|
|
|
Known as Persia until 1935, Iran became an Islamic republic in 1979 after the ruling monarchy was overthrown and Shah Mohammad Reza PAHLAVI was forced into exile. Conservative clerical forces established a theocratic system of government with ultimate political authority vested in a learned religious scholar referred to commonly as the Supreme Leader who, according to the constitution, is accountable only to the Assembly of Experts - a popularly elected 86-member body of clerics. US-Iranian relations have been strained since a group of Iranian students seized the US Embassy in Tehran on 4 November 1979 and held embassy personnel hostages until 20 January 1981. During 1980-88, Iran fought a bloody, indecisive war with Iraq that eventually expanded into the Persian Gulf and led to clashes between US Navy and Iranian military forces between 1987 and 1988. Iran has been designated a state sponsor of terrorism for its activities in Lebanon and elsewhere in the world and remains subject to US, UN, and EU economic sanctions and export controls because of its continued involvement in terrorism and its nuclear weapons ambitions. Following the election of reformer Hojjat ol-Eslam Mohammad KHATAMI as president in 1997 and a reformist Majles (legislature) in 2000, a campaign to foster political reform in response to popular dissatisfaction was initiated. The movement floundered as conservative politicians, through the control of unelected institutions, prevented reform measures from being enacted and increased repressive measures. Starting with nationwide municipal elections in 2003 and continuing through Majles elections in 2004, conservatives reestablished control over Iran's elected government institutions, which culminated with the August 2005 inauguration of hardliner Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD as president. His controversial reelection in June 2009 sparked nationwide protests over allegations of electoral fraud. The UN Security Council has passed a number of resolutions (1696 in July 2006, 1737 in December 2006, 1747 in March 2007, 1803 in March 2008, and 1835 in September 2008 and 1929 in June 2010) calling for Iran to suspend its uranium enrichment and reprocessing activities and comply with its IAEA obligations and responsibilities. Resolutions 1737, 1747, 1803, and 1929 subject a number of Iranian individuals and entities involved in Iran's nuclear and ballistic missile programs to sanctions. Additionally, several Iranian entities are subject to US sanctions under Executive Order 13224 designation for support of terrorism and Executive Order 13382 designation for proliferation activities. In mid-February 2011, opposition activists conducted the largest antiregime rallies since December 2009, spurred by the success of uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt. Protester turnout probably was at most tens of thousands and security forces were deployed to disperse protesters. Additional protests in March 2011 failed to elicit significant participation largely because of the robust security response, although discontent still smolders. Deteriorating economic conditions due primarily to government mismanagement and international sanctions prompted at least two major economically-based protests in July and October 2012.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Middle East, bordering the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf, and the Caspian Sea, between Iraq and Pakistan
|
|
|
|
|
32 00 N, 53 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,648,195 sq km
country comparison to the world: 18
land:
1,531,595 sq km
water:
116,600 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Alaska
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,440 km
border countries:
Afghanistan 936 km, Armenia 35 km, Azerbaijan-proper 432 km, Azerbaijan-Naxcivan exclave 179 km, Iraq 1,458 km, Pakistan 909 km, Turkey 499 km, Turkmenistan 992 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,440 km; note - Iran also borders the Caspian Sea (740 km)
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
bilateral agreements or median lines in the Persian Gulf
continental shelf:
natural prolongation
|
|
|
|
|
mostly arid or semiarid, subtropical along Caspian coast
|
|
|
|
|
rugged, mountainous rim; high, central basin with deserts, mountains; small, discontinuous plains along both coasts
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
highest point:
Kuh-e Damavand 5,671 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, coal, chromium, copper, iron ore, lead, manganese, zinc, sulfur
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 9.78%
permanent crops:
1.29%
other:
88.93% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
89,930 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
137.5 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 72.88 cu km/yr (7%/2%/91%)
per capita:
1,048 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
periodic droughts, floods; dust storms, sandstorms; earthquakes
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution, especially in urban areas, from vehicle emissions, refinery operations, and industrial effluents; deforestation; overgrazing; desertification; oil pollution in the Persian Gulf; wetland losses from drought; soil degradation (salination); inadequate supplies of potable water; water pollution from raw sewage and industrial waste; urbanization
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on the Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz, which are vital maritime pathways for crude oil transport
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Iran |
|
|
|
noun: Iranian(s)
adjective:
Iranian
|
|
|
|
|
Persian 61%, Azeri 16%, Kurd 10%, Lur 6%, Baloch 2%, Arab 2%, Turkmen and Turkic tribes 2%, other 1%
|
|
|
|
|
Persian (official) 53%, Azeri Turkic and Turkic dialects 18%, Kurdish 10%, Gilaki and Mazandarani 7%, Luri 6%, Balochi 2%, Arabic 2%, other 2%
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (official) 98% (Shia 89%, Sunni 9%), other (includes Zoroastrian, Jewish, Christian, and Baha'i) 2%
|
|
|
|
|
78,868,711 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 23.9% (male 9,654,957/ female 9,174,944)
