|
The marketing race for "more megapixels" would like us to believe that "more is better". Unfortunately, it's not that simple. The number of pixels is only one of many factors affecting image quality and more pixels is not always better. The quality of a pixel value can be described in terms of geometrical accuracy, color accuracy, dynamic range, noise, and artifacts. The quality of a pixel value depends on the number of photodetectors that were used to determine it, the quality of the lens and sensor combination, the size of the photodiode(s), the quality of the camera components, the level of sophistication of the in-camera imaging processing software, the image file format used to store it, etc. Different sensor and camera designs make different compromises.
Geometrical or spatial accuracy is related to the number of pixel locations on the sensor and the ability of the lens to match the sensor resolution. The resolution topic explains how this is measured at this site. Interpolation will not improve geometrical accuracy as it cannot create what was not captured.
Conventional sensors using a color filter array have only one photodiode per pixel location and will display some color inaccuracies around the edges because the missing pixels in each color channel are estimated based on demosaicing algorithms. Increasing the number of pixel locations on the sensor will reduce the visibility of these artifacts. Foveon sensors have three photodetectors per pixel location and create therefore a higher color accuracy by eliminating the demosaicing artifacts. Unfortunately their sensitivities are currently lower than conventional sensors and the technology is only available in a few cameras.
The size of the pixel location and the fill factor determine the size of the photodiode and this has a big impact on the dynamic range. Higher quality sensors are more accurate and will be able to output a larger dynamic range which can be preserved when storing the pixel values into a RAW image file. A variant of the Fujifilm Super CCD, the Super CCD SR uses two photodiodes per pixel location with the objective to increase the dynamic range. A more sensitive photodiode measures the shadows, while a less sensitive photodiode measures the highlights.
The pixel value consists of two components:
(1) what you want to see (the actual measurement of the value in the scene)
(2) what you do not want to see (noise).
The higher (1), and the lower (2), the better the quality of the pixel. The quality of the sensor and the size of its pixel locations have a great impact on noise and how it changes with increasing sensitivity.
Besides noise, there are many other types of artifacts that determine pixel quality.

Unfortunately there is no single standard objective quality number to compare image quality across different types of sensors and cameras. For instance, a 3 megapixel Foveon type sensor uses 9 million photodetectors in 3 million pixel locations. The resulting quality is higher than a 3 megapixel but lower than a 9 megapixel conventional image and it also depends on the ISO level you compare it at. Likewise, a 6 megapixel Fujifilm Super CCD image is based on measurements in 3 million pixel locations. The quality is higher than a 3 megapixel image but lower than a 6 megapixel image. A 6 megapixel digital compact image will be of lower quality than a 6 megapixel digital SLR image with larger pixels. To determine an "equivalent" resolution is tricky at best.
