|
|
|
The Pacific coast of Nicaragua was settled as a Spanish colony from Panama in the early 16th century. Independence from Spain was declared in 1821 and the country became an independent republic in 1838. Britain occupied the Caribbean Coast in the first half of the 19th century, but gradually ceded control of the region in subsequent decades. Violent opposition to governmental manipulation and corruption spread to all classes by 1978 and resulted in a short-lived civil war that brought the Marxist Sandinista guerrillas to power in 1979. Nicaraguan aid to leftist rebels in El Salvador caused the US to sponsor anti-Sandinista contra guerrillas through much of the 1980s. After losing free and fair elections in 1990, 1996, and 2001, former Sandinista President Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra was elected president in 2006 and reelected in 2011. The 2008 municipal elections, 2010 regional elections, November 2011 presidential elections, and 2012 municipal elections were marred by widespread irregularities. Nicaragua's infrastructure and economy - hard hit by the earlier civil war and by Hurricane Mitch in 1998 - are slowly being rebuilt, but democratic institutions have been weakened under the ORTEGA administration.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
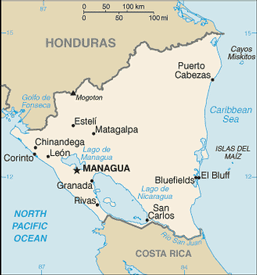
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa Rica and Honduras
|
|
|
|
|
13 00 N, 85 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 130,370 sq km
country comparison to the world: 98
land:
119,990 sq km
water:
10,380 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than New York state
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,231 km
border countries:
Costa Rica 309 km, Honduras 922 km
|
|
|
|
|
910 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
continental shelf:
natural prolongation
|
|
|
|
|
tropical in lowlands, cooler in highlands
|
|
|
|
|
extensive Atlantic coastal plains rising to central interior mountains; narrow Pacific coastal plain interrupted by volcanoes
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mogoton 2,438 m
|
|
|
|
|
gold, silver, copper, tungsten, lead, zinc, timber, fish
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 14.81%
permanent crops:
1.82%
other:
83.37% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
610 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
196.7 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.3 cu km/yr (15%/2%/83%)
per capita:
237 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
destructive earthquakes; volcanoes; landslides; extremely susceptible to hurricanes
volcanism:
significant volcanic activity; Cerro Negro (elev. 728 m), which last erupted in 1999, is one of Nicaragua's most active volcanoes; its lava flows and ash have been known to cause significant damage to farmland and buildings; other historically active volcanoes include Concepcion, Cosiguina, Las Pilas, Masaya, Momotombo, San Cristobal, and Telica
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
largest country in Central America; contains the largest freshwater body in Central America, Lago de Nicaragua
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Nicaragua |
|
|
|
noun: Nicaraguan(s)
adjective:
Nicaraguan
|
|
|
|
|
mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 69%, white 17%, black 9%, Amerindian 5%
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish (official) 97.5%, Miskito 1.7%, other 0.8% (1995 census)
note:
English and indigenous languages found on the Atlantic coast
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 58.5%, Protestant 23.2% (Evangelical 21.6%, Moravian 1.6%), Jehovah's Witnesses 0.9%, other 1.7%, none 15.7% (2005 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Despite being one of the poorest countries in Latin America, Nicaragua has improved its access to potable water and sanitation and has ameliorated its life expectancy, infant and child mortality, and immunization rates. However, income distribution is very uneven, and the poor, agriculturalists, and indigenous people continue to have less access to healthcare services. Nicaragua's total fertility rate has fallen from around 6 children per woman in 1980 to just above replacement level today, but the high birth rate among adolescents perpetuates a cycle of poverty and low educational attainment.
Nicaraguans emigrate primarily to Costa Rica and to a lesser extent the United States. Nicaraguan men have been migrating seasonally to Costa Rica to harvest bananas and coffee since the early 20th century. Political turmoil, civil war, and natural disasters from the 1970s through the 1990s dramatically increased the flow of refugees and permanent migrants seeking jobs, higher wages, and better social and healthcare benefits. Since 2000, Nicaraguan emigration to Costa Rica has slowed and stabilized. Today roughly 300,000 Nicaraguans are permanent residents of Costa Rica - about 75% of the foreign population - and thousands more migrate seasonally for work, many illegally.
