.286 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|

|
|
4.403 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18,880 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|

|
|
42,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|

|
|
2,200 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|

|
|
18,250 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|

|
|
50 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|

|
|
12.4 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|

|
|
3.85 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|

|
|
8.55 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|

|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|

|
|
283.2 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|

|
|
$652 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
$705 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$7.841 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
$6.862 billion (2009 est.)
note:
official export figures are grossly underestimated due to the value of timber, gems, narcotics, rice, and other products smuggled to Thailand, China, and Bangladesh
|
|
|
|

|
|
natural gas, wood products, pulses, beans, fish, rice, clothing, jade and gems
|
|
|
|

|
|
Thailand 46.57%, India 12.99%, China 9.01%, Japan 5.65% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$4.532 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
$4.02 billion (2009 est.)
note:
import figures are grossly underestimated due to the value of consumer goods, diesel fuel, and other products smuggled in from Thailand, China, Malaysia, and India
|
|
|
|

|
|
fabric, petroleum products, fertilizer, plastics, machinery, transport equipment; cement, construction materials, crude oil; food products, edible oil
|
|
|
|

|
|
China 33.1%, Thailand 26.28%, Singapore 15.18% (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$3.762 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
$3.561 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
$7.145 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$7.079 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
kyats (MMK) per US dollar -
966 (2010)
1,055 (2009)
1,205 (2008)
1,296 (2007)
1,280 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
812,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|

|
|
502,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|

|
|
general assessment: meets minimum requirements for local and intercity service for business and government
domestic:
system barely capable of providing basic service; mobile-cellular phone system is grossly underdeveloped
international:
country code - 95; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-3 optical telecommunications submarine cable that provides links to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2, Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and ShinSat (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
government controls all domestic broadcast media; 2 state-controlled television stations with 1 of the stations controlled by the armed forces; a third TV channel, a pay-TV station, is a joint state-private venture; access to satellite TV is limited; 1 state-controlled domestic radio station and 6 FM stations that are joint state-private ventures; transmissions of several international broadcasters are available in parts of Burma; the opposition-backed station Democratic Voice of Burma broadcasts into Burma via shortwave (2009)
|
|
|
|

|
|
.mm
|
|
|
|

|
|
172 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|

|
|
110,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
76 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 37
over 3,047 m:
12
2,438 to 3,047 m:
8
1,524 to 2,437 m:
15
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 39
over 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
11
under 914 m:
23 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
6 (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
gas 3,046 km; oil 551 km (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 5,031 km
country comparison to the world: 36
narrow gauge:
5,031 km 1.000-m gauge (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 27,000 km
country comparison to the world: 100
paved:
3,200 km
unpaved:
23,800 km (2006)
|
|
|
|

|
|
12,800 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|

|
|
total: 26
country comparison to the world: 91
by type:
bulk carrier 1, cargo 19, passenger 2, passenger/cargo 3, specialized tanker 1
foreign-owned:
3 (Cyprus 1, Germany 1, Japan 1)
registered in other countries:
3 (Panama 3) (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
Moulmein, Rangoon, Sittwe
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Myanmar Armed Forces (Tatmadaw): Army (Tatmadaw Kyi), Navy (Tatmadaw Yay), Air Force (Tatmadaw Lay) (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
18-35 years of age (men) and 18-27 years of age (women) for compulsory military service; service obligation 2 years; male (ages 18-45) and female (ages 18-35) professionals (including doctors, engineers, mechanics) serve up to 3 years; service terms may be extended to 5 years in an officially declared emergency; forced conscription of children, although officially prohibited, reportedly continues (2011)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 14,747,845
females age 16-49:
14,710,871 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
males age 16-49: 10,451,515
females age 16-49:
11,181,537 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
male: 522,478
female:
506,388 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|

|
|
2.1% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Burma |
|

|
|
over half of Burma's population consists of diverse ethnic groups who have substantial numbers of kin in neighboring countries; the Naf river on the border with Bangladesh serves as a smuggling and illegal transit route; Bangladesh struggles to accommodate 29,000 Rohingya, Burmese Muslim minority from Arakan State, living as refugees in Cox's Bazar; Burmese border authorities are constructing a 200 km (124 mi) wire fence designed to deter illegal cross-border transit and tensions from the military build-up along border with Bangladesh in 2010; Bangladesh referred its maritime boundary claims with Burma and India to the International Tribunal on the Law of the Sea; Burmese forces attempting to dig in to the largely autonomous Shan State to rout local militias tied to the drug trade, prompts local residents to periodically flee into neighboring Yunnan Province in China; fencing along the India-Burma international border at Manipur's Moreh town is in progress to check illegal drug trafficking and movement of militants; 140,000 mostly Karen refugees fleeing civil strife, political upheaval and economic stagnation in Burma live in remote camps in Thailand near the border
|
|
|
|

|
|
IDPs: 503,000 (government offensives against ethnic insurgent groups near the eastern borders; most IDPs are ethnic Karen, Karenni, Shan, Tavoyan, and Mon) (2007)
|
|
|
|

|
|
current situation: Burma is a source country for women, children, and men trafficked for the purpose of forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation; Burmese women and children are trafficked to East and Southeast Asia for commercial sexual exploitation, domestic servitude, and forced labor; Burmese children are subjected to conditions of forced labor in Thailand as hawkers and beggars; women are trafficked for commercial sexual exploitation to Malaysia and China; some trafficking victims transit Burma from Bangladesh to Malaysia and from China to Thailand; Burma's internal trafficking remains the most serious concern occurring primarily from villages to urban centers and economic hubs for labor in industrial zones, agricultural estates, and commercial sexual exploitation; the Burmese military continues to engage in the unlawful conscription of child soldiers, and continues to be the main perpetrator of forced labor inside Burma; ethnic insurgent groups also used compulsory labor of adults and unlawful recruitment of children; the regime's widespread use of and lack of accountability in forced labor and recruitment of child soldiers is particularly worrying and represents the top causal factor for Burma's significant trafficking problem
tier rating:
Tier 3 - serious problems remain in Burma, and in some areas, most notably in the area of forced labor, the Government of Burma is not making significant efforts to comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking, warranting a ranking of Tier 3; in other areas, particularly with regard to international sex trafficking of women and girls, the Government of Burma is making significant efforts (2010)
|
|
|
|

|
|
remains world's second largest producer of illicit opium with an estimated production in 2008 of 340 metric tons, an increase of 26%, and poppy cultivation in 2008 totaled 22,500 hectares, a 4% increase from 2007; production in the United Wa State Army's areas of greatest control remains low; Shan state is the source of 94% of Burma's poppy cultivation; lack of government will to take on major narcotrafficking groups and lack of serious commitment against money laundering continues to hinder the overall antidrug effort; major source of methamphetamine and heroin for regional consumption
(2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