End of the day, the most important thing is that you are happy with the quality level that comes out of your camera for the purpose that you need it for (e.g. website, viewing on computer, printing, enlargements, publishing, etc.). I strongly recommend that you look beyond megapixels when purchasing a digital camera.
© Vincent Bockaert
Below the list of CCD sensors used in modern digital cameras
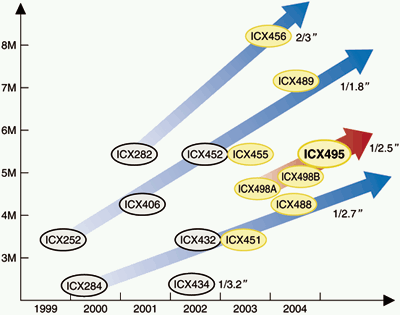
| Product name |
Pixels |
Type or
Size |
Effective pixels
(H x V) |
Frames
per sec. |
Pixel size |
Year |
| Sony |
|---|
| Exmor (CMOS) |
25.7M |
35 mm |
6,104 x 4,064 |
6.3 |
5.94 x 5.94 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| IMX021 (CMOS) |
13.1M |
1.8 |
4,320 x 2,888 |
10.39 |
5.49 x 5.49 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| IMX007AQ (CMOS) dsc |
12.4M |
1.8 |
4,288 x 2,848 |
5 |
5.49 x 5.49 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| ICX263 |
10.9M |
1.8 |
4,024 x 2,648 |
1.6 |
5.9 x 5.9 µm2 |
2003.4Q |
| ICX483 dsc |
10.9M |
1.8 |
3,900 x 2,616 |
5.57 |
6.05 x 6.05 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| ICX493 dsc |
10.8M |
1.8 |
3,900 x 2,616 |
3.3 |
6.05 x 6.05 µm2 |
2006.3Q |
| ICX413 dsc |
6.31M |
1.8 |
3,040 x 2,024 |
3.08 |
7.8 x 7.8 µm2 |
2002.1Q |
| IMX0??AQ (CMOS) dsc |
10.3M |
21.5 x 14.4 |
3,888 x 2,592 |
3 |
5.49 x 5.49 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| ICX456 dsc |
8.31M |
2/3 |
3,288 x 2,472 |
3.33 |
2.7 x 2.7 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| ICX282 dsc |
5.24M |
2/3 |
2,588 x 1,960 |
3.75 |
3.4 x 3.4 µm2 |
2000.3Q |
| ICX685 |
10.4M |
1/1.7 |
3,684 x 2,760 |
2.052 |
2.03 x 2.03 µm2 |
2009.3Q |
| ICX652 |
13.9M |
1/1.7 |
4,272 x 3,204 |
1.7 |
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2008.2Q |
| ICX612 |
12.4M |
1/1.7 |
4,032 x 3,024 |
2.336 |
1.85 x 1.85 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| ICX476 dsc |
8.30M |
1/1.8 |
3,288 x 2,472 |
3.33 |
2.22 x 2.22 µm2 |
2005.4Q |
| IMX017 (CMOS) |
6.60M |
1/1.8 |
2,928 x 2,184 |
60 |
2.5 x 2.5 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| ICX489 dsc |
7.41M |
1/1.8 |
3,112 x 2,328 |
3.33 |
2.35 x 2.35 µm2 |
2004.2Q |
| ICX452 dsc |
5.26M |
1/1.8 |
2,616 x 1,960 |
|
2.775 x 2.775 µm2 |
2002.3Q |
| ICX406 |
4.13M |
1/1.8 |
2,312 x 1,720 |
3.33 |
3.125 x 3.125 µm2 |
2001.2Q |
| ICX411 dsc |
4.13M |
1/1.8 |
2,312 x 1,720 |
4.28 |
3.125 x 3.125 µm2 |
2003.1Q |
| ICX252 |
3.34M |
1/1.8 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
4.28 |
3.45 x 3.45 µm2 |
1999.4Q |
| ICX262 dsc |
3.34M |
1/1.8 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
4.28 |
3.45 x 3.45 µm2 |
2000.4Q |
| ICX412 |
3.34M |
1/1.8 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
4.28 |
3.45 x 3.45 µm2 |
2003.2Q |
| ICX274 |
2.11M |
1/1.8 |
1,636 x 1,236 |
15 |
4.4 x 4.4 µm2 |
2002.1Q |
| ICX675 |
10.3M |
1/2.3 |
3,684 x 2,760 |
1.96 |
1.68 x 1.68 µm2 |
2008.2Q |
| ICX665 |
10.3M |
1/2.3 |
3,684 x 2,760 |
1.96 |
1.68 x 1.68 µm2 |
2008.2Q |
| IMX032 (CMOS) |
10.3M |
1/2.3 |
3,528 x 2,632 |
30 |
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2009.1Q |
| ICX224 |
2.11M |
1/2 |
1,636 x 1,236 |
7.5 |
3.9 x 3.9 µm2 |
1998.4Q |
| ICX284 |
2.11M |
1/2.7 |
1,636 x 1,236 |
7.5 |
3.275 x 3.275 µm2 |
1999.4Q |
| ICX205 |
1.51M |
1/2 |
1,392 x 1,040 |
7.5 |
4.65 x 4.65 µm2 |
1998.4Q |
| IMX060PQ (CMOS) |
12.2M |
1/2.5 |
4,040 x 3,032 |
10 |
1.4 x 1.4 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| ICX637 |
9.30M |
1/2.5 |
3,492 x 2,616 |
2.38 |
1.66 x 1.66 µm2 |
2008.2Q |
| IMX043 (CMOS) |
8.30M |
1/2.5 |
3,288 x 2,468 |
|
