|
|
|
The inhabitants of the area of Oman have long prospered on Indian Ocean trade. In the late 18th century, a newly established sultanate in Muscat signed the first in a series of friendship treaties with Britain. Over time, Oman's dependence on British political and military advisors increased, but it never became a British colony. In 1970, QABOOS bin Said Al-Said overthrew his father, and he has since ruled as sultan. His extensive modernization program has opened the country to the outside world while preserving the longstanding close ties with the UK. Oman's moderate, independent foreign policy has sought to maintain good relations with all Middle Eastern countries. Inspired by the popular uprisings that swept the Middle East and North Africa in 2010-11, Omanis began staging marches and demonstrations to demand economic benefits, an end to corruption, and greater political rights. In February and March 2011, in response to protester demands, QABOOS pledged to create more government jobs and promised to implement economic and political reforms, such as granting legislative and regulatory powers to the Majlis al-Shura and the introduction of unemployment benefits. Also in March, the Gulf Cooperation Council pledged $20 billion in financial aid to Oman and Bahrain over a 10-year period to assist the two nations in their struggle with Arab protests. Amid concessions made to oppositionists, the government during the summer continued to crack down on protests and demonstrations, and increasingly clamped down on the media. In October 2011, QABOOS issued a royal decree expanding the legislative powers of the Majlis al-Shura to draft and propose amendments to legislation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
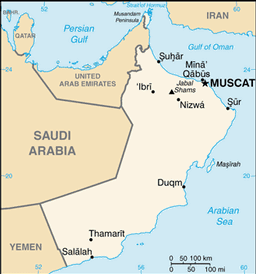
Middle East, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, between Yemen and UAE
|
|
|
|
|
21 00 N, 57 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 309,500 sq km
country comparison to the world: 71
land:
309,500 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Kansas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,374 km
border countries:
Saudi Arabia 676 km, UAE 410 km, Yemen 288 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,092 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
dry desert; hot, humid along coast; hot, dry interior; strong southwest summer monsoon (May to September) in far south
|
|
|
|
|
central desert plain, rugged mountains in north and south
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Arabian Sea 0 m
highest point:
Jabal Shams 2,980 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, copper, asbestos, some marble, limestone, chromium, gypsum, natural gas
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0.12%
permanent crops:
0.14%
other:
99.74% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
590 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
1 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.36 cu km/yr (7%/2%/90%)
per capita:
529 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
summer winds often raise large sandstorms and dust storms in interior; periodic droughts
|
|
|
|
|
rising soil salinity; beach pollution from oil spills; limited natural freshwater resources
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on Musandam Peninsula adjacent to Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oil
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Oman |
|
|
|
noun: Omani(s)
adjective:
Omani
|
|
|
|
|
Arab, Baluchi, South Asian (Indian, Pakistani, Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi), African
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic (official), English, Baluchi, Urdu, Indian dialects
|
|
|
|
|
Ibadhi Muslim (official) 75%, other (includes Sunni Muslim, Shia Muslim, Hindu) 25%
|
|
|
|
|
3,090,150 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
note:
includes 577,293 non-nationals
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 30.8% (male 488,762/ female 464,328)
15-64 years:
66% (male 1,157,119/ female 882,153)
65 years and over:
3.2% (male 49,660/ female 48,128) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24.4 years
male:
25.7 years
female:
22.8 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.043% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
24.33 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
3.42 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
|
|
|
|
|
-0.47 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 73% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
MUSCAT (capital) 634,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.31 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.03 male(s)/female
total population:
1.22 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
32 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14.95 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 115
male:
15.25 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
14.63 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 74.47 years
country comparison to the world: 104
male:
72.61 years
female:
76.43 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.87 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
|
|
|
|
|
3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
1.901 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 97% of population
rural: 61% of population
total: 87% of population
unimproved:
urban: 3% of population
rural: 39% of population
total: 13% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
1,100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
81.4%
male:
86.8%
female:
73.5% (2003 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
11 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Sultanate of Oman
conventional short form:
Oman
local long form:
Saltanat Uman
local short form:
Uman
former:
Muscat and Oman
|
|
|
|
|
monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Muscat
geographic coordinates:
23 37 N, 58 35 E
time difference:
UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
11 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazat); Ad Dakhiliyah, Al Buraymi, Al Wusta, Az Zahirah, Janub al Batinah (Al Batinah South), Janub ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah South), Masqat (Muscat), Musandam, Shamal al Batinah (Al Batinah North), Shamal ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah North), Zufar (Dhofar)
|
|
|
|
|
1650 (expulsion of the Portuguese)
|
|
|
|
|
Birthday of Sultan QABOOS, 18 November (1940)
|
|
|
|
|
none; note - on 6 November 1996, Sultan QABOOS issued a royal decree promulgating a basic law considered by the government to be a constitution which, among other things, clarifies the royal succession, provides for a prime minister, bars ministers from holding interests in companies doing business with the government, establishes a bicameral legislature, and guarantees basic civil liberties for Omani citizens
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of Anglo-Saxon law and Islamic law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
21 years of age; universal; note - members of the military and security forces by law are not allowed to vote
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972); note - the monarch is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the Ruling Family Council determines a successor from the Sultan's extended family; if the Council cannot form a consensus within three days of the Sultan's death or incapacitation, the Defense Council will relay a predetermined heir as chosen by the Sultan
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral - consists of Majlis al-Dawla or upper chamber (71 seats; members appointed by the sultan; has only advisory powers) and Majlis al-Shura or lower chamber (84 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms; body has authority to draft legislation but is subordinate to the Sultan)
elections:
last held on 15 October 2011 (next to be held in October 2015)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; note - three prominent figures from the spring 2011 protests won seats; one woman also won a seat
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court
note:
the nascent civil court system, administered by region, has judges who practice secular and sharia law
|
|
|
|
|
political parties are illegal
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Hunaina bint Sultan bin Ahmad al-MUGHAIRI
chancery:
2535 Belmont Road, NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 387-1980
FAX:
[1] (202) 745-4933
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires W. Johann SCHMONSEES
embassy:
Jameat A'Duwal Al Arabiya Street, Al Khuwair area, Muscat
mailing address:
P. O. Box 202, P.C. 115, Madinat Sultan Qaboos, Muscat
telephone:
[968] 24-643-400
FAX:
[968] 24-699771
|
|
|
|
|
