|
|
|
Explored and settled by the Spanish in the 16th century, Panama broke with Spain in 1821 and joined a union of Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela - named the Republic of Gran Colombia. When the latter dissolved in 1830, Panama remained part of Colombia. With US backing, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903 and promptly signed a treaty with the US allowing for the construction of a canal and US sovereignty over a strip of land on either side of the structure (the Panama Canal Zone). The Panama Canal was built by the US Army Corps of Engineers between 1904 and 1914. In 1977, an agreement was signed for the complete transfer of the Canal from the US to Panama by the end of the century. Certain portions of the Zone and increasing responsibility over the Canal were turned over in the subsequent decades. With US help, dictator Manuel NORIEGA was deposed in 1989. The entire Panama Canal, the area supporting the Canal, and remaining US military bases were transferred to Panama by the end of 1999. In October 2006, Panamanians approved an ambitious plan (estimated to cost $5.3 billion) to expand the Canal. The project, which began in 2007 and could double the Canal's capacity, is expected to be completed in 2014-15.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica
|
|
|
|
|
9 00 N, 80 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 75,420 sq km
country comparison to the world: 118
land:
74,340 sq km
water:
1,080 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than South Carolina
|
|
|
|
|
total: 555 km
border countries:
Colombia 225 km, Costa Rica 330 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,490 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm or edge of continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
tropical maritime; hot, humid, cloudy; prolonged rainy season (May to January), short dry season (January to May)
|
|
|
|
|
interior mostly steep, rugged mountains and dissected, upland plains; coastal areas largely plains and rolling hills
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Volcan Baru 3,475 m
|
|
|
|
|
copper, mahogany forests, shrimp, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 7.26%
permanent crops:
1.95%
other:
90.79% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
430 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
148 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.82 cu km/yr (67%/5%/28%)
per capita:
254 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
occasional severe storms and forest fires in the Darien area
|
|
|
|
|
water pollution from agricultural runoff threatens fishery resources; deforestation of tropical rain forest; land degradation and soil erosion threatens siltation of Panama Canal; air pollution in urban areas; mining threatens natural resources
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on eastern end of isthmus forming land bridge connecting North and South America; controls Panama Canal that links North Atlantic Ocean via Caribbean Sea with North Pacific Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Panama |
|
|
|
noun: Panamanian(s)
adjective:
Panamanian
|
|
|
|
|
mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 70%, Amerindian and mixed (West Indian) 14%, white 10%, Amerindian 6%
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish (official), English 14%
note:
many Panamanians are bilingual
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 85%, Protestant 15%
|
|
|
|
|
Panama is a country of demographic and economic contrasts. It is in the midst of a demographic transition, characterized by steadily declining rates of fertility, mortality, and population growth, but disparities persist based on wealth, geography, and ethnicity. Panama has one of the fastest growing economies in Latin America and dedicates substantial funding to social programs, yet poverty and inequality remain prevalent. The indigenous population accounts for a growing share of Panama's poor and extreme poor, while the non-indigenous rural poor have been more successful at rising out of poverty through rural-to-urban labor migration. The government's large expenditures on untargeted, indirect subsidies for water, electricity, and fuel have been ineffective, but its conditional cash transfer program has shown some promise in helping to decrease extreme poverty among the indigenous population.
Panama has expanded access to education and clean water, but the availability of sanitation and, to a lesser extent, electricity remains poor. The increase in secondary schooling - led by female enrollment - is spreading to rural and indigenous areas, which probably will help to alleviate poverty if educational quality and the availability of skilled jobs improve. Inadequate access to sanitation contributes to a high incidence of diarrhea in Panama's children, which is one of the main causes of Panama's elevated chronic malnutrition rate, especially among indigenous communities.
