|
|
|
The Sudanese Republic and Senegal became independent of France in 1960 as the Mali Federation. When Senegal withdrew after only a few months, what formerly made up the Sudanese Republic was renamed Mali. Rule by dictatorship was brought to a close in 1991 by a military coup that ushered in a period of democratic rule. President Alpha KONARE won Mali's first two democratic presidential elections in 1992 and 1997. In keeping with Mali's two-term constitutional limit, he stepped down in 2002 and was succeeded by Amadou TOURE, who was elected to a second term in 2007 elections that were widely judged to be free and fair.
Malian returnees from Libya in 2011 exacerbated tensions in northern Mali and Tuareg ethnic militias started a rebellion in January 2012. Low-mid level soldiers, frustrated with the poor handling of the rebellion overthrew TOURE on 22 March. Coup leader Capt. Amadou Haya SANOGO and his junta under the mediation of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) returned power to a civilian administration in April with the appointment of interim President Dioncounda TRAORE. Interim Prime Minister Chieck Modibo DIARRA immediately appointed a unity cabinet. The post-coup chaos led to rebels expelling the Malian military from the three northern regions of the country, which remain under the control of a Tuareg militia, Ansar al-Din, and its terrorist group allies. Hundreds of thousands of northern Malians fled the violence to southern Mali and neighboring countries, exacerbating regional food insecurity in host communities. TRAORE was attacked by an angry mob in May and spent two months recovering in Paris, he returned in July. TRAORE and DIARRA announced a second unity government in August and in September called upon the international community to assist them in reclaiming land lost to rebels. SANOGO forced DIARRA to resign in December 2012; Django CISSOKO immediately replaced him and announced a third unity cabinet. The interim government is working with ECOWAS to organize negotiations with Tuareg rebels and the international community to plan a military intervention to retake the three northern regions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
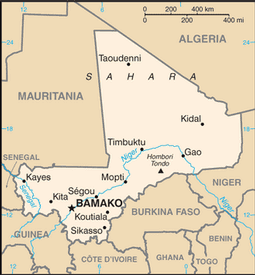
interior Western Africa, southwest of Algeria, north of Guinea, Cote d'Ivoire, and Burkina Faso, west of Niger
|
|
|
|
|
17 00 N, 4 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,240,192 sq km
country comparison to the world: 24
land:
1,220,190 sq km
water:
20,002 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than twice the size of Texas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7,243 km
border countries:
Algeria 1,376 km, Burkina Faso 1,000 km, Guinea 858 km, Cote d'Ivoire 532 km, Mauritania 2,237 km, Niger 821 km, Senegal 419 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
subtropical to arid; hot and dry (February to June); rainy, humid, and mild (June to November); cool and dry (November to February)
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat to rolling northern plains covered by sand; savanna in south, rugged hills in northeast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Senegal River 23 m
highest point:
Hombori Tondo 1,155 m
|
|
|
|
|
gold, phosphates, kaolin, salt, limestone, uranium, gypsum, granite, hydropower
note:
bauxite, iron ore, manganese, tin, and copper deposits are known but not exploited
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 3.76%
permanent crops:
0.03%
other:
96.21% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2,360 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
100 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6.55 cu km/yr (9%/1%/90%)
per capita:
484 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dust-laden harmattan haze common during dry seasons; recurring droughts; occasional Niger River flooding
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; inadequate supplies of potable water; poaching
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; divided into three natural zones: the southern, cultivated Sudanese; the central, semiarid Sahelian; and the northern, arid Saharan
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Mali |
|
|
|
noun: Malian(s)
adjective:
Malian
|
|
|
|
|
Mande 50% (Bambara, Malinke, Soninke), Peul 17%, Voltaic 12%, Songhai 6%, Tuareg and Moor 10%, other 5%
|
|
|
|
|
French (official), Bambara 80%, numerous African languages
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 90%, Christian 1%, indigenous beliefs 9%
|
|
|
|
|
15,494,466 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 47.8% (male 3,718,591/ female 3,689,889)
15-64 years:
49.2% (male 3,600,156/ female 4,017,716)
65 years and over:
3% (male 235,366/ female 232,748) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16.4 years
male:
16 years
female:
16.7 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.02% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
46.6 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
13.9 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
-5.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 36% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
4.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
BAMAKO (capital) 1.628 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.91 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
540 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
total: 108.7 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 2
male:
115.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
101.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 53.06 years
country comparison to the world: 207
male:
51.43 years
female:
54.73 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.35 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
7.5% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
0.049 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
0.57 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 54% of population
rural: 32% of population
total: 36% of population
unimproved:
urban: 46% of population
rural: 68% of population
total: 54% of population
|
|
|
|
|