15-64 years:
71.1% (male 28,498,325/ female 27,556,750)
65 years and over:
5.1% (male 1,871,299/ female 2,112,436) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 27.4 years
male:
27.1 years
female:
27.6 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.247% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
18.52 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
5.94 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
-0.11 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 71% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.9% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
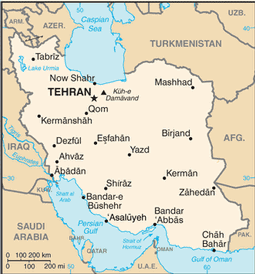
TEHRAN (capital) 7.19 million; Mashhad 2.592 million; Esfahan 1.704 million; Karaj 1.531 million; Tabriz 1.459 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.89 male(s)/female
total population:
1.03 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
21 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.11 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 57
male:
41.61 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
40.58 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 70.35 years
country comparison to the world: 147
male:
68.84 years
female:
71.93 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.87 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
0.89 physicians/1,000 population (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1.38 beds/1,000 population (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 86% of population
rural: 78% of population
total: 83% of population
unimproved:
urban: 14% of population
rural: 22% of population
total: 17% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
92,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
6,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases:
Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever and malaria
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
14.2% (2005)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
4.7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
77%
male:
83.5%
female:
70.4% (2002 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13 years
male:
13 years
female:
13 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23%
country comparison to the world: 38
male:
20.2%
female:
34% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Iran
conventional short form:
Iran
local long form:
Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Iran
local short form:
Iran
former:
Persia
|
|
|
|
|
theocratic republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Tehran
geographic coordinates:
35 42 N, 51 25 E
time difference:
UTC+3.5 (8.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins fourth Tuesday in March; ends fourth Thursday in September
|
|
|
|
|
31 provinces (ostanha, singular - ostan); Alborz, Ardabil, Azarbayjan-e Gharbi (West Azerbaijan), Azarbayjan-e Sharqi (East Azerbaijan), Bushehr, Chahar Mahal va Bakhtiari, Esfahan, Fars, Gilan, Golestan, Hamadan, Hormozgan, Ilam, Kerman, Kermanshah, Khorasan-e Jonubi (South Khorasan), Khorasan-e Razavi (Razavi Khorasan), Khorasan-e Shomali (North Khorasan), Khuzestan, Kohgiluyeh va Bowyer Ahmad, Kordestan, Lorestan, Markazi, Mazandaran, Qazvin, Qom, Semnan, Sistan va Baluchestan, Tehran, Yazd, Zanjan
|
|
|
|
|
1 April 1979 (Islamic Republic of Iran proclaimed); notable earlier dates: ca. 625 B.C. (unification of Iran under the Medes); ca. A.D. 1501 (Iran reunified under the Safavids); 12 December 1925 (modern Iran established under the Pahlavis)
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day, 1 April (1979)
|
|
|
|
|
2-3 December 1979; revised 1989
note:
the revision in 1989 expanded powers of the presidency and eliminated the prime ministership
|
|
|
|
|
religious legal system based on sharia law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Supreme Leader Ali Hoseini-KHAMENEI (since 4 June 1989)
head of government:
President Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD (since 3 August 2005); First Vice President Mohammad Reza RAHIMI (since 13 September 2009)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers selected by the president with legislative approval; the Supreme Leader has some control over appointments to the more sensitive ministries
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
note:
also considered part of the Executive branch of government are three oversight bodies: 1) Assembly of Experts (Majles-e Khoebregan), a popularly elected body charged with determining the succession of the Supreme Leader, reviewing his performance, and deposing him if deemed necessary; 2) Expediency Council or the Council for the Discernment of Expediency (Majma-ye- Tashkhis-e -Maslahat-e- Nezam) exerts supervisory authority over the executive, judicial, and legislative branches and resolves legislative issues when the Majles and the Council of Guardians disagree and since 1989 has been used to advise national religious leaders on matters of national policy; in 2005 the Council's powers were expanded to act as a supervisory body for the government; 3) Council of Guardians of the Constitution or Council of Guardians or Guardians Council (Shora-ye Negban-e Qanon-e Asasi) determines whether proposed legislation is both constitutional and faithful to Islamic law, vets candidates in popular elections for suitability, and supervises national elections
elections:
supreme leader appointed for life by the Assembly of Experts; president elected by popular vote for a four-year term (eligible for a second term and additional nonconsecutive term); election last held on 14 June 2009 (next presidential election slated for June 2013)
election results:
Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD reelected president; percent of vote - Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD 62.6%, Mir-Hosein MUSAVI-Khamenei 33.8%, other 3.6%; voter turnout 85% (according to official figures published by the government)