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| ICX646 |
8.29M |
1/2.5 |
3,298 x 2,472 |
2.5 |
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| ICX636 |
8.29M |
1/2.5 |
3,298 x 2,472 |
2.5 |
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| ICX629 |
7.41M |
1/2.5 |
3,112 x 2,328 |
3.33 |
1.86 x 1.86 µm2 |
2006.3Q |
| ICX624 dsc |
6.18M |
1/2.5 |
2,840 x 2,128 |
4.28 |
2.03 x 2.03 µm2 |
2005.4Q |
| ICX495 dsc |
5.26M |
1/2.5 |
2,616 x 1,960 |
4.28 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2004.4Q |
| ICX498 |
4.23M |
1/2.5 |
2,344 x 1,752 |
4.28 |
2.5 x 2.5 µm2 |
2004.2Q |
| ICX488 |
4.23M |
1/2.7 |
2,344 x 1,752 |
4.28 |
2.35 x 2.35 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| ICX432 |
3.34M |
1/2.7 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
|
2.575 x 2.575 µm2 |
2002.1Q |
| ICX454 |
2.11M |
1/2.7 |
1,648 x 1,240 |
8.563 |
3.275 x 3.275 µm2 |
2002.4Q |
| IMX020 (CMOS) |
5.31M |
1/2.7 |
2,616 x 1,968 |
15 |
2 x 2 µm2 |
2007.2Q |
| IMX011 (CMOS) |
2.13M |
1/3 |
1,656 x 1,249 |
15 |
2.925 x 2.925 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| IMX046PQ (CMOS) |
8.11M |
1/3.2 |
3,288 x 2,468 |
15 |
1.4 x 1.4 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| IMX034 (CMOS) |
5.33M |
1/3.2 |
2,616 x 1,968 |
|
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| ICX434 |
2.11M |
1/3.2 |
1,636 x 1,236 |
7.5 |
2.775 x 2.775 µm2 |
2002.1Q |
| IMX006 (CMOS) |
1.33M |
1/3.2 |
1,296 x 985 |
15 |
3.45 x 3.45 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| ICX232 |
1.31M |
1/3.6 |
1,290 x 966 |
7.5 |
3.125 x 3.125 µm2 |
1999.2Q |
| IMX045PQ (CMOS) |
5.15M |
1/4 |
2,616 x 1,968 |
15 |
1.4 x 1.4 µm2 |
2008.4Q |
| ICX098 |
0.33M |
1/4 |
659 x 494 |
30 |
5.6 x 5.6 µm2 |
1998.4Q |
| Sharp |
|---|
| RJ21Y3BA0ET |
12.5M |
1/1.7 |
4,032 x 3,024 |
|
1.88 x 1.88 µm2 |
2006.4Q |
| RJ21Y3DA0ET |
12.5M |
1/1.7 |
4,032 x 3,024 |
|
1.88 x 1.88 µm2 |
2006.4Q |
| RJ21W3BA0ET |
10.5M |
1/1.7 |
3,696 x 2,776 |
|
2.05 x 2.05 µm2 |
2005.4Q |
| RJ21V3BA0ET dsc |
8.50M |
1/1.8 |
3,320 x 2,496 |
5 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2005.1Q |
| RJ21T3AA0PT dsc |
6.36M |
1/1.8 |
2,872 x 2,160 |
2.7 |
2.5 x 2.5 µm2 |
2003.3Q |
| RJ21S3AA0PT |
5.19M |
1/1.8 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
2 |
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2003.1Q |
| RJ23V3BA0BT |
8.50M |
1/2.5 |
3,320 x 2,496 |
|
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| RJ23U3BA0ET |
7.40M |
1/2.5 |
3,096 x 2,328 |
|
1.9 x 1.9 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| RJ23T3BA0ET |
6.20M |
1/2.5 |
2,872 x 2,160 |
|
2.05 x 2.05 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| RJ23S3BA0ET |
5.05M |
1/2.5 |
2,600 x 1,944 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| RJ23R3BA0ET |
4.06M |
1/2.5 |
2,332 x 1,740 |
|
2.5 x 2.5 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| RJ24P3BA0ET |
3.27M |
1/3.2 |
2,096 x 1,560 |
3 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2004.2Q |
| Panasonic |
|---|
| MN39960 (CMOS) |
7.38M |
4/3 |
3,136 x 2,352 |
3 |
5.6 x 5.6 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| MN39750PM |
8.12M |
1/1.8 |
3,288 x 2,472 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| MN39593PT |
5.20M |
1/1.8 |
2,620 x 1,984 |
|
2.275 x 2.275 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| MN39591PT |
3.85M |
1/1.8 |
2,272 x 1,696 |
|
3.25 x 3.25 µm2 |
2001.3Q |
| MN39830PM |
6.37M |
1/2.5 |
2,864 x 2,160 |
|
2.025 x 2.025 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| MN39620PQ |
