










The multi-threaded server configuration eliminates the need for a dedicated server process for each connection (see Figure 4 - 2). A small number of shared server processes can perform the same amount of processing as many dedicated server processes. Also, the amount of memory required for each user is relatively small. Because less memory and process management are required, more users can be supported.
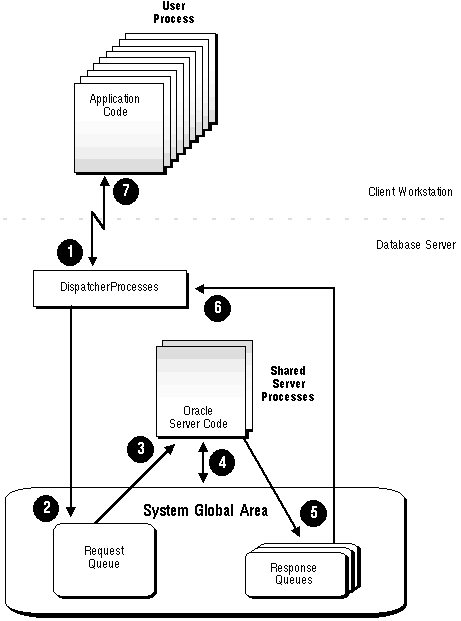
Figure 4 - 2. Oracle Multi-Threaded Sever Processes
To set up your system in a multi-threaded server configuration, start a network listener process and set the following initialization parameters:
After setting these initialization parameters, restart the instance, which at this point will use the multi-threaded server configuration. The multi-threaded server architecture requires SQL*Net Version 2. User processes targeting the multi-threaded server must connect through SQL*Net, even if they are on the same machine as the Oracle7 instance.
See Also: For more information about starting and managing the network listener process, see Oracle7 Server Distributed Systems, Volume I and the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide.
See Also: For more information about this parameter, see the Oracle7 Server Reference.
For more information about tuning, see the Oracle7 Server Tuning manual.
MTS_LISTENER_ADDRESS = "(addr)"
In the syntax above, addr is an address at which the listener will listen for connection requests for a specific protocol. The parameter file may contain multiple addresses.
The following examples specify listener addresses:
MTS_LISTENER_ADDRESS = "(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(PORT=5000)\ (HOST=ZEUS)"
MTS_LISTENER_ADDRESS = "(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=decnet)\ (OBJECT=OUTA)(NODE=ZEUS)"
See Also: For more information about specifying addresses for the network listener process, see your operating system-specific Oracle documentation and your SQL*Net documentation.
If you do not set the MTS_SERVICE parameter, its value defaults to the DB_NAME parameter. (If DB_NAME is also not set, Oracle7 returns the error ORA-00114, "missing value for system parameter mts_service," when you start the database.)
If the dispatcher's service name is TEST_DB, the parameter would be set as follows:
MTS_SERVICE = "test_db"
A connect string for connecting to this dispatcher looks like the following:
SQLPLUS scott/tiger@\ (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=decnet)(NODE=hq)\ (OBJECT=mts7))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=test_db)))
See Also: For more information about connect strings used with the multi-threaded server configuration, see your operating system-specific Oracle or SQL*Net documentation.
When setting the MTS_DISPATCHERS parameter, you can include any valid protocol.
The appropriate number of dispatcher processes for each instance depends upon the performance you want from your database, the host operating system's limit on the number of connections per process, (which is operating system-dependent) and the number of connections required per network protocol.
The instance must be able to provide as many connections as there are concurrent users on the database system; the more dispatchers you have, the better potential database performance users will see, since they will not have to wait as long for dispatcher service.
After instance startup, you can start more dispatcher processes if needed; however, you can only start dispatchers that use protocols mentioned in the database's parameter file. For example, if the parameter file starts dispatchers for protocol_A and protocol_B, you cannot later start dispatchers for protocol_C without changing the parameter file and restarting the instance.
See Also: For more information about dispatcher processes, see "Adding and Removing Dispatcher Processes" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
number maximum number of concurrent sessions
of = CEIL (--------------------------------------------------------------------------)
dispatchers connections per dispatcher
For example, assume that your system typically has 80 users concurrently connected via TCP/IP and 40 users connected via DECNet. In this case, the MTS_DISPATCHERS parameter should be set as follows:
MTS_DISPATCHERS = "TCP, 3"
MTS_DISPATCHERS = "DECNET, 3"
You can create as many dispatcher processes as you need, but the total number of processes, including dispatchers, cannot exceed the host operating system's limit on the number of running processes.
maximum number of concurrent sessions
MTS_MAX_DISPATCHERS = _____________________________________
connections per dispatcher
If you want Oracle7 to use shared servers, you must set MTS_SERVERS to at least 1. If you omit the parameter or set it to 0, Oracle7 does not start any shared servers at all. However, you can subsequently set MTS_SERVERS to a number greater than 0 while the instance is running.
It is best to estimate fewer initial shared server processes. Additional shared servers start automatically when needed and are deallocated automatically if they remain idle for too long. However, the initial servers always remain allocated, even if they are idle. If you set the initial number of servers high, your system might incur unnecessary overhead. Experiment with the number of initial shared server processes and monitor shared servers until you find the ideal system performance for typical database activity.
See Also: For more information about changing the number of shared servers, see "Changing the Minimum Number of Shared Server Processes" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.