three horizontal bands of white, red, and green of equal width with a broad, vertical, red band on the hoist side; the national emblem (a khanjar dagger in its sheath superimposed on two crossed swords in scabbards) in white is centered near the top of the vertical band; white represents peace and prosperity, red recalls battles against foreign invaders, and green symbolizes the Jebel Akhdar (Green Mountains) and fertility
|
|
|
|
|
Khanjar dagger superimposed on two crossed swords
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Nashid as-Salaam as-Sultani" (The Sultan's Anthem)
lyrics/music:
Rashid bin Uzayyiz al KHUSAIDI/James Frederick MILLS, arranged by Bernard EBBINGHAUS
note:
adopted 1932; new words were written after QABOOS bin Said al Said gained power in 1970; the anthem was first performed by the band of a British ship as a salute to the Sultan during a 1932 visit to Muscat; the bandmaster of the HMS Hawkins was asked to write a salutation to the Sultan on the occasion of his visiting the ship
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oman is a middle-income economy that is heavily dependent on dwindling oil resources. Because of declining reserves and a rapidly growing labor force, Muscat has actively pursued a development plan that focuses on diversification, industrialization, and privatization, with the objective of reducing the oil sector's contribution to GDP to 9% by 2020 and creating more jobs to employ the rising numbers of Omanis entering the workforce. Tourism and gas-based industries are key components of the government's diversification strategy. However, increases in social welfare benefits, particularly since the Arab Spring, will challenge the government's ability to effectively balance its budget if oil revenues decline. By using enhanced oil recovery techniques, Oman succeeded in increasing oil production, giving the country more time to diversify, and the increase in global oil prices through 2011 provided the government greater financial resources to invest in non-oil sectors.
|
|
|
|
|
$90.66 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
$86.38 billion (2011 est.)
$81.92 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$79.97 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
5.4% (2011 est.)
5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$28,500 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
$28,000 (2011 est.)
$27,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.5%
industry:
50.4%
services:
48.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
968,800
country comparison to the world: 143
note:
about 60% of the labor force is non-national (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: NA%
industry:
NA%
services:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
15% (2004 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
25.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $35.55 billion
expenditures:
$30.49 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
44.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
6.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
3.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
3.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
4.1% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
0.05% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
6.19% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.671 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
$7.971 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$71.42 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
$63.16 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$26.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
$23.18 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$19.72 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 63
$20.27 billion (31 December 2010)
$17.3 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
dates, limes, bananas, alfalfa, vegetables; camels, cattle; fish
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
$10.22 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$10.67 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$48.43 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
$47.09 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, reexports, fish, metals, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
China 30.2%, South Korea 10.9%, UAE 10.6%, Japan 10.4%, India 9.2%, Thailand 5.3%, US 4.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$23.37 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
$21.35 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, livestock, lubricants
|
|
|
|
|
UAE 27.7%, Japan 11.9%, US 6.1%, India 5.4%, China 4.2%, Saudi Arabia 4.1%, Germany 4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$15.87 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$14.37 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.768 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
$9.033 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
Omani rials (OMR) per US dollar -
0.3845 (2012 est.)
0.3845 (2011 est.)
0.3845 (2010 est.)
0.3845 (2009)
0.3845 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.59 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
15.34 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
4.202 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
890,500 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
701,600 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|
|
4.902 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
106,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
98,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
19,680 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
33,150 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
27.1 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
17.52 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
11.49 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
1.9 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
849.5 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
55.2 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
287,600 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
4.809 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modern system consisting of open-wire, microwave, and radiotelephone communication stations; limited coaxial cable; domestic satellite system with 8 earth stations
domestic:
fixed-line and mobile-cellular subscribership both increasing with fixed-line phone service gradually being introduced to remote villages using wireless local loop systems
international:
country code - 968; the Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable provide connectivity to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 state-run TV broadcaster; TV stations transmitting from Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen available via satellite TV; state-run radio operates multiple stations; first private radio station began operating in 2007 and 2 additional stations now operating (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.om
|
|
|
|
|
14,531 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
1.465 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
130 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12
over 3,047 m:
6
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 118
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
7
1,524 to 2,437 m:
51
914 to 1,523 m:
32
under 914 m:
26 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 107 km; gas 4,209 km; oil 3,558 km; refined products 263 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 53,430 km
country comparison to the world: 76
paved:
23,223 km (includes 1,384 km of expressways)
unpaved:
30,207 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5
country comparison to the world: 128
by type:
chemical tanker 1, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 3
registered in other countries:
15 (Malta 5, Panama 10) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Mina' Qabus, Salalah, Suhar
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sultan's Armed Forces (SAF): Royal Army of Oman, Royal Navy of Oman, Royal Air Force of Oman (al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Sultanat Oman) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 985,957
females age 16-49:
737,812 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 837,886
females age 16-49:
642,427 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 31,959
female:
30,264 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11.4% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Oman |
|
|
|
boundary agreement reportedly signed and ratified with UAE in 2003 for entire border, including Oman's Musandam Peninsula and Al Madhah exclave, but details of the alignment have not been made public
|
|
|
|
|
|