5.20M |
1/2.5 |
2,620 x 1,984 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2003.3Q |
| MN39720 |
5.20M |
1/2.5 |
2,620 x 1,984 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2003.3Q |
| MN39482PJ |
4.07M |
1/2.5 |
2,336 x 1,744 |
|
2.5 x 2.5 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| MN39592PJ |
3.24M |
1/2.5 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
|
2.75 x 2.75 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| MN39480PJ |
3.24M |
1/2.7 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
|
2.575 x 2.575 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| MN39922 |
3.24M |
1/3.2 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2004.4Q |
| MN39400 |
3.24M |
1/3.2 |
2,088 x 1,550 |
|
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2004.4Q |
| MN39472PJ |
2.04M |
1/3.2 |
1,648 x 1,236 |
|
2.75 x 2.75 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| MN39192FH |
1.24M |
1/4 |
1,290 x 966 |
|
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2001.3Q |
| Samsung (CMOS) |
|---|
| S5K2E1FX |
5.16M |
1/2.5 |
2,616 x 1,960 |
10 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K3C1FX |
3.20M |
1/3.2 |
2,056 x 1,544 |
15 |
2.25 x 2.25 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K3BAF |
2.00M |
1/3.2 |
1,600 x 1,200 |
|
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K3B2FA |
1.97M |
1/3.2 |
1,612 x 1,208 |
30 |
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K3AAE |
1.31M |
1/3.2 |
1,280 x 1,024 |
|
3.5 x 3.5 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K3C1FX |
3.15M |
1/3 |
2,048 x 1,536 |
|
2.25 x 2.25 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| S5K4AAF |
1.31M |
1/4 |
1,280 x 1,024 |
|
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| Micron Technology (CMOS) |
|---|
| MT9T001 |
3.15M |
1/2 |
2,048 x 1,536 |
12 |
3.2 x 3.2 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| MT9E001 |
7.99M |
1/2.5 |
3,264 x 2,448 |
|
1.75 x 1.75 µm2 |
2006.3Q |
| MT9P011 |
5.04M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
12 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| MT9P031 |
5.04M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
12 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| MT9P001 |
5.49M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
12 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| MT9T012 |
3.17M |
1/3.2 |
2,056 x 1,544 |
15 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| MT9D111 |
2.00M |
1/3.2 |
1,600 x 1,200 |
15 |
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2005.2Q |
| MT9M112 |
1.31M |
1/4 |
1,280 x 1,024 |
15 |
2.8 x 2.8 µm2 |
2005.4Q |
| MT9D112 |
1.92M |
1/4 |
1,600 x 1,200 |
15 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| Philips |
|---|
| FXA1012 |
2.09M |
2/3 |
1,616 x 1,296 |
5 |
5.1 x 5.1 µm2 |
1999.4Q |
| Canon (CMOS) |
|---|
| EOS 1Ds III (1060) |
21.0M |
35 mm |
5,616 x 3,744 |
5 |
6.4 x 6.4 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| EOS 1Ds II dsc |
16.6M |
35 mm |
4,992 x 3,328 |
4 |
7.2 x 7.2 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| EOS 5D (706P) dsc |
12.8M |
35 mm |
4,368 x 2,912 |
3 |
8.2 x 8.2 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| EOS 1Ds dsc |
11.0M |
35 mm |
4,064 x 2,704 |
3 |
8.8 x 8.8 µm2 |
2002.3Q |
| EOS 1D II dsc |
8.19M |
28.7 x 19.1 |
3,504 x 2,336 |
8.5 |
8.2 x 8.2 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| EOS 400D |
10.1M |
22.2 x 14.8 |
3,888 x 2,592 |
3 |
5.7 x 5.7 µm2 |
2006.4Q |
| EOS 10D (704F) dsc |
6.29M |
22.7 x 15.1 |