|
|
|
|
|
3,510,045 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 28.1% (male 504,035/ female 483,567)
15-64 years:
64.5% (male 1,144,595/ female 1,118,819)
65 years and over:
7.4% (male 119,866/ female 139,163) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 27.8 years
male:
27.4 years
female:
28.2 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.41% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
19.17 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
4.69 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
-0.38 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 75% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
PANAMA CITY (capital) 1.346 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.86 male(s)/female
total population:
1.01 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
92 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11.32 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 137
male:
12.09 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
10.52 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 77.96 years
country comparison to the world: 57
male:
75.18 years
female:
80.86 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.43 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
8.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 physicians/1,000 population (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 beds/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 75% of population
rural: 51% of population
total: 69% of population
unimproved:
urban: 25% of population
rural: 49% of population
total: 31% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.9% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
20,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
1,500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne disease:
dengue fever and malaria (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
3.8% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
91.9%
male:
92.5%
female:
91.2% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14.9%
country comparison to the world: 75
male:
11.7%
female:
21.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Panama
conventional short form:
Panama
local long form:
Republica de Panama
local short form:
Panama
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional democracy
|
|
|
|
|
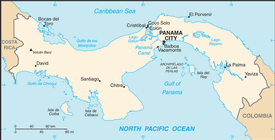
name: Panama City
geographic coordinates:
8 58 N, 79 32 W
time difference:
UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
9 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia) and 3 indigenous territories* (comarcas); Bocas del Toro, Chiriqui, Cocle, Colon, Darien, Embera-Wounaan*, Herrera, Kuna Yala*, Los Santos, Ngobe-Bugle*, Panama, Veraguas
|
|
|
|
|
3 November 1903 (from Colombia; became independent from Spain on 28 November 1821)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 3 November (1903)
|
|
|
|
|
11 October 1972; revised several times
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court of Justice
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Ricardo MARTINELLI Berrocal (since 1 July 2009); Vice President Juan Carlos VARELA (since 1 July 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Ricardo MARTINELLI Berrocal (since 1 July 2009); Vice President Juan Carlos VARELA (since 1 July 2009)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for five-year terms (president not eligible for immediate reelection and must sit out two additional terms (10 years) before becoming eligible for reelection); election last held on 3 May 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
Ricardo MARTINELLI Berrocal elected president; percent of vote - Ricardo MARTINELLI Berrocal 60%, Balbina HERRERA 38%, Guillermo ENDARA Galimany 2%
note:
the ruling government coalition - formerly comprised of CD (Democratic Change), Panamenista Party, MOLIRENA (Nationalist Republican Liberal Movement), and UP (Patriotic Union Party) - split in August 2011 when MARTINELLI relieved Vice President VARELA from his position as Foreign Minister prompting the Panamenistas to pull out of the coalition; UP has now merged with CD, and CD and the Panamenista Party will now run separate candidates for the presidency in 2014
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Asamblea Nacional (71 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 3 May 2009 (next to be held in May 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PRD 26, Panamenista 22, CD 14, UP 4, MOLIRENA 2, PP 1, independents 2; note - changes in political affiliation now reflect the following seat distribution: as of 5 December 2012 - seats by party - CD 38, PRD 17, Panamenista 9, MOLIRENA 6, PP 1
note:
legislators from outlying rural districts are chosen on a plurality basis while districts located in more populous towns and cities elect multiple legislators by means of a proportion-based formula
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court of Justice or Corte Suprema de Justicia (nine judges appointed for staggered 10-year terms); five superior courts; three courts of appeal
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Change or CD [Ricardo MARTINELLI]; Democratic Revolutionary Party or PRD [Francisco SANCHEZ Cardenas]; Nationalist Republican Liberal Movement or MOLIRENA [Sergio GONZALEZ-Ruiz]; Panamenista Party [Juan Carlos VARELA Rodriguez] (formerly the Arnulfista Party); Patriotic Union Party or UP (combination of the Liberal National Party or PLN and the Solidarity Party or PS)[Anibal GALINDO]; Popular Party or PP [Milton HENRIQUEZ] (formerly Christian Democratic Party or PDC)
note:
The Patriotic Union Party (UP) has now merged with Democratic Change (CD)
|
|
|
|
|
Chamber of Commerce; Concertacion Nacional (mechanism for government of Panama to formally dialogue with representatives of civil society); National Council of Organized Workers or CONATO; National Council of Private Enterprise or CONEP; National Union of Construction and Similar Workers (SUNTRACS); Panamanian Association of Business Executives or APEDE; Panamanian Industrialists Society or SIP; Workers Confederation of the Republic of Panama or CTRP
|
|
|
|
|
BCIE, CAN (observer), CD, CELAC, CSN (observer), FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, SICA, UN, UNASUR (observer), UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mario Ernesto JARAMILLO Castillo
