| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
CHAPTER 6
Oracle DBA Performance And Tuning
Aside from the basic features for applications programmers, the Oracle database administrator can benefit immensely benefit from an understanding of the Oracle performance features. These features can be especially useful for routine database administration tasks, such as exports/imports, index creation, and table replication. Topics will include:
- • Unrecoverable option
- • Read-only tablespaces
- • Implementing parallelism
- • init.ora parameters
- • Read-only tablespaces
Using The Unrecoverable Option
At specific times, Oracle allows its internal transaction logging mechanism to be turned off. With Oracle, the software maintains a read-consistent image of the data for long-running queries, while at the same time providing rollback capability for each update transaction. Of course, this level of recoverability carries a price tag, and significant performance improvements can be achieved with the prudent use of the “unrecoverable” option. In practice, use of the unrecoverable clause will improve response time from 40 to 60 percent. Care needs to be taken, of course, to synchronize the use of the unrecoverable clause with the traditional procedures used when taking backups of the archived redo logs.
Unrecoverable can be used for any of the following operations:
- • Create table . . . as select . . . unrecoverable—This type of operation is generally performed when a table is “cloned” or replicated from a master table, usually with a subset of columns and rows. For example, we would use this command to create a subset of a customer table, containing only those customers in a specific region. Of course, a failure during the creation of the table would leave a half-built table in the destination tablespace, and the table would need to be manually dropped.
- • Create index . . . unrecoverable—This is the most common use of the unrecoverable clause, and certainly the one that makes the most sense from an Oracle perspective. Regardless of any transaction failures, an index can always be re-created by dropping and redefining the index, so having an incomplete or corrupt index would never be a problem.
- • Alter table . . . add constraint . . . unrecoverable—As we know, when a referential integrity constraint is added to a table, the Oracle software will sometimes create an index to enforce the constraint. Primary key, foreign key, and unique constraints may cause Oracle to create an index, that is built in unrecoverable mode.
- • SQL*Loader—SQL*Loader is generally used when initially populating Oracle tables from external flat files. For very large numbers of inserts, it is best to leave the default. We already know that in the unlikely event of an abnormal termination, the incomplete tables must be dropped and SQL*Loader run again.
- • Create index . . . unrecoverable—This is the most common use of the unrecoverable clause, and certainly the one that makes the most sense from an Oracle perspective. Regardless of any transaction failures, an index can always be re-created by dropping and redefining the index, so having an incomplete or corrupt index would never be a problem.
Using Read-Only Tablespaces
In a busy environment where many different applications require access to a tablespace, it is sometimes desirable to use the read-only tablespace feature of Oracle 7.3. With read-only tablespaces, separate instances can be mapped to the same tablespaces, each accessing the tablespace in read-only mode. Of course, sharing a tablespace across Oracle instances increases the risk that I/O against the shared tablespaces may become excessive. As we can see in Figure 6.1, a read-only tablespace does not have the same overhead as an updatable tablespace.
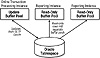
Figure 6.1 Oracle read-only tablespaces.
This approach has several advantages:
- • Buffer pool isolation—The foremost advantage is the isolation of the buffer pools for each instance that is accessing the tablespace. If user A on instance A flushes his buffer by doing a full-table scan, user B on instance B will still have the blocks needed in memory.
- • Easy sharing of table data—Read-only tablespaces offer an alternative to table replication and the update problems associated with replicated tables. Since a read-only tablespace may only be defined as updatable by one instance, updates are controlled at the system level.
Determining Where To Place Indexes
One of the primary responsibilities of the Oracle DBA is ensuring that Oracle indexes are present when they are needed to avoid full-table scans. In order to achieve this goal, the Oracle DBA needs to understand the types of indexes that Oracle provides as well as the proper time to create a table index.
Unfortunately, the Oracle dictionary does not gather statistics about how many times an index is used, so the DBA must rely upon the application developers to provide guidance regarding index placement. As Oracle moves toward Oracle8, this reliance may change, since most of the SQL will be stored within the Oracle dictionary, where the DBA can analyze the explain plan output. However, until that time, the best that an Oracle DBA can hope for is to keep the existing indexes clean and functioning optimally.
Listing 6.1 is a script that can be run to view SQL that has been loaded into the SGA shared pool.
Listing 6.1 The sqltext.sql shows all SQL in the SGA shared pool.
REM Written by Don Burleson
SET PAGESIZE 9999;
SET LINESIZE 79;
SET NEWPAGE 0;
SET VERIFY OFF;
BREAK ON ADDRESS SKIP 2;
COLUMN ADDRESS FORMAT 9;
SELECT
ADDRESS,
sql_text
FROM
v$sqltext
ORDER BY
ADDRESS, PIECE;
Listing 6.2 shows the output from sqltext.sql.
Listing 6.2 The output for sqltext.sql.
D09AFC4C SELECT DECODE(object_type, 'TABLE', 2, 'VIEW', 2, 'PACKAGE',
3, 'PACKAGE BODY', 3, 'PROCEDURE', 4, 'FUNCTION', 5, 0) from
all_objects where object_name = upper('V_$SQLTEXT') and
object_type in ('TABLE', 'VIEW', 'PACKAGE', 'PACKAGE BODY',
'PROCEDURE', 'FUNCTION') AND owner = upper('SYS')
D09B653C SELECT OWNER, table_name, table_owner, db_link FROM
all_synonyms where synonym_name = upper('V_$SQLTEXT') AND
owner = upper('SYS')
D09BC5AC SELECT OWNER, table_name, table_owner, db_link from
all_synonyms where synonym_name = upper('v$sqltext') AND
(owner = 'PUBLIC' or owner = USER)
D09C2D58 SELECT DECODE(object_type, 'TABLE', 2, 'VIEW', 2, 'PACKAGE',
3,'PACKAGE BODY', 3, 'PROCEDURE', 4, 'FUNCTION', 5, 0)
from user_objects where object_name = upper('v$sqltext')
AND object_type in ('TABLE', 'VIEW', 'PACKAGE', 'PACKAGE
BODY', 'PROCEDURE', 'FUNCTION')
D09CFF4C UPDATE SHPMT SET
amt_sum_ili=:b1,pmt_wght_sum_ili=:b2,cust_pmt_wght_sum_ili=
:b3 WHERE shpmt_id = :b4 AND shpmt_sys_src_cd = :b5
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |