|
|
|
The September 1993 Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements provided for a transitional period of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. Under a series of agreements signed between May 1994 and September 1999, Israel transferred to the Palestinian Authority (PA) security and civilian responsibility for many Palestinian-populated areas of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Negotiations to determine the permanent status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip stalled following the outbreak of the second intifada in September 2000. In April 2003, the Quartet (US, EU, UN, and Russia) presented a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005 based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. Following Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT's death in late 2004, Mahmud ABBAS was elected PA president in January 2005. A month later, Israel and the PA agreed to the Sharm el-Sheikh Commitments in an effort to move the peace process forward. In September 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew all of its settlers and soldiers and dismantled its military facilities in the Gaza Strip and withdrew settlers and redeployed soldiers from four small northern West Bank settlements. Nonetheless, Israel still controls maritime, airspace, and other access to the Gaza Strip. In January 2006, the Islamic Resistance Movement, HAMAS, won control of the Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC). HAMAS took control of the PA government in March 2006, but President ABBAS had little success negotiating with HAMAS to present a political platform acceptable to the international community, leading to the imposition of economic sanctions on the Palestinian government for its refusal to renounce violence, recognize Israel, and adhere to previous agreements. Violent clashes between Fatah and HAMAS supporters in the Gaza Strip in 2006 and early 2007 resulted in numerous Palestinian deaths and injuries. In February 2007, ABBAS and HAMAS Political Bureau chief Khalid MISHAL signed the Mecca Agreement in Saudi Arabia that resulted in the formation of a Palestinian National Unity Government (NUG) headed by HAMAS member Ismail HANIYA. However, fighting continued in the Gaza Strip, and in June 2007, HAMAS militants succeeded in a violent takeover of all military and governmental institutions in the Gaza Strip. ABBAS that same month dismissed the NUG and through a series of presidential decrees formed a PA government in the West Bank led by independent Salam FAYYAD. Fatah and HAMAS in May 2011, under the auspices of Egyptian-sponsored reconciliation negotiations, agreed to reunify the Palestinian territories, but the factions have struggled to implement details on governing and security structures despite subsequent agreements in February and May 2012. The status quo remains with HAMAS in control of the Gaza Strip and ABBAS and the Fatah-dominated PA governing the West Bank. FAYYAD and his PA government continue to implement a series of security and economic reforms to improve conditions in the West Bank. The Palestinians in November 2012 achieved observer state status at the UN, a step which gives the Palestinians higher speaking priority than their previous status as an observer entity, increased representation in the UN programs and funds, and the ability to accede to international treaties and conventions. ABBAS, since the collapse of direct talks between the Israelis and Palestinians in September 2010 has reaffirmed that he will not resume negotiations until Israel halts all settlement activity in the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
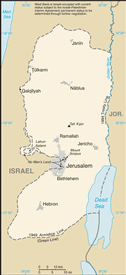
Middle East, west of Jordan, east of Israel
|
|
|
|
|
32 00 N, 35 15 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,860 sq km
country comparison to the world: 172
land:
5,640 sq km
water:
220 sq km
note:
includes West Bank, Latrun Salient, and the northwest quarter of the Dead Sea, but excludes Mt. Scopus; East Jerusalem and Jerusalem No Man's Land are also included only as a means of depicting the entire area occupied by Israel in 1967
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Delaware
|
|
|
|
|
total: 404 km
border countries:
Israel 307 km, Jordan 97 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; temperature and precipitation vary with altitude, warm to hot summers, cool to mild winters
|
|
|
|
|
mostly rugged dissected upland, some vegetation in west, but barren in east
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Dead Sea -408 m
highest point:
Tall Asur 1,022 m
|
|
|
|
|
arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 16.9%
permanent crops:
18.97%
other:
64.13% (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
180 sq km; note - includes Gaza Strip (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
droughts
|
|
|
|
|
adequacy of freshwater supply; sewage treatment
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; highlands are main recharge area for Israel's coastal aquifers; there are about 355 Israeli civilian sites including about 145 small outpost communities in the West Bank and 32 sites in East Jerusalem (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::West Bank |
|
|
|
noun: NA
adjective:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
Palestinian Arab and other 83%, Jewish 17%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic, Hebrew (spoken by Israeli settlers and many Palestinians), English (widely understood)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 75% (predominantly Sunni), Jewish 17%, Christian and other 8%
|
|
|
|
|
2,622,544 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
note:
approximately 325,500 Israeli settlers live in the West Bank (2011); approximately 186,929 Israeli settlers live in East Jerusalem (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 35.1% (male 472,011/ female 447,765)
15-64 years:
61.2% (male 822,690/ female 782,157)
65 years and over:
3.7% (male 40,765/ female 57,156) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.7 years
male:
21.5 years
female:
21.9 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.063% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
24.19 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
3.56 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 72% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
3.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.71 male(s)/female
total population:
1.04 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
64 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14.47 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 119
male:
16.22 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
12.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 75.24 years
country comparison to the world: 90
male:
73.17 years
female:
77.42 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.98 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
92.4%
male:
96.7%
female:
88% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 46.9%
country comparison to the world: 5
male:
38.8%
female:
47.3% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The West Bank - the larger of the two areas comprising the Palestinian territories - has sustained a moderate rate of economic growth since 2008. Inflows of donor aid and government spending have driven most of the gains, however, rather than private sector development. After a multiyear downturn following the start of the second intifada in 2000, overall standard-of-living measures have recovered and now exceed levels seen in the late 1990s. Despite the Palestinian Authority's (PA) largely successful implementation of economic and security reforms and the easing of some movement and access restrictions by the Israeli Government in 2010, Israeli closure policies continue to disrupt labor and trade flows, industrial capacity, and basic commerce, eroding the productive capacity of the West Bank economy. The biggest impediments to economic improvements in the West Bank remain Palestinians' inability to access land and resources in Israeli-controlled areas, import and export restrictions, and a high-cost capital structure. The PA for the foreseeable future will continue to rely heavily on donor aid for its budgetary needs, and West Bank economic activity will depend largely on the PA's ability to attract such aid.
|
|
|
|
|
$8.02 billion (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$7.59 billion (2010)
note:
includes Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
$6.641 billion
note:
includes Gaza Strip (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.7% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
6.8% (2010 est.)
7% (2009 est.)
note:
includes Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
$2,900 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
note:
includes Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 6.2%
industry:
12.5%
services:
81.3% (2012 est.)
note:
includes Gaza Strip (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
745,600 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 16.1%
industry:
28.4%
services:
55.5%
note:
includes Gaza Strip (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
23% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
23.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
18.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.2%
highest 10%:
28.2%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $2.15 billion
expenditures:
$3.23 billion
note:
includes Palestinian Authority expenditures in the Gaza Strip (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
31.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
-16.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
2.9% (2011 est.)
note:
includes Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
6.8% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
6.79% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$132.8 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
$100.4 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.674 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
$6.674 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$914.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
$851.1 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.532 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 94
$2.45 billion (31 December 2010)
$2.375 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
olives, citrus fruit, vegetables; beef, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
-$690.7 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
$-690.7 million (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$666.1 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
$518 million (2009)
note:
includes Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
stone, olives, fruit, vegetables, limestone
|
|
|
|
|
$4.319 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
$3.601 billion (2009)
note:
data include the Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
food, consumer goods, construction materials, petroleum, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
$1.04 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$1.3 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data include the Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
new Israeli shekels (ILS) per US dollar -
3.903 (2012 est.)
3.578 (2011 est.)
3.73 (2010)
3.932 (2009)
3.588 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
470 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
4.42 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2011)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
550 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
140,000 kW
country comparison to the world: 161
note:
includes Gaza Strip (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
|
|
|
|
|
29,310 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
1.92 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
15,420 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
3.382 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::West Bank |
|
|
|
337,000 (includes Gaza Strip) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
2.405 million (includes Gaza Strip) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: continuing political and economic instability has impeded significant liberalization of the telecommunications industry
domestic:
Israeli company BEZEK and the Palestinian company PALTEL are responsible for fixed line services; PALTEL plans to establish a fiber-optic connection to Jordan to route domestic mobile calls; the Palestinian JAWWAL company and WATANIYA PALESTINE provide cellular services
international:
country code - 970; 1 international switch in Ramallah (2009) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
the Palestinian Authority operates 1 TV and 1 radio station; about 30 independent TV and 25 radio stations; both Jordanian TV and satellite TV is accessible (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.ps; note - same as Gaza Strip
|
|
|
|
|
1.379 million (includes Gaza Strip) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::West Bank |
|
|
|
2 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 207
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
under 914 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,147 km
country comparison to the world: 153
paved:
5,147 km
note:
includes Gaza Strip (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 579,248
females age 16-49:
547,782 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 30,925
female:
29,440 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::West Bank |
|
|
|
The current status of the West Bank is subject to the Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement - permanent status to be determined through further negotiation; Israel continues construction of a "seam line" separation barrier along parts of the Green Line and within the West Bank; Israel withdrew from four settlements in the northern West Bank in August 2005; since 1948, about 350 peacekeepers from the UN Truce Supervision Organization (UNTSO), headquartered in Jerusalem, monitor ceasefires, supervise armistice agreements, prevent isolated incidents from escalating, and assist other UN personnel in the region
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 727,471 (Palestinian refugees (UNRWA)) (2012)
IDPs:
160,000 (persons displaced within the Palestinian Territories since 1967; largely from Israeli military operations in 2008-9) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
|