Oracle7 Server Distributed Systems Volume II: Replicated Data






Configurations
The symmetric replication facility supports both full-table replication and replication of subsets of tables. The following mechanisms are supported:
- single master with multiple read-only snapshot sites
- single master with multiple updatable snapshot sites
- hybrid configurations of the above
Read-Only Snapshot Sites
Multiple read-only snapshot sites can be used to provide local access to remote master tables. Having a local snapshot of the data improves query response time. Updates can only be issued against the remote master table.
A read-only snapshot is refreshed from its associated master table in a transactionally consistent manner at a time-based interval or on demand.
Read-only snapshots are easily maintained, and do not require the advanced replication option. Examples of read-only snapshot site uses are included ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Multi-Master Replication
As shown in Figure 1 - 3, multi-master replication supports full table, peer-to-peer replication between master tables. All master tables at all sites can be updated.
Changes applied to any master table are propagated and applied directly to all other master tables. These changes can be propagated either synchronously or asynchronously.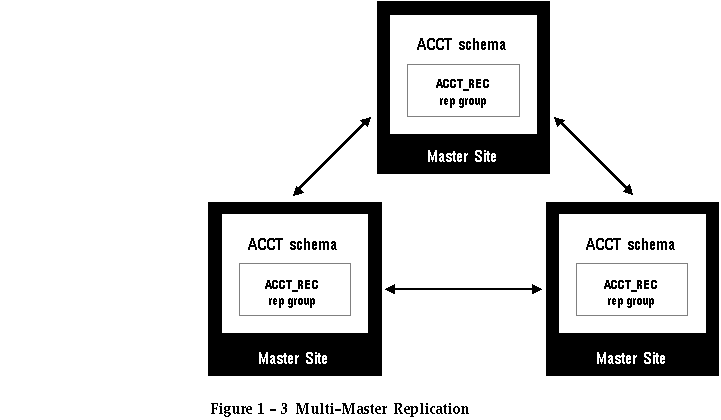
Updatable Snapshot Sites
A single master site can be used to consolidate information provided from multiple updatable snapshot sites. In the example shown in Figure 1 - 4, orders can be entered at each of your sales offices, but all orders are processed at the corporate headquarters site.
You can think of the ORDERS snapshot at each of the sales offices as a writeable subset of the ORDERS table at headquarters.
An updatable snapshot is refreshed from its associated master table in a transactionally consistent manner at a time-based interval or on demand. Changes from the updatable snapshot can be forwarded to its master table either synchronously or asynchronously.
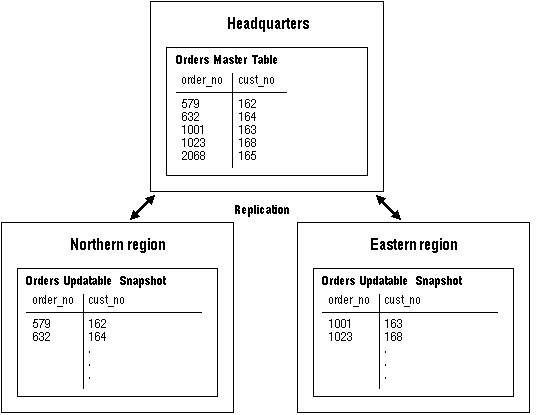 Figure 1 - 4. Using Updatable Snapshot Sites for Information Consolidation
Figure 1 - 4. Using Updatable Snapshot Sites for Information Consolidation
Hybrid Configurations
Multi-master table replication and updatable snapshots can be combined in hybrid (mixed) configurations to meet different needs. Specifically, snapshot masters can be n-way replicated (multi-mastered). N-way snapshot master replication means that
- there is any number of snapshot master sites
- full-table and table subset replication can be combined in one system
For example, as shown in Figure 1 - 5 n-way replication between two snapshot masters can support full-table replication between two master sites supporting two geographic regions. Snapshots can be defined on the snapshot masters to replicate full tables or table subsets to sites within each region. 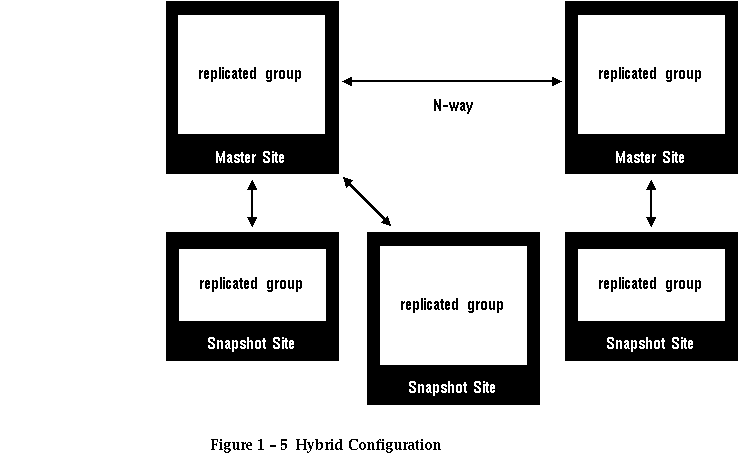
An added benefit of this n-way replication is that snapshots can be remastered from the other master sites to improve availability. If one master site fails, its snapshots can refresh themselves from the surviving master site and continue processing. This configuration, in which a master site resembles a "hub" with "spokes" to snapshot sites, also allows the two n-way connected master sites to function as fail-over sites for each other (see the "Survivability" section ![[*]](jump.gif) ).
).
Some of the key differences between updatable snapshots and replicated masters include the following:
- Replicated masters must contain data for the full table being replicated, whereas snapshots can replicate subsets of master table data.
- Multi-master replication allows you to replicate changes for each transaction as they occur, while snapshots are set-oriented, propagating changes from multiple transactions in a more efficient, batch-oriented operation, but at less frequent intervals.
- If any conflicts occur as the result of changes being made to multiple copies of the same data, these conflicts are detected and resolved by the master sites.
















![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
 Figure 1 - 4. Using Updatable Snapshot Sites for Information Consolidation
Figure 1 - 4. Using Updatable Snapshot Sites for Information Consolidation
![[*]](jump.gif) ).
).



