Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide






CHAPTER 14. Managing and Moving Data
This chapter describes how to use Oracle Data Manager to move data to and from an Oracle database. This chapter assumes that you have read "Overview of the Database Tools," ![[*]](jump.gif) , and that you are familiar with the interface elements of the database tools. The topics included in this chapter are:
, and that you are familiar with the interface elements of the database tools. The topics included in this chapter are:
For more information on the tasks Data Manager performs, see the sections on the Export, Import and SQL*Loader utilities in Oracle7 Server Utilities. For information about standard elements of your operating system, see your operating system-specific documentation.
Starting the Data Manager
To start the Data Manager, select a database object from the Navigator tree list. Then click on the Data Manager icon in the Applications Launch Palette, or choose Applications and then Oracle Data Manager from the Tools menu.
- If you have already connected to a database, the Oracle Data Manager main window displays.
- If a valid database connection has not been made, the Connect dialog box displays. This dialog box also appears when you launch Data Manager in standalone mode. See "Connecting to an Instance,"
![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Note: You can change the database connection with the Change Database Connection option in the File menu of the Console.
After the Data Manager has successfully connected to a database, the Oracle Data Manager property sheet displays.
Figure Figure 14 - 1 shows the first page of the Data Manager property sheet.
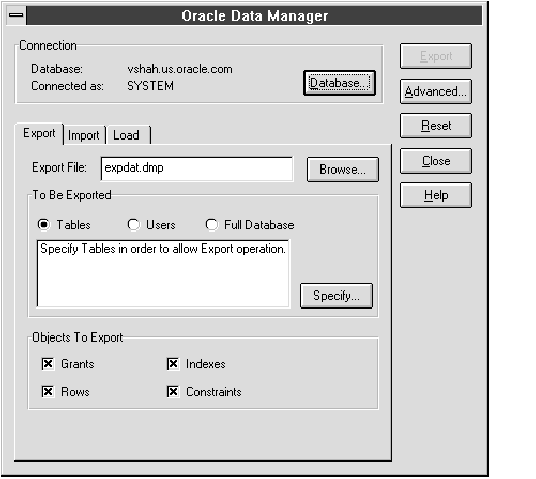 Figure 14 - 1. First Page of the Data Manager Property Sheet
Figure 14 - 1. First Page of the Data Manager Property Sheet
The Data Manager property sheet contains the following tabs:
For general information about:
- Dialog boxes, see page 7 - 11.
- Property sheets, see page 7 - 12.
Exporting Data to a File
You use the Export page of the Data Manager property sheet to transfer data from an Oracle database to an operating system file in Oracle-binary format. Files in this proprietary fomrat can only be read by using the Import component of Data Manager.
Export files can be used to transfer data between databases or used as backups. You can define how the data is exported.
To export data to a file, perform the following steps:
1. Click on the Export tab of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet.
The resulting Export page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet contains the following elements:
| Export File | Enter the operating system filename that will contain your exported data. (Specifies the value for the FILE parameter.) |
| Browse | Choose Browse to select the operating system filename that will contain your exported data. |
| To be Exported | Tables: Choose Tables to export tables to the file. You must then choose Specify to select the tables to export. (Specifies the value for the TABLES parameter.) |
| | Users: Choose Users to export database objects belonging to specified owners. You must then choose Specify to select users whose objects are to be exported. (Specifies the value for the OWNER parameter.) |
| | Full Database: Choose Full Database to export the entire database to the file. (Specifies the value for the FULL parameter.) |
| Specify | If you selected Tables or Users, choose Specify to select a list of tables or a list of users to export. |
| Objects to Export | Grants: Check this box to also export grants on the database objects that will be exported. (Specifies the value for the GRANTS parameter.) |
| | Rows: Check this box to export rows of tables. You can elect not to export rows if you want to export only table definitions. (Specifies the value for the ROWS parameter.) |
| | Indexes: Check this box to export indexes. (Specifies the value for the INDEXES parameter.) |
| | Constraints: Check this box to export table constraints. (Specifies the value for the CONSTRAINTS parameter.) |
| Export | Exports the data to the file. |
| Run on Host | Runs the export operation as an Enterprise Manager job on the node containing the selected database. For more information, see "Data Manager Tasks," ![[*]](jump.gif) . . |
| Advanced | Choose Advanced to edit advanced parameters. |
| Reset | Choose Reset to set all options to their default values. |
| Close | Closes Oracle Data Manager. |
2. Edit the parameters as desired.
3. When ready, choose Export.
Exporting Objects to a File
To export objects to a file, perform the following steps:
1. Choose the Specify button of the Export page.
The Export Objects property sheet displays. It contains the following elements:
| Export | Moves selected objects from the Remaining Tables/Owners list to the Selected Tables/Owners list. |
| Export All | Moves all objects from the Remaining Tables/Owners list to the Selected Tables/Owners list. |
| Don't Export | Moves selected objects from the Selected Tables/Owners list to the Remaining Tables/Owners list. |
| Export None | Moves all objects from the Selected Tables/Owners list to the Remaining Tables/Owners list. |
2. Edit the parameters as desired.
3. When ready, choose OK.
Exporting Table(s) to a File
To export a table or a list of tables that you own or have privileged access to, from the Export page of the Oracle Data Manager, perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that Tables is selected.