1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
76,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
4,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
27.9% (2006)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
31.1%
male:
43.4%
female:
20.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8 years
male:
9 years
female:
7 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Mali
conventional short form:
Mali
local long form:
Republique de Mali
local short form:
Mali
former:
French Sudan and Sudanese Republic
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Bamako
geographic coordinates:
12 39 N, 8 00 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
8 regions (regions, singular - region), 1 district*; District de Bamako*, Gao, Kayes, Kidal, Koulikoro, Mopti, Segou, Sikasso, Tombouctou (Timbuktu)
|
|
|
|
|
22 September 1960 (from France)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 22 September (1960)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 12 January 1992
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on the French civil law model and influenced by customary law; judicial review of legislative acts in Constitutional Court
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: [Interim] President Dioncounda TRAORE (since 12 April 2012)
note:
in the aftermath of the March 2012 coup, deposed President TOURE, in a brokered deal, resigned to facilitate the naming of an interim president and transition back toward democratic rule
head of government:
[Interim] Prime Minister Django CISSOKO (since 11 December 2012)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 29 April 2007 (election scheduled for 29 April 2012 delayed indefinitely following the military coup); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Amadou Toumani TOURE reelected president; percent of vote - Amadou Toumani TOURE 71.2%, Ibrahim Boubacar KEITA 19.2%, other 9.6%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (147 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 1 and 22 July 2007 (July 2012 scheduled election indefinitely delayed after the military coup)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - ADP coalition 113 (ADEMA 51, URD 34, MPR 8, CNID 7, UDD 3, and other 10), FDR coalition 15 (RPM 11, PARENA 4), SADI 4, independent 15
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme
|
|
|
|
|
African Solidarity for Democracy and Independence or SADI [Oumar MARIKO, secretary general]; Alliance for Democracy or ADEMA [Diounconda TRAORE]; Alliance for Democracy and Progress or ADP (a coalition of political parties including ADEMA and URD formed in December 2006 to support the presidential candidacy of Amadou TOURE); Alliance for Democratic Change (political group comprised mainly of Tuareg from Mali's northern region); Convergence 2007 [Soumeylou Boubeye MAIGA]; Convergence for the development of Mali or CODEM [Housseyni GUINDO]; Front for Democracy and the Republic or FDR (a coalition of political parties including RPM and PARENA formed to oppose the presidential candidacy of Amadou TOURE); National Congress for Democratic Initiative or CNID [Mountaga TALL]; Party for Democracy and Progress or PDP [Mady KONATE]; Party for National Renewal or PARENA [Tiebile DRAME]; Patriotic Movement for Renewal or MPR [Choguel MAIGA]; Rally for Democracy and Labor or RDT [Amadou Ali NIANGADOU]; Rally for Mali or RPM [Ibrahim Boubacar KEITA]; Sudanese Union/African Democratic Rally or US/RDA [Mamadou Basir GOLOGO]; Union for Democracy and Development or UDD [Moussa Balla COULIBALY]; Union for Republic and Democracy or URD [Soumaila CISSE]
|
|
|
|
|
other: the army; Islamic authorities; state-run cotton company CMDT
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, ECOWAS, EITI (compliant country), FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Al Maamoun Baba Lamine KEITA
chancery:
2130 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 332-2249, 939-8950
FAX:
[1] (202) 332-6603
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mary Beth LEONARD
embassy:
located just off the Roi Bin Fahad Aziz Bridge just west of the Bamako central district
mailing address:
ACI 2000, Rue 243, Porte 297, Bamako
telephone:
[223] 270-2300
FAX:
[223] 270-2479
|
|
|
|
|
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), yellow, and red
note:
uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the colors from left to right are the same as those of neighboring Senegal (which has an additional green central star) and the reverse of those on the flag of neighboring Guinea
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Le Mali" (Mali)
lyrics/music:
Seydou Badian KOUYATE/Banzoumana SISSOKO
note:
adopted 1962; the anthem is also known as "Pour L'Afrique et pour toi, Mali" (For Africa and for You, Mali) and "A ton appel Mali" (At Your Call, Mali)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Among the 25 poorest countries in the world, Mali is a landlocked country highly dependent on gold mining and agricultural exports for revenue. The country's fiscal status fluctuates with gold and agricultural commodity prices and the harvest. Mali remains dependent on foreign aid. Economic activity is largely confined to the riverine area irrigated by the Niger River and about 65% of its land area is desert or semidesert. About 10% of the population is nomadic and about 80% of the labor force is engaged in farming and fishing. Industrial activity is concentrated on processing farm commodities. The government in 2011 completed an IMF extended credit facility program that has helped the economy grow, diversify, and attract foreign investment. Mali is developing its cotton and iron ore extraction industries to diversify foreign exchange revenue away from gold. Mali has invested in tourism but security issues are hurting the industry. Mali experienced economic growth of about 5% per year between 1996-2010, but the global recession and a military coup caused a decline in output in 2012. The interim government slashed public spending in the context of a declining state of security and declining international aid.
|
|
|
|
|
$17.35 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
$18.17 billion (2011 est.)
