| Introduction ::Netherlands |
|
|
|
The Dutch United Provinces declared their independence from Spain in 1579; during the 17th century, they became a leading seafaring and commercial power, with settlements and colonies around the world. After a 20-year French occupation, a Kingdom of the Netherlands was formed in 1815. In 1830 Belgium seceded and formed a separate kingdom. The Netherlands remained neutral in World War I, but suffered invasion and occupation by Germany in World War II. A modern, industrialized nation, the Netherlands is also a large exporter of agricultural products. The country was a founding member of NATO and the EEC (now the EU), and participated in the introduction of the euro in 1999. In October 2010, the former Netherlands Antilles was dissolved and the three smallest islands - Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba - became special municipalities in the Netherlands administrative structure. The larger islands of Sint Maarten and Curacao joined the Netherlands and Aruba as constituent countries forming the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
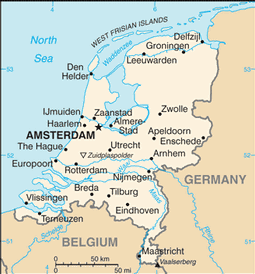
Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between Belgium and Germany
|
|
|
|
|
52 30 N, 5 45 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41,543 sq km
country comparison to the world: 135
land:
33,893 sq km
water:
7,650 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than twice the size of New Jersey
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,027 km
border countries:
Belgium 450 km, Germany 577 km
|
|
|
|
|
451 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive fishing zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; marine; cool summers and mild winters
|
|
|
|
|
mostly coastal lowland and reclaimed land (polders); some hills in southeast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Zuidplaspolder -7 m
highest point:
Mount Scenery 862 m (on the island of Saba in the Caribbean, now considered an integral part of the Netherlands following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles)
note:
the highest point on continental Netherlands is Vaalserberg at 322 m
|
|
|
|
|
natural gas, petroleum, peat, limestone, salt, sand and gravel, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 21.96%
permanent crops:
0.77%
other:
77.27% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
4,600 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
89.7 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8.86 cu km/yr (6%/60%/34%)
per capita:
544 cu m/yr (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding
|
|
|
|
|
water pollution in the form of heavy metals, organic compounds, and nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates; air pollution from vehicles and refining activities; acid rain
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
located at mouths of three major European rivers (Rhine, Maas or Meuse, and Schelde)
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Netherlands |
|
|
|
noun: Dutchman(men), Dutchwoman(women)
adjective:
Dutch
|
|
|
|
|
Dutch 80.7%, EU 5%, Indonesian 2.4%, Turkish 2.2%, Surinamese 2%, Moroccan 2%, Caribbean 0.8%, other 4.8% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Dutch (official), Frisian (official)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 30%, Protestant 20% (Dutch Reformed 11%, Calvinist 6%, other Protestant 3%), Muslim 5.8%, other 2.2%, none 42% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
16,730,632 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 17.2% (male 1,474,530/ female 1,408,144)
15-64 years:
66.2% (male 5,569,934/ female 5,505,269)
65 years and over:
16.6% (male 1,231,914/ female 1,540,841) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.5 years
male:
40.7 years
female:
42.3 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.452% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
10.89 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
8.39 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
2.02 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 83% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.8% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
AMSTERDAM (capital) 1.044 million; Rotterdam 1.008 million; The Hague (seat of government) 629,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.8 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.73 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 204
male:
4.03 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.41 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 80.91 years
country comparison to the world: 21
male:
78.84 years
female:
83.08 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.78 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
10.8% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
3.921 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
4.25 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
22,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
5.3% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17 years
male:
17 years
female:
17 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6.6%
country comparison to the world: 119
male:
7.1%
female:
6.2% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of the Netherlands
conventional short form:
Netherlands
local long form:
Koninkrijk der Nederlanden
local short form:
Nederland
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Amsterdam
geographic coordinates:
52 21 N, 4 55 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note:
The Hague is the seat of government; time descriptions apply to the continental Netherlands only, not to the Caribbean components
|
|
|
|
|
12 provinces (provincies, singular - provincie); Drenthe, Flevoland, Fryslan (Friesland), Gelderland, Groningen, Limburg, Noord-Brabant (North Brabant), Noord-Holland (North Holland), Overijssel, Utrecht, Zeeland (Zealand), Zuid-Holland (South Holland)
|
|
|
|
|
Aruba, Curacao, Sint Maarten
|
|
|
|
|
23 January 1579 (the northern provinces of the Low Countries conclude the Union of Utrecht breaking with Spain; on 26 July 1581 they formally declared their independence with an Act of Abjuration; however, it was not until 30 January 1648 and the Peace of Westphalia that Spain recognized this independence)
|
|
|
|
|
Queen's Day (Birthday of deceased Queen-Mother JULIANA and accession to the throne of her oldest daughter BEATRIX), 30 April (1909 and 1980)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 1815; amended many times
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on the French system; constitution does not permit judicial review of acts of the States General
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Queen BEATRIX (since 30 April 1980); Heir Apparent WILLEM-ALEXANDER (born 27 April 1967), son of the monarch
head of government:
Prime Minister Mark RUTTE (since 14 October 2010); Deputy Prime Minister Lodewijk ASSCHER (since 5 November 2012); note - Mark RUTTE tendered his resignation 23 April 2012; new elections were held on 12 September 2012 in which his party won the most seats; during the interim period he remained in office in a care-taking position; he was sworn in again to be prime minister on 5 November 2012
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; following Second Chamber elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch; deputy prime ministers appointed by the monarch
note:
there is also a Council of State composed of the monarch, heir apparent, and councilors that provides consultations to the cabinet on legislative and administrative policy
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral States General or Staten Generaal consists of the First Chamber or Eerste Kamer (75 seats; members indirectly elected by the country's 12 provincial councils to serve four-year terms) and the Second Chamber or Tweede Kamer (150 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve at most four-year terms)
elections:
First Chamber - last held on May 2011 (next to be held in May 2015); Second Chamber - last held on 12 September 2012 (next to be held by September 2016)
election results:
First Chamber - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - VVD 16, PvdA 14, CDA 11, PVV 10, SP 8, D66 5, GL 5, other 6; Second Chamber - percent of vote by party - VVD 26.6%, PvdA 24.8%, PVV, 10.1%, SP 9.7%, CDA 8.5%, D66 8.0%, CU 3.1%, GL 6.7%, other 2.5%; seats by party - VVD 41, PvdA 38, PVV 15, SP 15, CDA 13, D66 12, CU 5, GL 4, other 7
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Hoge Raad (justices are nominated for life by the monarch)
|
|
|
|
|
Christian Democratic Appeal or CDA [Sybrand VAN HAERSMA BUMA]; Christian Union or CU [Arie SLOB]; Democrats 66 or D66 [Alexander PECHTOLD]; Green Left or GL [Bram VAN OJIK]; Labor Party or PvdA [Diederik SAMSOM]; Party for Freedom or PVV [Geert WILDERS]; Party for the Animals or PvdD [Marianne THIEME]; People's Party for Freedom and Democracy or VVD [Halbe ZIJLSTRA]; Reformed Political Party of SGP [Kees VAN DER STAAIJ]; Socialist Party of SP [Emile ROEMER]; plus a few minor parties
|
|
|
|
|
Christian Trade Union Federation or CNV [Jaap SMIT]; Confederation of Netherlands Industry and Employers or VNO-NCW [Bernard WIENTJES]; Federation for Small and Medium-sized businesses or MKB [Hans BIESHEUVEL]; Netherlands Trade Union Federation or FNV [Ton HEERTS]; Social Economic Council or SER [Wiebe DRAIJER]; Trade Union Federation of Middle and High Personnel or MHP [Reginald VISSER]
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, Benelux, BIS, CBSS (observer), CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Rudolf Simon BEKINK
chancery:
4200 Linnean Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 244-5300, [1] 877-388-2443
FAX:
[1] (202) 362-3430
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, San Francisco, Miami, New York
consulate(s):
Boston
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires ad interim Edwin NOLAN
embassy:
Lange Voorhout 102, 2514 EJ, The Hague
mailing address:
PSC 71, Box 1000, APO AE 09715
telephone:
[31] (70) 310-2209
FAX:
[31] (70) 361-4688
consulate(s) general:
Amsterdam
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and blue; similar to the flag of Luxembourg, which uses a lighter blue and is longer; the colors were those of WILLIAM I, Prince of Orange, who led the Dutch Revolt against Spanish sovereignty in the latter half of the 16th century; originally the upper band was orange, but because it tended to fade to red over time, the red shade was eventually made the permanent color; the banner is perhaps the oldest tricolor in continuous use
|
|
|
|
|
lion
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Het Wilhelmus" (The William)
lyrics/music:
Philips VAN MARNIX van Sint Aldegonde (presumed)/unknown
note:
adopted 1932, in use since the 17th century, making it the oldest national anthem in the world; also known as "Wilhelmus van Nassouwe" (William of Nassau), it is in the form of an acrostic, where the first letter of each stanza spells the name of the leader of the Dutch Revolt
