










This section is intended only to provide an overview of Network Manager's capabilities. See the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide for detailed information on how to configure a network using Oracle Network Manager.
Networking products require a number of configuration files. These configuration files, which have a very precise syntax, would be tedious to create manually. Network Manager provides a graphical user interface (GUI) through which administrators can create the configuration files quickly and accurately.
After creating a network definition using Network Manager, the configuration files are generated. Network Manager ensures that all resulting files are free from common syntax and semantic errors often made in manually created files. In fact, Oracle only supports files that are created with Network Manager (except for PROTOCOL.ORA and SQLNET.ORA files, which contain parameters that can be included only through manual editing).
Network Manager is similar to the utilities in Oracle's Cooperative Development Environment (CDE). If you are familiar with CDE, you will quickly be able to use Network Manager. Figure 3 - 1 shows Network Manager's interface running under Microsoft Windows.
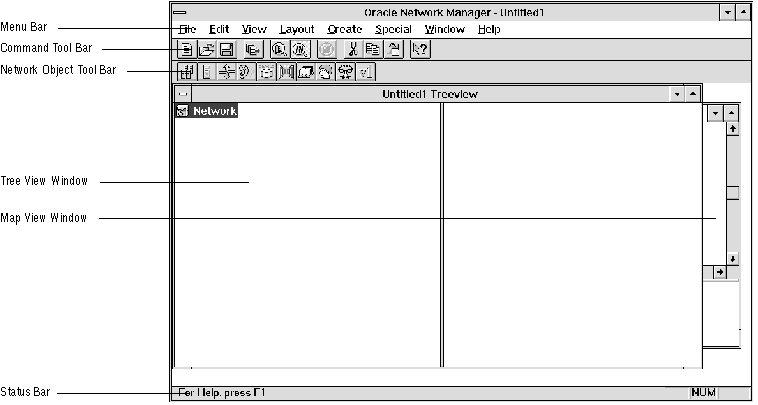
Figure 3 - 1. Network Manager Interface
Network components, such as clients, servers, communities, etc. are treated as objects that can be selected, dragged and dropped, linked, among other operations within the network map.
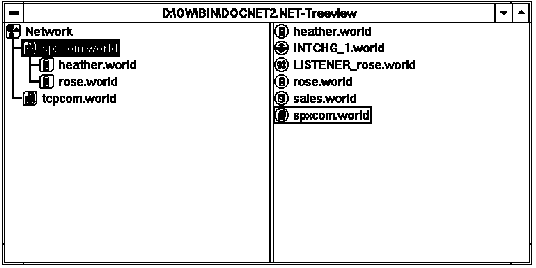
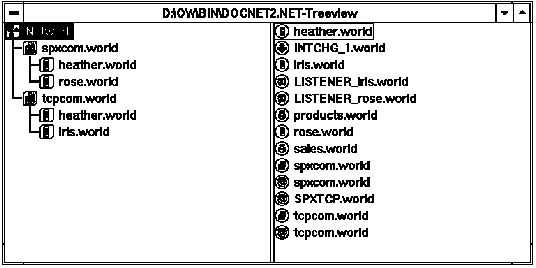
Figure 3 - 2. Two Tree Views of a Network
In Figure 3 - 2, the window on the left side of the screen displays domains or communities as well as their respective network components. The window on the right displays all network services belonging to the highlighted domain. This parent-child framework allows the administrator to clearly display network components and their relationships.
The administrator configures a network object either by selecting it from the toolbar and entering the appropriate information in its property sheet, or by dragging and dropping the selected toolbar object onto another predefined object. When a network object is dropped onto another one, Oracle Network Manager automatically updates it with the information from the object upon which is has been dropped.
For example, when a node is dropped onto a predefined community, the node is automatically linked to the community.
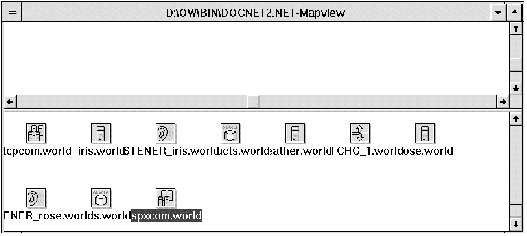
Figure 3 - 3. Map View Window
When you create a network object, an icon representing it appears in the bottom half of the Map View window. At any time you can select the icons in this window and move them to the upper part of the window.
Lines showing the objects' relationships will be displayed between them. Individual icons representing the network services will automatically connect to related nodes when placed on the map.
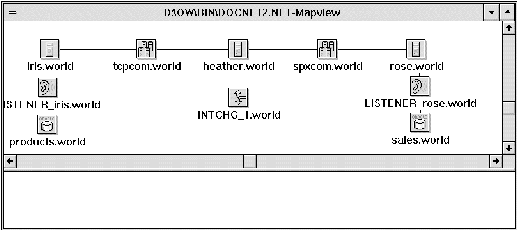
Figure 3 - 4. Map View with Network Objects Arranged
![[*]](jump.gif) for introductory information about Server Manager. For detailed information, see the Oracle Server Manager User's Guide and
related documentation.
for introductory information about Server Manager. For detailed information, see the Oracle Server Manager User's Guide and
related documentation.
Oracle Network Manager also makes moving from SQL*Net version 1 or SQL*Net version 2 easier. Network Manager can import a file of version 1 connect strings and aliases into a TNSNAMES.ORA file. They can then be recognized and used on operating systems (such as UNIX and VMS) that use TNSNAMES.ORA as their source of information about network destinations once SQL*Net version 2 is installed.
Network Manager provides an easy way to create a service name for a SQL*Net version 1 connect string that does not already have an alias mapped to it.