chancery:
2862 McGill Terrace NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 483-1407
FAX:
[1] (202) 483-8416
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Houston, Miami, New Orleans, New York, Philadelphia, San Diego, San Francisco, Tampa
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jonathan D. FARRAR
embassy:
Edificio 783, Avenida Demetrio Basilio Lakas Panama, Apartado Postal 0816-02561, Zona 5, Panama City
mailing address:
American Embassy Panama, Unit 0945, APO AA 34002
telephone:
[507] 207-7000
FAX:
[507] 317-5568
|
|
|
|
|
divided into four, equal rectangles; the top quadrants are white (hoist side) with a blue five-pointed star in the center and plain red; the bottom quadrants are plain blue (hoist side) and white with a red five-pointed star in the center; the blue and red colors are those of the main political parties (Conservatives and Liberals respectively) and the white denotes peace between them; the blue star stands for the civic virtues of purity and honesty, the red star signifies authority and law
|
|
|
|
|
harpy eagle
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Himno Istemno" (Isthmus Hymn)
lyrics/music:
Jeronimo DE LA OSSA/Santos A. JORGE
note:
adopted 1925
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Panama's dollar-based economy rests primarily on a well-developed services sector that accounts for more than three-quarters of GDP. Services include operating the Panama Canal, logistics, banking, the Colon Free Zone, insurance, container ports, flagship registry, and tourism. Economic growth will be bolstered by the Panama Canal expansion project that began in 2007 and is scheduled to be completed by 2014 at a cost of $5.3 billion - about 10% of current GDP. The expansion project will more than double the Canal's capacity, enabling it to accommodate ships that are too large to traverse the existing canal. The United States and China are the top users of the Canal. Panama also plans to construct a metro system in Panama City, valued at $1.2 billion and scheduled to be completed by 2014. Panama's booming transportation and logistics services sectors, along with aggressive infrastructure development projects, have lead the economy to continued high growth in 2012. Strong economic performance has not translated into broadly shared prosperity, as Panama has the second worst income distribution in Latin America. About 30% of the population lives in poverty; however, from 2006 to 2012 poverty was reduced by 10 percentage points, while unemployment dropped from 12% to 4.4% of the labor force in 2012. A US-Panama Trade Promotion Agreement was approved by Congress and signed into law in October 2011. Seeking removal from the Organization of Economic Development's gray-list of tax havens, Panama has also recently signed various double taxation treaties with other nations.
|
|
|
|
|
$55.8 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
$51.43 billion (2011 est.)
$46.51 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$34.82 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
10.6% (2011 est.)
7.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$15,300 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
$14,300 (2011 est.)
$13,200 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.8%
industry:
16.8%
services:
79.4% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.509 million
country comparison to the world: 129
note:
shortage of skilled labor, but an oversupply of unskilled labor (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17%
industry:
18.6%
services:
64.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
4.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
29% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.1%
highest 10%:
40.1% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
51.9 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
56.1 (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
30.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $9.219 billion
expenditures:
$10.21 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
26.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
-2.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
37% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
40% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
5.9% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.6% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
6.91% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$7.488 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
$6.107 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$29.72 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
$25.73 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$31.47 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
$28.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$10.68 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 70
$10.92 billion (31 December 2010)
$8.048 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
bananas, rice, corn, coffee, sugarcane, vegetables; livestock; shrimp
|
|
|
|
|
10.9% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
-$4.191 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
-$3.892 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$17.97 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
$16.93 billion (2011 est.)
note:
includes the Colon Free Zone
|
|
|
|
|
gold, bananas, shrimp, sugar, iron and steel waste, pineapples, watermelons
|
|
|
|
|
US 13.1%, South Korea 12.5%, Honduras 10.2%, Japan 9.3%, India 7%, Canada 4.4%, Mexico 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$24.04 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
$22.95 billion (2011 est.)
note:
includes the Colon Free Zone
|
|
|
|
|
fuel products, medicines, vehicles, iron and steel rods, cellular phones
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 23.5%, China 23%, Singapore 18.1%, US 13%, South Korea 6% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.314 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
$2.315 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$13.13 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$12.21 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
balboas (PAB) per US dollar -
1 (2012 est.)