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Dutch economy is the fifth-largest economy in the euro-zone and is noted for its stable industrial relations, moderate unemployment and inflation, a sizable trade surplus, and an important role as a European transportation hub. Industrial activity is predominantly in food processing, chemicals, petroleum refining, and electrical machinery. A highly mechanized agricultural sector employs only 2% of the labor force but provides large surpluses for the food-processing industry and for exports. The Netherlands, along with 11 of its EU partners, began circulating the euro currency on 1 January 2002. After 26 years of uninterrupted economic growth, the Dutch economy - highly dependent on an international financial sector and international trade - contracted by 3.5% in 2009 as a result of the global financial crisis. The Dutch financial sector suffered, due in part to the high exposure of some Dutch banks to U.S. mortgage-backed securities. In 2008, the government nationalized two banks and injected billions of dollars of capital into other financial institutions, to prevent further deterioration of a crucial sector. The government also sought to boost the domestic economy by accelerating infrastructure programs, offering corporate tax breaks for employers to retain workers, and expanding export credit facilities. The stimulus programs and bank bailouts, however, resulted in a government budget deficit of 5.3% of GDP in 2010 that contrasted sharply with a surplus of 0.7% in 2008. The government of Prime Minister Mark RUTTE began implementing fiscal consolidation measures in early 2011, mainly reductions in expenditures, which resulted in an improved budget deficit of 3.8% of GDP. In 2012 tax revenues dropped nearly 9%, and GDP contracted. Although jobless claims continued to grow, the unemployment rate remained relatively low at 6.8 percent.
|
|
|
|
|
$709.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$712.8 billion (2011 est.)
$705.1 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$770.2 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
1.1% (2011 est.)
1.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$42,300 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$42,700 (2011 est.)
$42,400 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2.8%
industry:
24.1%
services:
73.2% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.746 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2%
industry:
18%
services:
80% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
5.8% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.5% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.5%
highest 10%:
22.9% (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
30.9 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 112
32.6 (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
16.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $347.4 billion
expenditures:
$386.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
45.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
-5.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
68.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
65.1% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment. Debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions.
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
2.3% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 127
1.75% (31 December 2010)
note:
this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
|
|
|
|
|
2.5% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
3.18% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$375.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
$367.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|
|
$1.119 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$1.088 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.693 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
$1.644 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$594.7 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 18
$661.2 billion (31 December 2010)
$542.5 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
grains, potatoes, sugar beets, fruits, vegetables; livestock
|
|
|
|
|
-0.6% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
$77.2 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$70.92 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$556.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$550.2 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels; foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 26.2%, Belgium 14.1%, France 9.3%, UK 7.7%, Italy 4.8% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$490.1 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
$492.1 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, fuels, foodstuffs, clothing
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 14.5%, China 11.8%, Belgium 8.6%, UK 6.1%, Russia 6%, US 5.9%, France 4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$51.27 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$46.24 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.655 trillion (30 June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 7
$3.733 trillion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$608.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
$589.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$971.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$943.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7838 (2012 est.)
