










Oracle also encrypts passwords during transmission to ensure the security of client/server authentication.
Because database administrators perform special database operations, Oracle requires special authentication procedures for database administrators.
SQLPLUS /
Additional Information: For more information about authenticating via your operating system, see your Oracle operating system-specific documentation.
If you use a network authentication service, there are some special considerations for network roles and database links. See Oracle7 Server Distributed Systems, Volume I for more information about network authentication.
When Oracle uses database authentication, you create each user with an associated password. A user provides the correct password when establishing a connection to prevent unauthorized use of the database. Oracle stores a user's password in the data dictionary. However, all passwords are stored in an encrypted format to maintain security for the user. A user can change his/her password at any time.
For more information about encrypting passwords in client/server systems, see Oracle7 Server Distributed Systems, Volume I.
Depending on whether you wish to administer your database locally on the same machine on which the database resides or if you wish to administer many different database machines from a single remote client, you can choose between operating system authentication or password files to authenticate database administrators. Figure 17 - 1 illustrates the choices you have for database administrator authentication schemes.
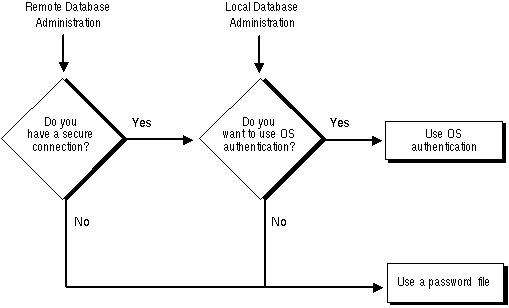
Figure 17 - 1. Database Administrator Authentication Methods
On most operating systems, OS authentication for database administrators involves placing the OS username of the database administrator in a special group (on UNIX systems, this is the dba group) or giving that OS username a special process right.
Additional Information: For information about OS authentication of database administrators, see your Oracle operating system-specific documentation.
Password files are files used by the database to keep track of database usernames who have been granted the SYSDBA and SYSOPER privileges. These privileges allow database administrators to perform the following actions:
SYSOPER Permits you to perform STARTUP, SHUTDOWN, ALTER DATABASE OPEN/MOUNT, ALTER DATABASE BACKUP, ARCHIVE LOG, and RECOVER, and includes the RESTRICTED SESSION privilege.
SYSDBA Contains all system privileges with ADMIN OPTION, and the SYSOPER system privilege; permits CREATE DATABASE and time-based recovery.
For information about password files, see the Oracle7 Server Administrator's Guide.