|
|
|
|
|
5,727,707 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 30.8% (male 899,555/ female 865,652)
15-64 years:
64.6% (male 1,782,174/ female 1,916,031)
65 years and over:
4.6% (male 119,995/ female 144,300) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23.4 years
male:
22.6 years
female:
24.2 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.067% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
19.12 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
5.04 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
-3.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 57% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
MANAGUA (capital) 934,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.83 male(s)/female
total population:
0.96 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
95 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.86 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 87
male:
25.05 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
18.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 72.18 years
country comparison to the world: 130
male:
70.07 years
female:
74.39 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.08 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
9.5% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
0.37 physicians/1,000 population (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
0.9 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 63% of population
rural: 37% of population
total: 52% of population
unimproved:
urban: 37% of population
rural: 63% of population
total: 48% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
6,900 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
dengue fever and malaria
water contact disease:
leptospirosis (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
4.3% (2004)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% of GDP (2003)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
67.5%
male:
67.2%
female:
67.8% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11 years
male:
11 years
female:
11 years (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8.6%
country comparison to the world: 112
male:
8.1%
female:
9.7% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Nicaragua
conventional short form:
Nicaragua
local long form:
Republica de Nicaragua
local short form:
Nicaragua
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Managua
geographic coordinates:
12 08 N, 86 15 W
time difference:
UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
15 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento) and 2 autonomous regions* (regiones autonomistas, singular - region autonoma); Atlantico Norte*, Atlantico Sur*, Boaco, Carazo, Chinandega, Chontales, Esteli, Granada, Jinotega, Leon, Madriz, Managua, Masaya, Matagalpa, Nueva Segovia, Rio San Juan, Rivas
|
|
|
|
|
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
|
|
|
|
|
9 January 1987; revised in 1995, 2000, and 2005
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; Supreme Court may review administrative acts
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
16 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (since 10 January 2007); Vice President Moises Omar HALLESLEVENS Acevedo (since 10 January 2012); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra (since 10 January 2007); Vice President Moises Omar HALLESLEVENS Acevedo (since 10 January 2012)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held on 6 November 2011 (next to be held by November 2016)
election results:
Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra reelected president; percent of vote - Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra 62.5%, Fabio GADEA 31%, Arnoldo ALEMAN 5.9%, other 0.6%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Asamblea Nacional (92 seats; 90 members elected by proportional representation and party lists to serve five-year terms; 1 seat for the previous president, 1 seat for the runner-up in previous presidential election)
elections:
last held on 6 November 2011 (next to be held by November 2016)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - FSLN 64, PLI/MRS 26, PLC 2
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Corte Suprema de Justicia (16 judges elected for five-year terms by the National Assembly); note - in 2010, President ORTEGA directly replaced seven justices on the Supreme Court
|
|
|
|
|
Alliance for the Republic or APRE; Conservative Party or PC [Alejandro BOLANOS Davis]; Independent Liberal Party or PLI [Eduardo MONTEALEGRE]; Liberal Constitutionalist Party or PLC [Maria Haydee OSUNA]; Nicaraguan Liberal Alliance or ALN [Alejandro MEJIA Ferreti]; Sandinista National Liberation Front or FSLN [Jose Daniel ORTEGA Saavedra]; Sandinista Renovation Movement or MRS [Enrique SAENZ-NAVARRETE]
|
|
|
|
|
National Workers Front or FNT (a Sandinista umbrella group of eight labor unions including: Farm Workers Association or ATC, Health Workers Federation or FETASALUD, Heroes and Martyrs Confederation of Professional Associations or CONAPRO, National Association of Educators of Nicaragua or ANDEN, National Union of Employees or UNE, National Union of Farmers and Ranchers or UNAG, Sandinista Workers Central or CST, and Union of Journalists of Nicaragua or UPN); Permanent Congress of Workers or CPT (an umbrella group of four non-Sandinista labor unions including: Autonomous Nicaraguan Workers Central or CTN-A, Confederation of Labor Unification or CUS, Independent General Confederation of Labor or CGT-I, and Labor Action and Unity Central or CAUS); Nicaraguan Workers' Central or CTN (an independent labor union); Superior Council of Private Enterprise or COSEP (a confederation of business groups)
|
|
|
|
|
BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Francisco Obadiah CAMPBELL Hooker
chancery:
1627 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 939-6570, 6573
FAX:
[1] (202) 939-6545
consulate(s) general:
Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Phyllis M. POWERS
embassy:
Kilometer 5.5 Carretera Sur, Managua
mailing address:
American Embassy Managua, APO AA 34021
telephone:
[505] 252-7100, 252-7888; 252-7634 (after hours)
FAX:
[505] 252-7304
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of blue (top), white, and blue with the national coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms features a triangle encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE NICARAGUA on the top and AMERICA CENTRAL on the bottom; the banner is based on the former blue-white-blue flag of the Federal Republic of Central America; the blue bands symbolize the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, while the white band represents the land between the two bodies of water
note:
similar to the flag of El Salvador, which features a round emblem encircled by the words REPUBLICA DE EL SALVADOR EN LA AMERICA CENTRAL centered in the white band; also similar to the flag of Honduras, which has five blue stars arranged in an X pattern centered in the white band
|
|
|
|
|
turquoise-browed motmot (bird)
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Salve a ti, Nicaragua" (Hail to Thee, Nicaragua)
lyrics/music:
Salomon Ibarra MAYORGA/traditional, arranged by Luis Abraham DELGADILLO
note:
although only officially adopted in 1971, the music was approved in 1918 and the lyrics in 1939; the tune, originally from Spain, was used as an anthem for Nicaragua from the 1830's until 1876
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nicaragua, the poorest country in Central America and the second poorest in the Hemisphere, has widespread underemployment and poverty. The US-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) has been in effect since April 2006 and has expanded export opportunities for many agricultural and manufactured goods. Textiles and apparel account for nearly 60% of Nicaragua's exports, but increases in the minimum wage during the ORTEGA administration will likely erode its comparative advantage in this industry. ORTEGA's promotion of mixed business initiatives, owned by the Nicaraguan and Venezuelan state oil firms, together with the weak rule of law, could undermine the investment climate for domestic and international private firms in the near-term. Nicaragua relies on international economic assistance to meet internal- and external-debt financing obligations. Foreign donors have curtailed this funding, however, in response to November 2008 electoral fraud. In early 2004, Nicaragua secured some $4.5 billion in foreign debt reduction under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative. Managua still struggles with a high public debt burden, however, it succeeded in reducing that burden in 2011. The economy grew at a rate of about 4% in 2012.