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Islamic Consultative Assembly or Majles-e Shura-ye Eslami or Majles (290 seats; members elected by popular vote from single and multimember districts to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 2 March 2012 (first round); second round held on 4 May 2012; (next election to be held in 2016)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA
|
|
|
|
|
The Supreme Court (Qeveh Qazaieh) and the four-member High Council of the Judiciary have a single head and overlapping responsibilities; together they supervise the enforcement of all laws and establish judicial and legal policies; lower courts include a special clerical court, a revolutionary court, and a special administrative court
|
|
|
|
|
Note: formal political parties are a relatively new phenomenon in Iran and most conservatives still prefer to work through political pressure groups rather than parties; often political parties or coalitions are formed prior to elections and disbanded soon thereafter; a loose pro-reform coalition called the 2nd Khordad Front, which includes political parties as well as less formal groups and organizations, achieved considerable success in elections for the sixth Majles in early 2000; groups in the coalition included the Islamic Iran Participation Front (IIPF), Executives of Construction Party (Kargozaran), Solidarity Party, Islamic Labor Party, Mardom Salari, Mojahedin of the Islamic Revolution Organization (MIRO), and Militant Clerics Society (MCS; Ruhaniyun); the coalition participated in the seventh Majles elections in early 2004 but boycotted them after 80 incumbent reformists were disqualified; following his defeat in the 2005 presidential elections, former MCS Secretary General and sixth Majles Speaker Mehdi KARUBI formed the National Trust Party; a new conservative group, Islamic Iran Developers Coalition (Abadgaran), took a leading position in the new Majles after winning a majority of the seats in February 2004; ahead of the 2008 Majles elections, traditional and hardline conservatives attempted to close ranks under the United Front of Principlists and the Broad Popular Coalition of Principlists; several reformist groups, such as the MIRO and the IIPF, also came together as a reformist coalition in advance of the 2008 Majles elections; the IIPF has repeatedly complained that the overwhelming majority of its candidates were unfairly disqualified from the 2008 elections
|
|
|
|
|
groups that generally support the Islamic Republic: Ansar-e Hizballah-; Followers of the Line of the Imam and the Leader; Islamic Coalition Party (Motalefeh); Islamic Engineers Society; Tehran Militant Clergy Association (MCA; Ruhaniyat)
active pro-reform student group:
Office of Strengthening Unity (OSU)
opposition groups:
Freedom Movement of Iran; Green Path movement [Mehdi KARUBI, Mir-Hosein MUSAVI]; Marz-e Por Gohar; National Front; various ethnic and monarchist organizations
armed political groups repressed by the government:
Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan (KDPI); Jundallah; Komala; Mojahedin-e Khalq Organization (MEK or MKO); People's Fedayeen; People's Free Life Party of Kurdistan (PJAK)
|
|
|
|
|
CICA, CP, D-8, ECO, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, SAARC (observer), SCO (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
none; note - Iran has an Interests Section in the Pakistani Embassy; address: Iranian Interests Section, Pakistani Embassy, 2209 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007; telephone: [1] (202) 965-4990; FAX [1] (202) 965-1073
|
|
|
|
|
none; note - the US Interests Section is located in the Embassy of Switzerland No. 39 Shahid Mousavi (Golestan 5th), Pasdaran Ave., Tehran, Iran; telephone [98] 21 2254 2178/2256 5273; FAX [98] 21 2258 0432
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and red; the national emblem (a stylized representation of the word Allah in the shape of a tulip, a symbol of martyrdom) in red is centered in the white band; ALLAH AKBAR (God is Great) in white Arabic script is repeated 11 times along the bottom edge of the green band and 11 times along the top edge of the red band; green is the color of Islam and also represents growth, white symbolizes honesty and peace, red stands for bravery and martyrdom
|
|
|
|
|
lion
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Soroud-e Melli-ye Jomhouri-ye Eslami-ye Iran" (National Anthem of the Islamic Republic of Iran)
lyrics/music:
multiple authors/Hassan RIAHI
note:
adopted 1990
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iran's economy is marked by statist policies and an inefficient state sector, which create major distortions throughout the system, and reliance on oil, which provides the majority of government revenues. Price controls, subsidies, and other rigidities weigh down the economy, undermining the potential for private-sector-led growth. Private sector activity is typically limited to small-scale workshops, farming, and services. Significant informal market activity flourishes and corruption is widespread. Tehran since the early 1990s has recognized the need to reduce these inefficiencies, and in December 2010 the legislature passed President Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD's Targeted Subsidies Law (TSL) to reduce state subsidies on food and energy. This was the most extensive economic reform since the government implemented gasoline rationing in 2007. Over a five-year period the bill will phase out subsidies that previously cost Tehran $60-$100 billion annually and mostly benefited Iran's upper and middle classes. Cash payouts of $45 per person to more than 90% of Iranian households mitigated initial widespread resistance to the TSL program, though popular acceptance remains vulnerable to rising inflation. A rise in world oil prices in 2011 increased Iran's oil export revenue by roughly $28 billion over 2010, easing some of the financial impact of international sanctions. However, expansionary fiscal and monetary policies, government mismanagement, the sanctions, and a depreciating currency are fueling inflation, and GDP growth remains stagnant. Iran also continues to suffer from double-digit unemployment and underemployment. Underemployment among Iran's educated youth has convinced many to seek jobs overseas, resulting in a significant "brain drain."