3,072 x 2,048 |
3 |
7.4 x 7.4 µm2 |
2003.1Q |
| EOS 20D (704W) dsc |
8.19M |
22.5 x 15 |
3,504 x 2,336 |
5 |
6.4 x 6.4 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| EOS 350D dsc |
8.00M |
22.2 x 14.8 |
3,456 x 2,304 |
3 |
6.4 x 6.4 µm2 |
2005.1Q |
| Kodak |
|---|
| KAI-16000 |
16.5M |
35 mm |
4,904 x 3,280 |
3 |
7.4 x 7.4 µm2 |
2006.4Q |
| KAI-11002 |
11.1M |
35 mm |
4,032 x 2,688 |
5 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2006.1Q |
| KAI-11000 |
11.1M |
35 mm |
4,032 x 2,688 |
5 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| KAF-10500 |
11.2M |
27 x 18 |
4,010 x 2,686 |
2.4 |
6.8 x 6.8 µm2 |
2006.3Q |
| KAF-6303 |
6.35M |
27 x 18 |
3,072 x 2,048 |
0.6 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| KAF-6302 |
6.25M |
27 x 18 |
3,072 x 2,034 |
0.6 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2002.3Q |
| KAF-10010 |
10.3M |
26.4 x 17.6 |
3,876 x 2,584 |
2.4 |
6.8 x 6.8 µm2 |
2003.2Q |
| KAI-10100 |
11.2M |
4/3 |
3,776 x 2,856 |
5 |
4.75 x 4.75 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| KAF-8300 dsc |
8.52M |
4/3 |
3,358 x 2,536 |
2.48 |
5.4 x 5.4 µm2 |
2004.3Q |
| KAF-5101 dsc |
5.32M |
4/3 |
2,654 x 2,006 |
3.1 |
6.8 x 6.8 µm2 |
2003.2Q |
| KAC-5000 (CMOS) |
5.04M |
1/1.8 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
6 |
2.7 x 2.7 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| KAC-05010 (CMOS) |
5.04M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
7 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| KAC-3100 (CMOS) |
3.15M |
1/2.7 |
2,048 x 1,536 |
12 |
2.7 x 2.7 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| Nikon (CMOS) |
|---|
| D3 |
12.1M |
35 mm |
4,256 x 2,832 |
9 |
8.45 x 8.45 µm2 |
2007.3Q |
| D2H dsc |
4.02M |
23.7 x 15.5 |
2,464 x 1,632 |
8 |
9.6 x 9.6 µm2 |
2003.2Q |
| Dalsa |
|---|
| FTF4027C |
10.7M |
35 mm |
4,008 x 2,672 |
7.5 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2004.2Q |
| FTF3020C |
6.29M |
35 mm |
3,072 x 2,048 |
20 |
12 x 12 µm2 |
2004.1Q |
| FTF2416C |
4.03M |
22.1 x 14.8 |
2,460 x 1,640 |
9 |
9 x 9 µm2 |
2003.1Q |
| ATMEL |
|---|
| AT71200M |
8.05M |
35 mm |
3,500 x 2,300 |
2.8 |
10 x 10 µm2 |
2003.2Q |
Foveon  (CMOS) (CMOS) |
|---|
| Fx17-78-F13 |
4.82M |
20.7 x 13.8 |
2,652 x 1,768 |
5 |
7.8 x 7.8 µm2 |
2006.3Q |
| F7X3-C9110 |
3.40M |
20.7 x 13.8 |
2,268 x 1,512 |
4.4 |
9.12 x 9.12 µm2 |
2002.1Q |
| FO18-50-F19 |
1.50M |
1/1.8 |
1,420 x 1,060 |
7 |
5 x 5 µm2 |
2003.1Q |
| Cypress (CMOS) |
|---|
| CYIHDSC9000AA |
9.03M |
1.8 |
3,710 x 2,434 |
5 |
6.4 x 6.4 µm2 |
2005.4Q |
Toshiba  (CMOS) (CMOS) |
|---|
| ET8E99-AS |
3.24M |
1/2.6 |
2,080 x 1,560 |
|
2.7 x 2.7 µm2 |
2005.3Q |
| OmniVision (CMOS) |
|---|
| OV5623 |
5.04M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
7.5 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| OV5620 |
5.04M |
1/2.5 |
2,592 x 1,944 |
7.5 |
2.2 x 2.2 µm2 |
2007.1Q |
| Type |
Aspect
ratio |
Sensor size (mm) |
| Diagonal |
Width |
Height |
| 1/4 |
4:3 |
4.450 |
3.560 |
2.670 |
| 1/3.6 |
4:3 |
5.000 |
4.000 |
3.000 |
| 1/3 |
4:3 |
5.500 |
4.400 |
3.300 |
| 1/3.2 |
4:3 |
5.700 |
4.560 |
3.420 |
| 1/2.7 |
4:3 |
6.750 |
5.400 |
4.050 |
| 1/2.6 |
4:3 |
7.000 |
5.600 |
4.200 |
| 1/2.5 |
4:3 |
7.170 |
5.740 |
4.300 |
| 1/2.3 |
4:3 |
7.750 |
6.200 |
4.650 |
| 1/2 |
4:3 |
8.000 |
6.400 |
4.800 |
| 1/1.8 |
4:3 |
9.000 |
7.200 |
5.400 |
| 1/1.7 |
4:3 |
9.500 |
7.600 |
5.700 |
| 2/3 |
4:3 |
11.000 |
8.800 |
6.600 |
| 4/3 |
4:3 |
22.500 |
18.000 |
13.500 |
| 1.8 |
3:2 |
28.400 |
23.630 |
15.750 |
| 35 mm |
3:2 |
43.267 |
36.000 |
24.000 |
|