|
|
|
Formerly part of the Ottoman Empire, Iraq was occupied by Britain during the course of World War I; in 1920, it was declared a League of Nations mandate under UK administration. In stages over the next dozen years, Iraq attained its independence as a kingdom in 1932. A "republic" was proclaimed in 1958, but in actuality a series of strongmen ruled the country until 2003. The last was SADDAM Husayn. Territorial disputes with Iran led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war (1980-88). In August 1990, Iraq seized Kuwait but was expelled by US-led, UN coalition forces during the Gulf War of January-February 1991. Following Kuwait's liberation, the UN Security Council (UNSC) required Iraq to scrap all weapons of mass destruction and long-range missiles and to allow UN verification inspections. Continued Iraqi noncompliance with UNSC resolutions over a period of 12 years led to the US-led invasion of Iraq in March 2003 and the ouster of the SADDAM Husayn regime. US forces remained in Iraq under a UNSC mandate through 2009 and under a bilateral security agreement thereafter, helping to provide security and to train and mentor Iraqi security forces. In October 2005, Iraqis approved a constitution in a national referendum and, pursuant to this document, elected a 275-member Council of Representatives (COR) in December 2005. The COR approved most cabinet ministers in May 2006, marking the transition to Iraq's first constitutional government in nearly a half century. In January 2009, Iraq held elections for provincial councils in all governorates except for the three governorates comprising the Kurdistan Regional Government and Kirkuk Governorate. Iraq held a national legislative election in March 2010 - choosing 325 legislators in an expanded COR - and, after nine months of deadlock the COR approved the new government in December 2010. Nearly nine years after the start of the Second Gulf War in Iraq, US military operations there ended in mid-December 2011.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait
|
|
|
|
|
33 00 N, 44 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 438,317 sq km
country comparison to the world: 59
land:
437,367 sq km
water:
950 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than twice the size of Idaho
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,650 km
border countries:
Iran 1,458 km, Jordan 181 km, Kuwait 240 km, Saudi Arabia 814 km, Syria 605 km, Turkey 352 km
|
|
|
|
|
58 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf:
not specified
|
|
|
|
|
mostly desert; mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers; northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding in central and southern Iraq
|
|
|
|
|
mostly broad plains; reedy marshes along Iranian border in south with large flooded areas; mountains along borders with Iran and Turkey
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
unnamed peak; 3,611 m; note - this peak is neither Gundah Zhur 3,607 m nor Kuh-e Hajji-Ebrahim 3,595 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, phosphates, sulfur
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 13.12%
permanent crops:
0.61%
other:
86.27% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
35,250 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
96.4 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 42.7 cu km/yr (3%/5%/92%)
per capita:
1,482 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
dust storms; sandstorms; floods
|
|
|
|
|
government water control projects have drained most of the inhabited marsh areas east of An Nasiriyah by drying up or diverting the feeder streams and rivers; a once sizable population of Marsh Arabs, who inhabited these areas for thousands of years, has been displaced; furthermore, the destruction of the natural habitat poses serious threats to the area's wildlife populations; inadequate supplies of potable water; development of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers system contingent upon agreements with upstream riparian Turkey; air and water pollution; soil degradation (salination) and erosion; desertification
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on Shatt al Arab waterway and at the head of the Persian Gulf
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Iraq |
|
|
|
noun: Iraqi(s)
adjective:
Iraqi
|
|
|
|
|
Arab 75%-80%, Kurdish 15%-20%, Turkoman, Assyrian, or other 5%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic (official), Kurdish (official), Turkmen (a Turkish dialect) and Assyrian (Neo-Aramaic) are official in areas where they constitute a majority of the population), Armenian
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (official) 97% (Shia 60%-65%, Sunni 32%-37%), Christian or other 3%
note:
while there has been voluntary relocation of many Christian families to northern Iraq, recent reporting indicates that the overall Christian population may have dropped by as much as 50 percent since the fall of the Saddam HUSSEIN regime in 2003, with many fleeing to Syria, Jordan, and Lebanon
|
|
|
|
|
31,129,225 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 37.6% (male 5,959,562/ female 5,751,970)
15-64 years:
59.3% (male 9,355,176/ female 9,094,953)
65 years and over:
3.1% (male 450,516/ female 517,048) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.1 years
male:
21 years
female:
21.2 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.345% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