|
|
|
|
|
$997.4 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$1.007 trillion (2011 est.)
$986.8 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data in US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$483.8 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
2% (2011 est.)
5.9% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$13,100 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$13,400 (2011 est.)
$13,300 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 11%
industry:
38.4%
services:
50.6% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
27.05 million
country comparison to the world: 24
note:
shortage of skilled labor (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 25%
industry:
31%
services:
45% (June 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
15.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
15.3% (2011 est.)
note:
data are according to the Iranian Government
|
|
|
|
|
18.7% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.6%
highest 10%:
29.6% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
44.5 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
31.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $131.2 billion
expenditures:
$92.63 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
13.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
|
|
|
|
|
-5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
18.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
18.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
includes publicly guaranteed debt
|
|
|
|
|
23.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
20.6% (2011 est.)
note:
official Iranian estimate
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
16% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
12.5% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$58.77 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$54.88 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$199.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
$183.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$138.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$138.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$107.2 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 44
$86.62 billion (31 December 2010)
$63.3 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, rice, other grains, sugar beets, sugarcane, fruits, nuts, cotton; dairy products, wool; caviar
|
|
|
|
|
-2.7% (2011 est.) (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
|
|
|
|
|
-$9.078 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
$26.19 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$66.37 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$109.5 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum 80%, chemical and petrochemical products, fruits and nuts, carpets
|
|
|
|
|
China 21.4%, Japan 9.1%, Turkey 8.8%, India 8.1%, South Korea 8%, Italy 5.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$66.97 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
$74.41 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
industrial supplies, capital goods, foodstuffs and other consumer goods, technical services
|
|
|
|
|
UAE 30.9%, China 17.4%, South Korea 7.1%, Germany 4.8%, Turkey 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$69.86 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$109.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.452 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$17.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$24.76 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
$23.61 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.881 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
$2.531 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Iranian rials (IRR) per US dollar -
12,260 (2012 est.)
10,616.3 (2011 est.)
10,254.18 (2010 est.)
