










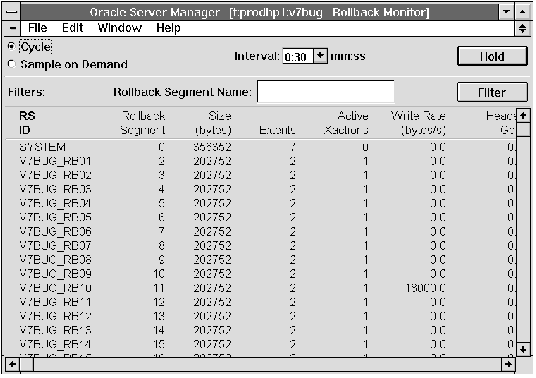
 Figure 11 - 9. Rollback Monitor
Figure 11 - 9. Rollback Monitor
The Rollback Monitor is described below:
| RS ID | Name of the rollback segment. |
| Rollback Segment | Rollback segment number. |
| Size (bytes) | Size of the rollback segment, in bytes. |
| Extents | Number of extents in the rollback segment. |
| Active Xactions | Number of active transactions using the rollback segment. |
| Write Rate (bytes/s) | Rate at which bytes were written to the rollback segment since the last sample. |
| Header Gets | Number of times the rollback segment's header was accessed since the last sample. |
| Header Waits | Number of times a process had to wait to access the rollback segment's header since the last sample. |
| Optimal Size | Optimal size of the rollback segment. |
| HWM Size | High water mark for the rollback segment (the largest size the rollback segment has grown to), in bytes. |
| Average Active | Current average size of active extents (extents that contain uncommitted transaction data), in bytes. |
| Average Shrink | Total size of freed extents divided by number of shrinks, in bytes. |
| Wraps | Number of times the rollback segment wraps from one extent to another. |
| Extends | Number of times the rollback segment was extended and allocated a new extent. |
| Shrinks | Number of times the rollback segment shrank, deallocating one or more extents. |
| Rollback Segment Name | Filter for the rollback segment name. Monitor displays information only for rollback segments whose names match the Rollback Segment Name filter. |
MONITOR ROLLBACK
If the value in the Extents column is high, you may want to create additional rollback segments or increase the size of current segments.
A high value in the Header Waits column indicates contention for the headers of rollback segments. In this case, you should consider adding more rollback segments.