The Export Objects property sheet appears, and displays a list of tables that you may export.
3. Select the tables you want to export from the list on the right and choose Export. (Or, choose Export All to export the entire list.)
4. When ready, choose OK.
5. The Export page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
6. Verify that all values in the Objects to Export group are as you want them.
8. When ready, choose Export.
Exporting Owner(s) to a File
To export all objects belonging to an owner or list of owners, from the Export page, perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that Owners is selected.
The Export Objects property sheet appears, and displays a list of owners whose objects you may export.
3. Select the owners whose objects you want to export from the list on the right and choose Export. (Or, choose Export All to export the entire list.)
4. When ready, choose OK.
The Export page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
5. Verify that all values in the Objects to Export group are as you want them.
7. When ready, choose Export.
Exporting the Full Database
To export the full database to a file, from the Export page, perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that Full Database is selected.
2. Verify that all values in the Export These Objects box are as you want them.
4. When ready, choose Export.
Selecting Advanced Export Options
To select advanced export options, from the Export page, perform the following steps:
The Advanced Export Options property sheet appears. It contains the following elements:
| Record Length | Enter a value for the length in bytes of the file record. (Specifies the value for the RECORDLENGTH parameter.). |
| Buffer Size | Enter a value for the size in bytes of the buffer used to fetch data rows. ( Specifies the value for the BUFFER parameter.) |
| Generate Log File | Select if you want a log file generated for the export (Specifies the value for the EXP parameter). You must specify the name of the log file. |
| Log File | Name of log file. Used only when Generate Log File is selected. (Specifies the value for the LOG parameter.) Use the associated Browse button to specify the path and filename for the log file. |
| Export Read-Consistent View of Data | Select if you want to export a read-consistent view of the database (Specifies the value for the CONSISTENT parameter). |
| Increment Type | Select the type of incremental export. (Specifies the value for the INCTYPE parameter). Valid values for Windows are None, Incremental, Complete, and Cumulative. |
| Statistics Type | Select type of database optimizer statistics to generate when exported data is imported back into Oracle. (Specifies the value for the STATISTICS parameter). Valid values for Windows are None, Estimate, and Compute. |
| Merge Extents for Export | Select if you want to compress table data into one extent during an import (Specifies the value for the COMPRESS parameter). |
2. Edit the parameters as desired.
3. When ready, choose OK.
The Export page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
Using the Command-line Option
In certain situations, you may want to use the command-line option to export data from an Oracle database to a file.
To start the Export process, type:
c:\> EXP72 [options]
Note: The Run on Host feature is not available as a command line option.
For more information about command-line options for the Export utility, see Oracle7 Server Utilities.
BUFFER and RECORDLENGTH Defaults
When running the Data Manager, note that the default values for certain parameters are operating-system specific. Specifically, the BUFFER parameter defaults to a value of 4K under Windows NT and the RECORDLENGTH parameter defaults to 2K.
Importing Data from a File
You use the Import page of the Data Manager property sheet to transfer data from an export file to an Oracle database. Import can only read data that has been created with the Export component of Data Manager. You can define how the data is imported.
To import data to a file, perform the following steps:
1. Click on the Import tab of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet.
The resulting Import page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet contains the following elements:
| Import File | Specify operating system file to import into an Oracle database. (Specifies the value for the FILE parameter.) |
| Browse | Use this to select the operating system filename that will be imported into an Oracle database. |
| To be Imported | Tables: Choose Tables to import tables from the file. You must then choose Specify to select the tables to import. (Specifies the value for the TABLES parameter.) |
| | Users: Choose Users to import database objects belonging to specified owners. You must then choose Specify to select users whose objects are to be imported. (Specifies the value for the OWNER parameter.) |
| | Full Database: Choose Full Database to import the entire database from the file. (Specifies the value for the FULL parameter.) |
| Specify | If you selected Tables or Users, choose Specify to select a list of tables or a list of users to import. |
| Objects to Export | Grants: Check this box to also import grants on the database objects that will be imported. (Specifies the value for the GRANTS parameter.) |
| | Rows: Check this box to export rows of tables. You can elect not to import rows if you want to import only table definitions. (Specifies the value for the ROWS parameter.) |
| | Indexes: Check this box to import indexes. (Specifies the value for the INDEXES parameter.) |
| Import | Imports the data from the file to the Oracle database. |
| Run on Host | Runs the import operation as an Enterprise Manager job on the node containing the selected database. For more information, see "Data Manager Tasks," ![[*]](jump.gif) . . |
| Advanced | Choose Advanced to edit advanced parameters. |
| Reset | Choose Reset to set all options to their default values. |
| Close | Closes Oracle Data Manager. |
| Ignore Creation Errors | If selected, Import will not report "object already exists" errors when attempting to create database objects. (Specifies the value for the IGNORE parameter.) |
2. Edit the parameters as desired.
3. When ready, choose Import.
Importing Table(s) From a File
To import a list of tables from an operating system file, from the Import page, perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that Tables is selected.
The Import Objects property sheet appears, and displays a list of Remaining Tables that you may import.
3. Select the table(s) that you want to import from the Remaining Tables list and choose Import. (Or, choose Import All to import the entire list.)
4. When finished, choose OK.
The Import page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
5. Verify that all values in the Objects to Import box are as you want them.
6. If necessary, select advanced import options by choosing Advanced.
5. When ready, choose Import.
Importing User(s) Objects From a File
To import a list of objects owned by specified users from an operating system file, from the Import page, perform the following steps:
1. Make sure that Users is selected.
The Import Objects property sheet appears.
3. Choose a name from Import this User.
4. Assuming you have the proper privileges, if you want to import the user's objects into the schema of a user other than the one logged in, choose a user from To This User.
6. Repeat steps 5-6 to import any additional user(s).
7. Choose Done when finished. The Import page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
8. Verify that all values in the Object to Import box are as you want them.
9. If necessary, select advanced import options by choosing Advanced.
10. When ready, choose Import.
Importing a Full Database From a File
To import a full database from an operating system file, from the Import page, perform the following steps:
2. Verify that all values in the Import Objects box are as you want them.
6. If necessary, select advanced import options by choosing Advanced.
7. When ready, choose Import.
Selecting Advanced Import Options
To select advanced import options, perform the following steps:
1. From the Import page, choose Advanced.
The Advanced Import Options property sheet appears. It contains the following elements:
| Record Length | Enter the length in bytes of the file record. (Specifies the value for the RECORDLENGTH parameter). |
| Buffer Size | Enter the size in bytes of the buffer used to transfer data rows. (Specifies the value for the BUFFER parameter.) |
| Generate Log File | If selected, Import will generate an import log file. |
| Log File | The name of the log file that contains the screen output. (Specifies the value for the LOG parameter.) Use the associated Browse button to specify the path and filename for the log file. |
| Increment Type | Select which type of incremental import, System, Restore, or None. (Specifies the value for the INCTYPE parameter.) |
| Write Index- Creation Commands to a File | If selected, Import will create a file to hold the index-creation SQL statement. |
| | |
| Index File | The name of the file that will contain the index- creation SQL statement. Use the associated Browse button to specify the path and filename for the index file. (Specifies the value for the INDEXFILE parameter.) |
| Commit After Each Array | If selected, Import will commit after each array insert. (Specifies the value for the COMMIT parameter.) |
| Overwrite Existing Data Files | When doing a full database import, select this if you want to overwrite the existing data files making up the database. (Specifies the value for the DESTROY parameter.) |
2. Verify that all values in the Advanced Import Options property sheet are as you want them.
3. When finished, choose OK.
Using the Command-line Option
In certain situations, you may want to use the command-line option to import data from a file to an Oracle database.
To start the Import process, type:
c:\> IMP72 [options]
Note: The Run on Host feature is not available as a command line option.
For more information about command-line options for the Import utility, see Oracle7 Server Utilities.
BUFFER and RECORDLENGTH Defaults
When running the Data Manager, note that the default values for certain parameters are operating-system specific. Specifically, the BUFFER parameter defaults to a value of 4K under Windows NT and the RECORDLENGTH parameter defaults to 2K.
Loading Data from an External File
You use the Load page of the Data Manager property sheet to transfer data to an Oracle database from files that have a different format from export files. By using a control file you specify how the data is stored externally and how it is to be loaded into the database.
To load data from an external file to an Oracle database, perform the following steps:
1. Click on the Load tab of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet.
The resulting Load page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet contains the following elements:
| Control File | Enter the path and filename for the control file, or choose the Control File Browse button to select the control file from a list. |
Note: You cannot load data until you supply a control filename. The Load button will remain disabled until you do so.
| Optional Files | Data File: Either enter the path and filename for the data file, or choose the Optional Files Browse button to select the data file from a list. |
| | Log File: Enter the path and filename for the log file. |
| | Bad File: Enter the path and filename for the bad file. |
| | Discard: Enter the path and filename for the discard file. |
| Load | Loads the data from the external file to the Oracle database. |
| Run on Host | Runs the load operation as an Enterprise Manager job on the node containing the selected database. For more information, see "Data Manager Tasks," ![[*]](jump.gif) . . |
| Advanced | Choose Advanced to edit advanced parameters. |
| Reset | Choose Reset to set all options to their default values. |
| Close | Exits Data Manager. |
2. Enter the path and filename for the control file, or choose the Browse button to select the filename from a list.
3. If you do not have a control file set up, see Oracle7 Server Utilities.
4. Enter the path and filename for the data file, or choose the Optional Files Browse button to select the data file. The default data file is the control file.
5. If you want, you may change the path and filename of the SQL*Loader log file.
6. Specify the bad file. During the execution of SQL*Loader, a bad file is generated to contain those data records, if any, that are rejected by SQL*Loader or by Oracle.
7. Specify the discard file. During the execution of SQL*Loader, a discard file is generated to contain those data records, if any, that are neither rejected nor inserted by SQL*Loader or by Oracle. Such records are filtered out because they did not match any of the record-selection criteria specified in the control file.
8. If necessary, edit advanced options by choosing Advanced. For further information, please refer to "Selecting Advanced Loader Options" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
9. When finished, choose Load.
10. After you choose Load, a status window appears and reports on the status of the load, including feedback on number of records processed, errors, and so on.
Selecting Advanced Loader Options
To select advanced loader options, perform the following steps:
1. From the Load page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet, choose Advanced.
The Advanced Load Options property sheet appears. Each field is filled either with default values, or with inherited values from the last time these options were edited and saved. After each load is run, these values revert back to default values.
The Advanced Load Options property sheet contains the following information:
| Records to Skip | Specifies the number of logical records from the beginning of the file that should not be loaded. Use this parameter to continue loads that have been interrupted. (Specifies the value for the SKIP parameter.) |
| Records to Load | Specifies the number of logical records to load (LOAD parameter) after skipping the number of records specified in Records to Skip. |
| Rows per Commit | This parameter (ROWS) indicates the number of rows in the bind array. |
| Maximum Errors | Specifies the number of insert errors (ERRORS parameter.) to allow before the Loader process terminates with an error. |
| Maximum Discards | Specifies the number of discards (DISCARDS parameter) to allow before the Loader process terminates with an error. |
| Maximum Bind Array | Specifies the maximum size of the bind array (BINDSIZE parameter) in Bytes. |
| Data Path | Conventional: Indicates that a conventional data path will be used to load your data into an Oracle7 database. |
| | Direct: Sets the DIRECT parameter to TRUE. |
| Defaults | Sets all options in this property sheet to their default values. |
2. When you have finished editing your advanced Load options, choose OK.
The Load page of the Oracle Data Manager property sheet appears.
Using the Command-line Option
In certain situations, you may want to use the command-line option to load data from an external file to an Oracle database.
To start the SQL*Loader process, type:
c:\> IMP72 [options]
Note: The Run on Host feature is not available as a command line option.
For more information about command-line options for the SQL*Loader utility, see Oracle7 Server Utilities.
Data Manager Tasks
When you click on the Run On Host button on one of the Data Manager property sheet pages, you create a job to perform one of the export, import, or load operations. You then use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Job system to execute those jobs. The following tasks are defined in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Job system and executed by Oracle Enterprise Manager intelligent agents residing on managed hosts. For information on using the job system, see Chapter 4, Job Scheduling, in this guide.
This job exports data from an Oracle database to a file.
The parameters match those of the Export page of the Data Manager property sheet, except for the following elements:
This job imports data from a file to an Oracle database.
The parameters match those of the Import page of the Data Manager property sheet, except for the following elements:
This job loads data from an external file to an Oracle database.
The parameters match those of the Load page of the Data Manager property sheet, except for the following elements:





<Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts GuideOracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide











![[*]](jump.gif) , and that you are familiar with the interface elements of the database tools. The topics included in this chapter are:
, and that you are familiar with the interface elements of the database tools. The topics included in this chapter are:![[*]](jump.gif) .
. Figure 14 - 1. First Page of the Data Manager Property Sheet
Figure 14 - 1. First Page of the Data Manager Property Sheet![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.