|
|
|
|
|
$19.89 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
$19.18 billion (2011 est.)
$18.33 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$7.828 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.7% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
4.7% (2011 est.)
4.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3,300 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
$3,300 (2011 est.)
$3,200 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17.5%
industry:
25.8%
services:
56.7% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.961 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 28%
industry:
19%
services:
53% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
7.3% (2011 est.)
note:
underemployment was 46.5% in 2008
|
|
|
|
|
46.2% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.4%
highest 10%:
41.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
40.5 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 57
60.3 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
34.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $2.619 billion
expenditures:
$2.56 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
33.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
0.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
70.5% of GDP (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
78.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
8.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% (31 December 2010 est.)
NA% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
11.5% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
10.54% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.287 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
$1.125 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.136 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
$2.924 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.138 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
$4.195 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, bananas, sugarcane, cotton, rice, corn, tobacco, sesame, soya, beans; beef, veal, pork, poultry, dairy products; shrimp, lobsters
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
-$1.476 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
-$1.259 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.16 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
$3.941 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, beef, shrimp and lobster, tobacco, sugar, gold, peanuts; cigars, automobile wiring harnesses, textiles and apparel
|
|
|
|
|
US 60.1%, Canada 8.3%, El Salvador 4.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.519 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$5.996 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
consumer goods, machinery and equipment, raw materials, petroleum products
|
|
|
|
|
US 21.3%, Venezuela 14%, Costa Rica 8.7%, China 8.5%, Mexico 8.2%, Guatemala 8%, El Salvador 5.4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
$1.892 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.228 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
$5.012 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
cordobas (NIO) per US dollar -
23.58 (2012 est.)
22.424 (2011 est.)
21.356 (2010 est.)
20.34 (2009)
19.374 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.585 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
2.646 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
100,000 kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
2 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
1.104 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
67.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
9.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|
|
22.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
16,080 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
14,680 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
31,930 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
999.6 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
14,170 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
4.825 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Nicaragua |
|
|
|
287,600 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
4.822 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: system being upgraded by foreign investment; nearly all installed telecommunications capacity now uses digital technology, owing to investments since privatization of the formerly state-owned telecommunications company
domestic:
since privatization, access to fixed-line and mobile-cellular services has improved; fixed-line teledensity roughly 5 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone subscribership has increased to roughly 85 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 505; the Americas Region Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1) fiber optic submarine cable provides connectivity to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; satellite earth stations - 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region) and 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
multiple privately-owned terrestrial TV networks, supplemented by cable TV in most urban areas; of more than 100 radio stations, nearly all are privately owned; Radio Nicaragua is government-owned and Radio Sandino is controlled by the Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.ni
|
|
|
|
|
296,068 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
199,800 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Nicaragua |
|
|
|
143 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
4 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 132
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
16
under 914 m:
115 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
oil 54 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 19,137 km
country comparison to the world: 111
paved:
2,033 km
unpaved:
17,104 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2,220 km (navigable waterways as well as the use of the large Lake Managua and Lake Nicaragua; rivers serve only the sparsely populated eastern part of the country) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
Bluefields, Corinto
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
National Army of Nicaragua (Ejercito Nacional de Nicaragua, ENN; includes Navy, Air Force) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; tour of duty 18-36 months; requires Nicaraguan nationality and 6th-grade education (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,452,107
females age 16-49:
1,552,698 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,227,757
females age 16-49:
1,335,653 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 69,093
female:
67,522 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Nicaragua |
|
|
|
the 1992 ICJ ruling for El Salvador and Honduras advised a tripartite resolution to establish a maritime boundary in the Gulf of Fonseca, which considers Honduran access to the Pacific; legal dispute over navigational rights of San Juan River on border with Costa Rica
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for cocaine destined for the US and transshipment point for arms-for-drugs dealing
|
|
|
|
|
|