1 (2011 est.)
1 (2010 est.)
1 (2009)
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.546 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
5.805 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
39 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
71 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
1.815 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
51.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
48.4% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|
|
98,890 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
46,370 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
|
|
|
|
|
15.46 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
560,200 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
6.735 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: domestic and international facilities well developed
domestic:
mobile-cellular telephone subscribership has increased rapidly
international:
country code - 507; landing point for the Americas Region Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1), the MAYA-1, and PAN-AM submarine cable systems that together provide links to the US and parts of the Caribbean, Central America, and South America; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean); connected to the Central American Microwave System
|
|
|
|
|
multiple privately-owned TV networks and a government-owned educational TV station; multi-channel cable and satellite TV subscription services are available; more than 100 commercial radio stations (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.pa
|
|
|
|
|
11,022 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
959,800 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
118 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
total: 55
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
18
under 914 m:
30 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 63
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
11
under 914 m:
51 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
oil 128 km
|
|
|
|
|
total: 76 km
country comparison to the world: 127
standard gauge:
76 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11,978 km
country comparison to the world: 130
paved:
4,300 km
unpaved:
7,678 km (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
800 km (includes the 82-km Panama Canal that is being widened) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6,413
country comparison to the world: 1
by type:
barge carrier 1, bulk carrier 2,525, cargo 1,115, carrier 27, chemical tanker 588, combination ore/oil 1, container 742, liquefied gas 205, passenger 42, passenger/cargo 51, petroleum tanker 545, refrigerated cargo 191, roll on/roll off 87, specialized tanker 3, vehicle carrier 290
foreign-owned:
5,162 (Albania 4, Argentina 5, Australia 4, Bahamas 6, Bangladesh 5, Belgium 1, Bermuda 27, Brazil 3, Bulgaria 6, Burma 3, Canada 6, Chile 14, China 534, Colombia 2, Croatia 2, Cuba 2, Cyprus 5, Denmark 41, Ecuador 3, Egypt 11, Finland 2, France 7, Gabon 1, Germany 24, Gibraltar 1, Greece 379, Hong Kong 144, India 24, Indonesia 10, Iran 5, Ireland 1, Israel 1, Italy 25, Japan 2372, Jordan 11, Kuwait 12, Lebanon 2, Lithuania 3, Luxembourg 1, Malaysia 12, Maldives 2, Malta 2, Mexico 5, Monaco 11, Netherlands 6, Nigeria 6, Norway 81, Oman 10, Pakistan 3, Peru 9, Philippines 5, Portugal 10, Qatar 1, Romania 3, Russia 49, Saudi Arabia 11, Singapore 92, South Korea 373, Spain 30, Sweden 2, Switzerland 15, Syria 34, Taiwan 328, Tanzania 2, Thailand 6, Turkey 62, UAE 83, UK 37, UK 5, Ukraine 8, US 90, Venezuela 13, Vietnam 43, Yemen 4)
registered in other countries:
1 (Honduras 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Balboa, Colon, Cristobal
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
no regular military forces; Panamanian public forces include: Panamanian National Police (PNP), National Air-Naval Service (SENAN), National Border Service (SENAFRONT) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 890,006 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 731,254
females age 16-49:
728,329 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 32,142
female:
30,879 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
on 10 February 1990, the government of then President ENDARA abolished Panama's military and reformed the security apparatus by creating the Panamanian Public Forces; in October 1994, Panama's Legislative Assembly approved a constitutional amendment prohibiting the creation of a standing military force but allowing the temporary establishment of special police units to counter acts of "external aggression"
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Panama |
|
|
|
organized illegal narcotics operations in Colombia operate within the remote border region with Panama
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 15,598 (Colombia) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
major cocaine transshipment point and primary money-laundering center for narcotics revenue; money-laundering activity is especially heavy in the Colon Free Zone; offshore financial center; negligible signs of coca cultivation; monitoring of financial transactions is improving; official corruption remains a major problem
|
|
|
|
|
|