Oracle7 Server Distributed Systems Volume II: Replicated Data






Determining Differences Between Replicated Tables
When administering a replicated environment, you may periodically want to check whether the contents of two replicated tables are identical. The following procedures in the DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF package let you identify, and optionally rectify, the differences between two tables when both sites are release 7.3 or higher:
| DIFFERENCES | The DIFFERENCES procedure compares two replicas of a table, and determines all rows in the first replica that are not in the second and all rows in the second that are not in the first. The output of this procedure is stored in two user-created tables. The first table stores the values of the missing rows, and the second table is used to indicate which site contains each row. |
| RECTIFY | The RECTIFY procedure uses the information generated by the DIFFERENCES procedure to rectify the two tables. Any rows found in the first table and not in the second are inserted into the second table. Any rows found in the second table and not in the first are deleted from the second table. |
To restore equivalency between all copies of a replicated table, you should complete the following steps:
1. Select one copy of the table to be the "reference" table. This copy will be used to update all other replicas of the table as needed.
2. Determine if it is necessary to check all rows and columns in the table for differences, or only a subset. For example, it may not be necessary to check rows that have not been updated since the last time that you checked for differences. Although it is not necessary to check all columns, your column list must include all columns that make up the primary key (or that you designated as a substitute primary key by calling DBMS_REPCAT.SET_COLUMNS) for the table.
3. After determining which columns you will be checking in the table, you need to create two tables to hold the results of the comparison.
You must create one table that can hold the data for the columns being compared. For example, if you decide to compare the EMPNO, SAL, and BONUS columns of the EMPLOYEE table, your CREATE statement would need to be similar to the one shown below.
CREATE TABLE missing_rows_data
(
empno NUMBER,
sal NUMBER,
bonus NUMBER
)
You must also create a table that indicates where the row is found. This table must contain three columns with the data types shown in the following example:
CREATE TABLE missing_rows_location
(
present VARCHAR2(128),
absent VARCHAR2(128),
r_id ROWID
)
4. Quiesce the object group containing the tables that you want to compare by calling DBMS_REPCAT.SUSPEND_MASTER_ACTIVITY. Although quiescing the replicated object group is not a requirement, rectifying tables that were not quiesced first can result in inconsistencies in your data.
5. At the site containing the "reference" table, call the DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.DIFFERENCES procedure. For example, if you wanted to compare the EMPLOYEE tables at the New York and San Francisco sites, your procedure call would look similar to the following:
DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.DIFFERENCES(
sname1 => 'hr',
oname1 => 'employee',
reference_site => 'ny.com',
sname2 => 'hr',
oname2 => 'employee',
comparison_site => 'sf.com',
where_clause => '',
column_list => 'empno,sal,bonus',
missing_rows_sname => 'scott',
missing_rows_oname1 => 'missing_rows_data',
missing_rows_oname2 => 'missing_rows_location',
missing_rows_site => 'ny.com',
max_missing => 100,
commit_rows => 50);
Figure 7 - 1 shows an example of two replicas of the EMPLOYEE table and what the resulting missing rows tables would look like if you executed the DIFFERENCES procedure on these replicas.
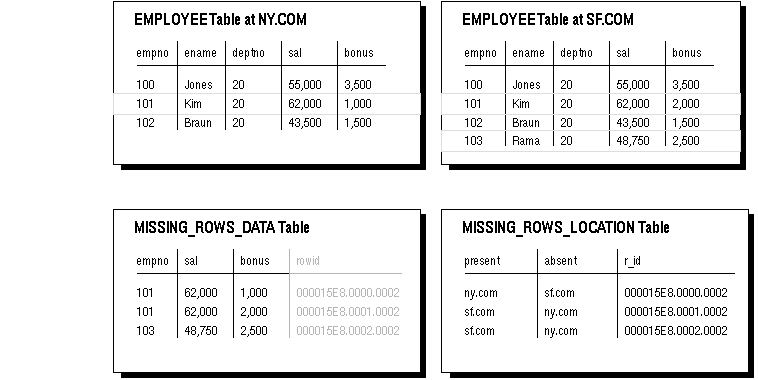 Figure 7 - 1. Determining Differences Between Replicas
Figure 7 - 1. Determining Differences Between Replicas
Notice that the two missing rows tables are related by the ROWID and r_id columns.
6. Now you can rectify the table at the "comparison" site to be equivalent to the table at the "reference" site by calling the DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.RECTIFY procedure as shown in the following example:
DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.RECTIFY(
sname1 => 'hr',
oname1 => 'employee',
reference_site => 'ny.com',
sname2 => 'hr',
oname2 => 'employee',
comparison_site => 'sf.com',
column_list => 'empno,sal,bonus',
missing_rows_sname => 'scott',
missing_rows_oname1 => 'missing_rows_data',
missing_rows_oname2 => 'missing_rows_location',
missing_rows_site => 'ny.com',
commit_rows => 50);
The RECTIFY procedure temporarily disables replication at the "comparison" site while it performs the necessary insertions and deletions, as you would not want to propagate these changes. RECTIFY first performs all of the necessary DELETEs and then performs all of the INSERTs. This ensures that there are no violations of a PRIMARY KEY constraint.
Attention: If you have any additional constraints on the "comparison" table you must ensure that they will not be violated when you call RECTIFY. You may need to update the table directly using the information from the missing rows table. If so, be certain to DELETE the appropriate rows from the missing rows tables.
7. After you have successfully executed the RECTIFY procedure, your missing rows tables should be empty. You can now repeat steps 5 and 6 for the remaining copies of the replicated table. Remember to use the same "reference" table each time to ensure that all copies are identical when you complete this procedure.
8. You may now resume replication activity by calling DBMS_REPCAT.RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY.
















 Figure 7 - 1. Determining Differences Between Replicas
Figure 7 - 1. Determining Differences Between Replicas