28.19 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
4.73 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 66% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.6% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
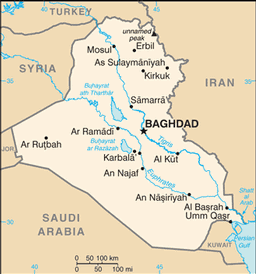
BAGHDAD (capital) 5.751 million; Mosul 1.447 million; Erbil 1.009 million; Basra 923,000; As Sulaymaniyah 836,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.87 male(s)/female
total population:
1.03 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
63 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
total: 40.25 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 62
male:
44.43 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
35.86 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 70.85 years
country comparison to the world: 145
male:
69.41 years
female:
72.35 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.58 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
9.7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
0.69 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 76% of population
rural: 66% of population
total: 73% of population
unimproved:
urban: 24% of population
rural: 34% of population
total: 27% of population
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
7.1% (2006)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
78.2%
male:
86%
female:
70.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10 years
male:
11 years
female:
8 years (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Iraq
conventional short form:
Iraq
local long form:
Jumhuriyat al-Iraq/Komar-i Eraq
local short form:
Al Iraq/Eraq
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Baghdad
geographic coordinates:
33 20 N, 44 24 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
18 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah (Arabic); parezgakan, singular - parezga (Kurdish)) and 1 region*; Al Anbar; Al Basrah; Al Muthanna; Al Qadisiyah (Ad Diwaniyah); An Najaf; Arbil (Erbil) (Arabic), Hewler (Kurdish); As Sulaymaniyah (Arabic), Slemani (Kurdish); Babil; Baghdad; Dahuk (Arabic), Dihok (Kurdish); Dhi Qar; Diyala; Karbala'; Kirkuk; Kurdistan Regional Government*; Maysan; Ninawa; Salah ad Din; Wasit
|
|
|
|
|
3 October 1932 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration); note - on 28 June 2004 the Coalition Provisional Authority transferred sovereignty to the Iraqi Interim Government
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day, July 14 (1958); note - the Government of Iraq has yet to declare an official national holiday but still observes Republic Day
|
|
|
|
|
ratified 15 October 2005 (subject to review by the Constitutional Review Committee and a possible public referendum)
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of civil and Islamic law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Jalal TALABANI (since 6 April 2005); Vice Presidents Tariq al-HASHIMI and Khudayr Musa Jafar Abbas al-KHUZAI
head of government:
Prime Minister Nuri al-MALIKI (since 20 May 2006)
cabinet:
The Council of Ministers consists of the prime minister and cabinet ministers he proposes; approved by an absolute majority vote by the Council of Representatives
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by Council of Representatives (parliament) to serve a four-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11 November 2010 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
President Jalal TALABANI reelected on 11 November 2010; parliamentary vote count on second ballot - 195 votes; Nuri al-MALIKI reselected prime minister
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Council of Representatives (325 seats consisting of 317 members elected by an optional open-list and representing a specific governorate, proportional representation system and 8 seats reserved for minorities; members serve four-year terms); note - Iraq's Constitution calls for the establishment of an upper house, the Federation Council
elections:
last held on 7 March 2010 for an enlarged 325-seat parliament (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
Council of Representatives - percent of vote by coalition - Iraqi National Movement 25.9%, State of Law coalition 25.8%, Iraqi National Alliance 19.4%, Kurdistan Alliance 15.3%, Goran (Change) List 4.4%, Tawafuq Front 2.7%, Iraqi Unity Alliance 2.9%, Kurdistan Islamic Union 2.3%, Kurdistan Islamic Group 1.4%; seats by coalition - NA
|
|
|
|
|
the Iraq Constitution calls for the federal judicial power to be comprised of the Higher Judicial Council, Federal Supreme Court, Federal Court of Cassation, Public Prosecution Department, Judiciary Oversight Commission and other federal courts that are regulated in accordance with the law
|
|
|
|
|
Badr Organization [Hadi al-AMIRI]; Da'wa Party [Prime Minister Nuri al-MALIKI]; Da'wa Tanzim [Hashim al-MUSAWI branch]; Da-wa Tanzim [Abd al-Karim al-ANZI branch]; Fadilah Party [Hasan al-SHAMMARI and Ammar TUAMA]; Goran (Change) List [Nushirwan MUSTAFA]; Iraqi Covenant Gathering [Ahmad Abd al-Ghafur al-SAMARRAI]; Iraqi Constitutional Party [Jawad al-BULANI]; Iraqi Front for National Dialogue [Deputy Prime Minister Salih al-MUTLAQ]; Iraqi Islamic Party or IIP [Usama al-TIKRITI]; Iraqi Justice and Reform Movement [Shaykh Abdallah al-YAWR]; Iraqi National Congress or INC [Ahmad CHALABI]; Iraqi National Accord or INA [Ayad ALLAWI]; Islamic Supreme Council of Iraq or ISCI [Ammar al-HAKIM]; Kurdistan Democratic Party or KDP [Kurdistan Regional Government President Masud BARZANI]; Future National Gathering [Finance Minister Rafi al-ISSAWI]; National Iraqiyun Gathering [Usama al-NUJAYFI]; National Movement for Reform and Development [Jamal al-KARBULI]; National Reform Trend [former Prime Minister Ibrahim al-JAFARI]; Patriotic Union of Kurdistan or PUK [President Jalal TALABANI]; Renewal List [Vice President Tariq al-HASHIMI]; Sadrist Trend [Muqtada al-SADR]; Sahawa al-Iraq [Ahmad al-RISHAWI]