9,864.3 (2009)
9,142.8 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
21 March - 20 March
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
213.7 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
173.1 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
6.154 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
2.068 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
56.17 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
86.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
13.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
4.231 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
2.295 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
|
|
|
|
|
151.2 billion bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
1.801 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
1.694 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
246,500 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
187,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
146.1 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
144.6 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
8.42 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
6.85 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
33.07 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
560.3 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.767 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
56.043 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: currently being modernized and expanded with the goal of not only improving the efficiency and increasing the volume of the urban service but also bringing telephone service to several thousand villages, not presently connected
domestic:
the addition of new fiber cables and modern switching and exchange systems installed by Iran's state-owned telecom company have improved and expanded the fixed-line network greatly; fixed-line availability has more than doubled to more than 27 million lines since 2000; additionally, mobile-cellular service has increased dramatically serving roughly 56 million subscribers in 2011; combined fixed and mobile-cellular subscribership now exceeds 100 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 98; submarine fiber-optic cable to UAE with access to Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG); Trans-Asia-Europe (TAE) fiber-optic line runs from Azerbaijan through the northern portion of Iran to Turkmenistan with expansion to Georgia and Azerbaijan; HF radio and microwave radio relay to Turkey, Azerbaijan, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Syria, Kuwait, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan; satellite earth stations - 13 (9 Intelsat and 4 Inmarsat)
|
|
|
|
|
state-run broadcast media with no private, independent broadcasters; Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting (IRIB), the state-run TV broadcaster, operates 5 nationwide channels, a news channel, about 30 provincial channels, and several international channels; about 20 foreign Persian-language TV stations broadcasting on satellite TV are capable of being seen in Iran; satellite dishes are illegal and, while their use had been tolerated, authorities began confiscating satellite dishes following the unrest stemming from the 2009 presidential election; IRIB operates 8 nationwide radio networks, a number of provincial stations, and an external service; most major international broadcasters transmit to Iran (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
.ir
|
|
|
|
|
197,804 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
8.214 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
324 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
total: 136
over 3,047 m:
42
2,438 to 3,047 m:
29
1,524 to 2,437 m:
24
914 to 1,523 m:
34
under 914 m:
7 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 188
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
10
914 to 1,523 m:
142
under 914 m:
34 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
21 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 7 km; condensate/gas 12 km; gas 20,155 km; liquid petroleum gas 570 km; oil 7,123 km; refined products 7,937 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8,442 km
country comparison to the world: 25
broad gauge:
94 km 1.676-m gauge
standard gauge:
8,348 km 1.435-m gauge (148 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 172,927 km
country comparison to the world: 28
paved:
125,908 km (includes 1,429 km of expressways)
unpaved:
47,019 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
850 km (on Karun River; some navigation on Lake Urmia) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
total: 76
country comparison to the world: 60
by type:
bulk carrier 8, cargo 51, chemical tanker 3, container 4, liquefied gas 1, passenger/cargo 3, petroleum tanker 2, refrigerated cargo 2, roll on/roll off 2
foreign-owned:
2 (UAE 2)
registered in other countries:
71 (Barbados 5, Cyprus 10, Hong Kong 3, Malta 48, Panama 5) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Assaluyeh, Bandar Abbas, Bandar-e-Eman Khomeyni
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Islamic Republic of Iran Regular Forces (Artesh): Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force (IRIAF), Khatemolanbia Air Defense Headquarters; Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (Sepah-e Pasdaran-e Enqelab-e Eslami, IRGC): Ground Resistance Forces, Navy, Aerospace Force, Quds Force (special operations); Law Enforcement Forces (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
19 years of age for compulsory military service; 16 years of age for volunteers; 17 years of age for Law Enforcement Forces; 15 years of age for Basij Forces (Popular Mobilization Army); conscript military service obligation - 18 months; women exempt from military service (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 23,619,215
females age 16-49:
22,628,341 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 20,149,222
females age 16-49:
19,417,275 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 715,111
female:
677,372 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.5% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Iran |
|
|
|
Iran protests Afghanistan's limiting flow of dammed Helmand River tributaries during drought; Iraq's lack of a maritime boundary with Iran prompts jurisdiction disputes beyond the mouth of the Shatt al Arab in the Persian Gulf; Iran and UAE dispute Tunb Islands and Abu Musa Island, which are occupied by Iran; Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Russia ratified Caspian seabed delimitation treaties based on equidistance, while Iran continues to insist on a one-fifth slice of the sea; Afghan and Iranian commissioners have discussed boundary monument densification and resurvey
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 1,027,577 (Afghanistan); 3,511 (Iraq) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Iran is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of sexual exploitation and involuntary servitude; Iranian women are trafficked internally for the purpose of forced prostitution and for forced marriages to settle debts; Iranian and Afghan children living in Iran are trafficked internally for the purpose of forced marriages, commercial sexual exploitation and involuntary servitude as beggars or laborers to pay debts, provide income, or support drug addiction of their families; press reports indicate that criminal organizations play a significant role in human trafficking to and from Iran, in connection with smuggling of migrants, drugs, and arms; Iranian women and children are also subjected to sex trafficking in Pakistan, Turkey, Qatar, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Iraq, France, Germany, and the United Kingdom
tier rating:
Tier 3 - Iran did not report any law enforcement efforts to punish trafficking offenders and continues to lack any semblance of victim protection measures; victims of trafficking are, by government policy, detained and deported if foreign, or simply jailed or turned away if Iranian; lack of access to Iran by US Government officials impedes the collection of information on the country's human trafficking problem and the government's efforts to curb it (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
despite substantial interdiction efforts and considerable control measures along the border with Afghanistan, Iran remains one of the primary transshipment routes for Southwest Asian heroin to Europe; suffers one of the highest opiate addiction rates in the world, and has an increasing problem with synthetic drugs; lacks anti-money laundering laws; has reached out to neighboring countries to share counter-drug intelligence
|
|
|
|
|
|