0.7185 (2011 est.)
755 (2010 est.)
0.7198 (2009 est.)
0.6827 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
108 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
107.4 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
12.81 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
15.58 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
25.99 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
84.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
13.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
41,990 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
13,140 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
964,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
287.4 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
1.239 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
1.01 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
1.858 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
1.61 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
81.09 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
49.05 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
54.8 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
22.76 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
1.303 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
263.4 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Netherlands |
|
|
|
7.135 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
19.835 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: highly developed and well maintained
domestic:
extensive fixed-line fiber-optic network; large cellular telephone system with 5 major operators utilizing the third generation of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) technology; one in five households now use Voice over the Internet Protocol (VoIP) services
international:
country code - 31; submarine cables provide links to the US and Europe; satellite earth stations - 5 (3 Intelsat - 1 Indian Ocean and 2 Atlantic Ocean, 1 Eutelsat, and 1 Inmarsat
|
|
|
|
|
more than 90% of households are connected to cable or satellite TV systems that provide a wide range of domestic and foreign channels; public service broadcast system includes multiple broadcasters, 3 with a national reach and the remainder operating in regional and local markets; 2 major nationwide commercial television companies, each with 3 or more stations, and many commercial TV stations in regional and local markets; nearly 600 radio stations with a mix of public and private stations providing national or regional coverage (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.nl
|
|
|
|
|
13.699 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
14.872 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Netherlands |
|
|
|
27 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
total: 20
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
10
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
5
under 914 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
4 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 4,413 km; oil 365 km; refined products 716 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,896 km
country comparison to the world: 58
standard gauge:
2,896 km 1.435-m gauge (2,195 km electrified) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 136,827 km (includes 2,631 km of expressways) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
6,214 km (navigable for ships of 50 tons) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
total: 744
country comparison to the world: 15
by type:
bulk carrier 4, cargo 514, carrier 15, chemical tanker 56, container 67, liquefied gas 21, passenger 17, passenger/cargo 14, petroleum tanker 4, refrigerated cargo 10, roll on/roll off 19, specialized tanker 3
foreign-owned:
196 (Australia 1, Bermuda 1, Denmark 27, Finland 13, France 2, Germany 86, Ireland 8, Italy 6, Japan 1, Norway 19, Sweden 12, UAE 4, US 16)
registered in other countries:
233 (Antigua and Barbuda 17, Bahamas 23, Belize 1, Canada 1, Curacao 43, Cyprus 23, Germany 1, Gibraltar 34, Italy 2, Liberia 31, Luxembourg 3, Malta 3, Marshall Islands 21, Panama 6, Paraguay 1, Philippines 17, Russia 2, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1, Singapore 1, UK 1, unknown 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Amsterdam, IJmuiden, Moerdijk, Rotterdam, Terneuzen, Vlissingen
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Royal Netherlands Army, Royal Netherlands Navy (includes Naval Air Service and Marine Corps), Royal Netherlands Air Force (Koninklijke Luchtmacht, KLu), Royal Military Police (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
20 years of age for an all-volunteer force (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 3,911,098
females age 16-49:
3,817,031 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 3,201,328
females age 16-49:
3,122,889 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 103,462
female:
98,383 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.6% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Netherlands |
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
major European producer of synthetic drugs, including ecstasy, and cannabis cultivator; important gateway for cocaine, heroin, and hashish entering Europe; major source of US-bound ecstasy; large financial sector vulnerable to money laundering; significant consumer of ecstasy
|
|
|
|
|
|