note:
numerous smaller local, tribal, and minority parties
|
|
|
|
|
Sunni militias; Shia militias, some associated with political parties
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, CICA, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jabir Habib JABIR
chancery:
3421 Massachusetts Ave, NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 742-1600
FAX:
[1] (202) 333-1129
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Robert Stephen BEECROFT
embassy:
Baghdad
mailing address:
APO AE 09316
telephone:
1-240-553-0589 ext. 5340 or 5635; note - Consular Section
FAX:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black; the Takbir (Arabic expression meaning "God is great") in green Arabic script is centered in the white band; the band colors derive from the Arab Liberation flag and represent oppression (black), overcome through bloody struggle (red), to be replaced by a bright future (white); the Council of Representatives approved this flag in 2008 as a compromise temporary replacement for the Ba'athist Saddam-era flag
note:
similar to the flag of Syria, which has two stars but no script, Yemen, which has a plain white band, and that of Egypt, which has a gold Eagle of Saladin centered in the white band
|
|
|
|
|
golden eagle
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Mawtini" (My Homeland)
lyrics/music:
Ibrahim TOUQAN/Mohammad FLAYFEL
note:
adopted 2004; following the ousting of Saddam HUSSEIN, Iraq adopted "Mawtini," a popular folk song throughout the Arab world, which also serves as an unofficial anthem of the Palestinian people
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An improving security environment and foreign investment are helping to spur economic activity, particularly in the energy, construction, and retail sectors. Broader economic development, long-term fiscal health, and sustained improvements in the overall standard of living still depend on the central government passing major policy reforms. Iraq's largely state-run economy is dominated by the oil sector, which provides more than 90% of government revenue and 80% of foreign exchange earnings. Iraq in 2012 boosted oil exports to a 30-year high of 2.6 million barrels per day, a significant increase from Iraq's average of 2.2 million in 2011. Government revenues increased as global oil prices remained persisently high for much of 2012. Iraq's contracts with major oil companies have the potential to further expand oil exports and revenues, but Iraq will need to make significant upgrades to its oil processing, pipeline, and export infrastructure to enable these deals to reach their economic potential. Iraq is making slow progress enacting laws and developing the institutions needed to implement economic policy, and political reforms are still needed to assuage investors' concerns regarding the uncertain business climate, which may have been harmed by the November 2012 standoff between Baghdad and Erbil. The government of Iraq is eager to attract additional foreign direct investment, but it faces a number of obstacles including a tenuous political system and concerns about security and societal stability. Rampant corruption, outdated infrastructure, insufficient essential services, skilled labor shortages, and antiquated commercial laws stifle investment and continue to constrain growth of private, nonoil sectors. In 2010, Baghdad signed agreements with both the IMF and World Bank for conditional aid programs designed to help strengthen Iraq's economic institutions. Iraq is considering a package of laws to establish a modern legal framework for the oil sector and a mechanism to equitably divide oil revenues within the nation, although these reforms are still under contentious and sporadic negotiation. Political and economic tensions between Baghdad and local governments have led some provincial councils to use their budgets to independently promote and facilitate investment at the local level. The Central Bank has successfully held the exchange rate at about 1,170 Iraqi dinar/US dollar since January 2009. Inflation has remained under control since 2006 as security improved. However, Iraqi leaders remain hard pressed to translate macroeconomic gains into an improved standard of living for the Iraqi populace. Unemployment remains a problem throughout the country despite a bloated public sector. Encouraging private enterprise through deregulation would make it easier for Iraqi citizens and foreign investors to start new businesses. Rooting out corruption and implementing reforms - such as restructuring banks and developing the private sector - would be important steps in this direction.
|
|
|
|
|
$155.4 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
$141 billion (2011 est.)
$129.6 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$130.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.2% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
8.9% (2011 est.)
3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4,600 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
$4,300 (2011 est.)
