Oracle7 Server Administrator's Guide






Database Administrator Authentication
Database administrators must often perform special operations such as shutting down or starting up a database. Because these operations should not be performed by normal database users, the database administrator usernames need a more secure authentication scheme.
This section includes the following topics:
Selecting an Authentication Method
The following methods for authenticating database administrators replace the CONNECT INTERNAL syntax provided with earlier versions of the Oracle7 Server (CONNECT INTERNAL continues to be supported for backwards compatibility only):
- operating system authentication
Depending on whether you wish to administer your database locally on the same machine that the database resides or if you wish to administer many different databases from a single remote client, you can choose between operating system authentication or password files to authenticate database administrators. Figure 1 - 1 illustrates the choices you have for database administrator authentication schemes.
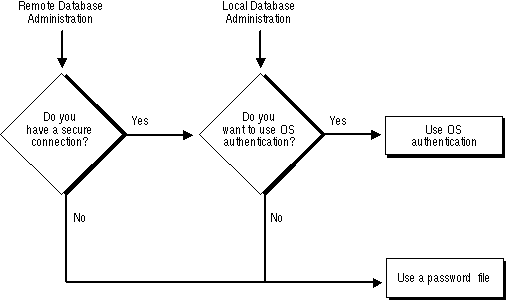
Figure 1 - 1. Database Administrator Authentication Methods
On most operating systems, OS authentication for database administrators involves placing the OS username of the database administrator in a special group (on UNIX systems, this is the DBA group) or giving that OS username a special process right.
The database uses password files to keep track of database usernames that have been granted administrator privileges.
See Also: "User Authentication" in Oracle7 Server Concepts.
Using Operating System Authentication
If you choose, you can have your operating system authenticate users performing database administration operations.
To Use Operating System Authentication
1. Set up the user to be authenticated by the operating system.
2. Make sure that the initialization parameter, REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORD, is set to NONE, which is the default value for this parameter.
3. Authenticated users should now be able to connect to a local database, or to connect to a remote database over a secure connection, by typing one of the following commands:
CONNECT / AS SYSOPER
CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
If you successfully connect as INTERNAL using an earlier release of Oracle7, you should be able to continue to connect successfully using the new syntax shown in step 3.
Note: Note that to connect as SYSOPER or SYSDBA using OS authentication you do not have to have been granted the SYSOPER or SYSDBA system privileges. Instead, the server verifies that you have been granted the appropriate OSDBA or OSOPER roles at the operating system level.
See Also: "Operating System Authentication" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
OSOPER and OSDBA
Two special operating system roles control database administrator logins when using operating system authentication: OSOPER and OSDBA.
OSOPER and OSDBA can have different names and functionality, depending on your operating system.
The OSOPER and OSDBA roles can only be granted to a user through the operating system. They cannot be granted through a GRANT statement, nor can they be revoked or dropped. When a user logs on with administrator privileges and REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE is set to NONE, Oracle7 communicates with the operating system and attempts to enable first OSDBA and then, if unsuccessful, OSOPER. If both attempts fail, the connection fails. How you grant these privileges through the operating system is operating system-specific.
If you are performing remote database administration, you should consult your SQL*Net documentation to determine if you are using a secure connection. Most popular connection protocols, such as TCP/IP and DECnet, are not secure, regardless of which version of SQL*Net you are using.
See Also: For information about OS authentication of database administrators, see your operating system-specific Oracle documentation.
Using an Authentication Password File
If you have determined that you need to use a password file to authenticate users performing database administration, you must complete the steps outlined below. Each of these steps is explained in more detail in the following sections of this chapter.
To Use a Password File to Authenticate Users
1. Create the password file using the ORAPWD utility.
ORAPWD FILE=filename PASSWORD=password ENTRIES=max_users
2. Set the REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE initialization parameter to EXCLUSIVE.
3. Add users to the password file by using SQL to grant the appropriate privileges to each user who needs to perform database administration, as shown in the following examples.
GRANT SYSDBA TO scott
GRANT SYSOPER TO scott
The privilege SYSDBA permits the user to perform the same operations as OSDBA. Likewise, the privilege SYSOPER permits the user to perform the same operations as OSOPER.
4. Privileged users should now be able to connect to the database by using a command similar to the one shown below.
CONNECT scott/tiger@acct.hq.com AS SYSDBA
See Also: "OSOPER and OSDBA" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.
Some platforms provided support for password files before release 7.1. If you are currently using such a password file, you should consult your operating system-specific Oracle documentation for additional information on migrating to the new password file utility.

















![[*]](jump.gif) .
.![[*]](jump.gif) .
.