$17.69 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$9.603 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-4.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
2.7% (2011 est.)
5.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1,100 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
$1,100 (2011 est.)
$1,200 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 36.9%
industry:
23.4%
services:
39.7% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.241 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 80%
industry and services:
20% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
30% (2004 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
36.1% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.5%
highest 10%:
25.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
40.1 (2001)
country comparison to the world: 59
50.5 (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $1.391 billion
expenditures:
$2.107 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
14.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
|
|
|
|
|
-7.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|
|
23.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
23.3% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
2.9% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
16% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
4.25% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
9.3% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
9% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.382 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
$2.156 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.401 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
$2.929 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.938 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
$1.669 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
cotton, millet, rice, corn, vegetables, peanuts; cattle, sheep, goats
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
-$1.421 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
-$1.301 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.557 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
$2.453 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
cotton, gold, livestock
|
|
|
|
|
China 31%, South Korea 14.5%, Indonesia 12.2%, Thailand 6.3%, Malaysia 5.4%, Bangladesh 5% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.209 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
$3.026 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, machinery and equipment, construction materials, foodstuffs, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
Senegal 14.9%, France 11.6%, China 8.2%, Cote dIvoire 6.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.725 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
$2.652 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.556 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
$2.351 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$77.44 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
$48 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -
514.1 (2012 est.)
471.87 (2011 est.)
495.28 (2010 est.)
472.19 (2009)
493.51 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
520 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
483.6 million kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
|
|
|
|
|
304,000 kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
48.4% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
|
|
|
|
|
51.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
4,994 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
|
|
|
|
|
4,568 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
893,700 Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104,700 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
10.822 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: domestic system unreliable but improving; increasing use of local radio loops to extend network coverage to remote areas
domestic:
fixed-line subscribership remains less than 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular subscribership has increased sharply to about 70 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 223; satellite communications center and fiber-optic links to neighboring countries; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean, 1 Indian Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
national public TV broadcaster; 2 privately-owned companies provide subscription services to foreign multi-channel TV packages; national public radio broadcaster supplemented by a large number of privately-owned and community broadcast stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are available (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.ml
|
|
|
|
|
437 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 187
|
|
|
|
|
249,800 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 593 km
country comparison to the world: 109
narrow gauge:
593 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18,912 km
country comparison to the world: 113
paved:
3,597 km
unpaved:
15,315 km (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
1,800 km (downstream of Koulikoro; low water levels on the River Niger cause problems in dry years; in the months before the rainy season the river is not navigable by commercial vessels) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
Koulikoro
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Malian Armed Forces: Army (Armee de Terre), Republic of Mali Air Force (Force Aerienne de la Republique du Mali, FARM), National Guard (Garde National du Mali) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for selective compulsory and voluntary military service; conscript service obligation - 2 years (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,848,412
females age 16-49:
2,981,106 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,825,779
females age 16-49:
1,968,563 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 158,031
female:
159,733 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Mali |
|
|
|
demarcation is underway with Burkina Faso
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 12,442 (Mauritania) (2011)
IDPs:
228,918 (Tuareg rebellion in 2012) (2013)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Mali is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; women and girls are forced into domestic servitude, agricultural labor, and support roles in gold mines, as well as subjected to sex trafficking; Malian boys are found in conditions of forced labor in agricultural settings, gold mines, and the informal commercial sector, as well as forced begging both within mali and neighboring countries; Malians and other Africans who travel through Mali to Mauritania, Algeria, or Libya, in hopes of reaching Europe are particularly at risk of becoming victims of human trafficking; men and boys, primarily of Songhai ethnicity, are subjected to the longstanding practice of debt bondage in the salt mines of Taoudenni in northern Mali; some members of Mali's black Tamachek community are subjected to traditional slavery-related practices, and this involuntary servitude reportedly has extended to their children
tier rating:
Tier 2 - the Government of Mali does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government acknowledged that human trafficking is a problem in Mali, but it did not demonstrate significant efforts to prosecute and convict trafficking offenders; Mali was not placed on Tier 3 because the government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is devoting sufficient resources to implement that plan (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
|