$4,000 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 8.7%
industry:
63.8%
services:
25.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.9 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 21.6%
industry:
18.7%
services:
59.8% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
16% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
15% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
25% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.6%
highest 10%:
25.7% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.1% of GDP (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $104.4 billion
expenditures:
$98.49 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
79.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
6.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
5.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6% (December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 61
6% (December 2011)
|
|
|
|
|
14.13% (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
14.35% (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$62.19 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
$53.52 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$71.48 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
$61.81 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.779 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
$1.727 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4 billion (9 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 93
$2.6 billion (31 July 2010)
$2 billion (31 July 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, barley, rice, vegetables, dates, cotton; cattle, sheep, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
4.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
|
|
|
|
|
$20.63 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$21.68 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$88.27 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
$79.68 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil 84%, crude materials excluding fuels, food and live animals
|
|
|
|
|
India 22.5%, US 22.3%, China 13.4%, South Korea 11.7%, Japan 4.8%, Netherlands 4.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$56.89 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
$47.8 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
food, medicine, manufactures
|
|
|
|
|
Turkey 25.3%, Syria 18.3%, China 11.7%, US 7.4%, South Korea 4.7% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$61.84 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$58.96 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$50.26 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
$50.79 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Iraqi dinars (IQD) per US dollar -
1,168 (2012 est.)
1,170 (2011 est.)
1,170 (2010 est.)
1,170 (2009)
1,176 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.4 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
35.12 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
|
|
|
|
|
12.28 billion kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
10.11 million kW (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
69% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
31% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 million bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
2.6 million bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
143.1 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
410,500 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
818,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
|
|
|
|
|
144,100 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
1.303 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
|
|
|
|
|
3.171 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
118.3 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.794 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
27 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: the 2003 liberation of Iraq severely disrupted telecommunications throughout Iraq including international connections; widespread government efforts to rebuild domestic and international communications through fiber optic links are in progress; the mobile cellular market has expanded rapidly to some 27 million subscribers by the end of 2012
domestic:
repairs to switches and lines destroyed during 2003 continue; additional switching capacity is improving access; 3 GSM operators since 2007 have expanded beyond their regional roots and offer near country-wide access to second-generation services; third-generation mobile services are not available nationwide; wireless local loop is available in some metropolitan areas and additional licenses have been issued with the hope of overcoming the lack of fixed-line infrastructure
international:
country code - 964; satellite earth stations - 4 (2 Intelsat - 1 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean, 1 Intersputnik - Atlantic Ocean region, and 1 Arabsat (inoperative)); local microwave radio relay connects border regions to Jordan, Kuwait, Syria, and Turkey; international terrestrial fiber-optic connections have been established with Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Kuwait, Jordan, and Iran; links to the Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and the Gulf Bridge International (GBI) submarine fiber-optic cables are planned
|
|
|
|
|
the number of private radio and TV stations has increased rapidly since 2003; government-owned TV and radio stations are operated by the publicly-funded Iraqi Public Broadcasting Service; private broadcast media are mostly linked to political, ethnic, or religious groups; satellite TV is available to an estimated 70% of viewers and many of the broadcasters are based abroad; transmissions of multiple international radio broadcasters are accessible (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.iq
|
|
|
|
|
26 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 219
|
|
|
|
|
325,900 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
total: 75
over 3,047 m:
20
2,438 to 3,047 m:
36
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
8 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 29
over 3,047 m:
3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
4
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
13
under 914 m:
6 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
20 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 2,447 km; liquid petroleum gas 918 km; oil 5,104 km; refined products 1,637 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,272 km
country comparison to the world: 66
standard gauge:
2,272 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 44,900 km
country comparison to the world: 81
paved:
37,851 km
unpaved:
7,049 km (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
5,279 km (the Euphrates River (2,815 km), Tigris River (1,899 km), and Third River (565 km) are the principal waterways) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2
country comparison to the world: 142
by type:
petroleum tanker 2
registered in other countries:
2 (Marshall Islands 2) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Al Basrah, Khawr az Zubayr, Umm Qasr
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Counterterrorism Service Forces: Counterterrorism Command; Iraqi Special Operations Forces (ISOF); Ministry of Defense Forces: Iraqi Army (includes Army Aviation Directorate, former National Guard Iraqi Intervention Forces, and Strategic Infrastructure Battalions), Iraqi Navy (former Iraqi Coastal Defense Force, includes Iraq Marine Force), Iraqi Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Iraqiya) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18-40 years of age for voluntary military service (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 7,767,329
females age 16-49:
7,461,766 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 6,591,185
females age 16-49:
6,421,717 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 332,194
female:
322,010 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.6% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Iraq |
|
|
|
approximately two million Iraqis have fled the conflict in Iraq, with the majority taking refuge in Syria and Jordan, and lesser numbers to Egypt, Lebanon, Iran, and Turkey; Iraq's lack of a maritime boundary with Iran prompts jurisdiction disputes beyond the mouth of the Shatt al Arab in the Persian Gulf; Turkey has expressed concern over the autonomous status of Kurds in Iraq
|
|
|
|
|
15,606 (Turkey); 10,798 (West Bank and Gaza Strip); 7,989 (Iran) (2011); 77,415 (Syria) (2013)
IDPs:
1.3 million (since 2006 from ethno-sectarian violence) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
|