|
|
|
The Dutch began to colonize Indonesia in the early 17th century; Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence after Japan's surrender, but it required four years of intermittent negotiations, recurring hostilities, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949. After decades of repressive rule, free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999. Indonesia is now the world's third most populous democracy, the world's largest archipelagic state, and home to the world's largest Muslim population. Current issues include: alleviating poverty, improving education, preventing terrorism, consolidating democracy after four decades of authoritarianism, implementing economic and financial reforms, stemming corruption, reforming the criminal justice system, holding the military and police accountable for human rights violations, addressing climate change, and controlling infectious diseases, particularly those of global and regional importance. In 2005, Indonesia reached a historic peace agreement with armed separatists in Aceh, which led to democratic elections in Aceh in December 2006. Indonesia continues to face low intensity armed resistance by the separatist Free Papua Movement.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
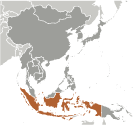
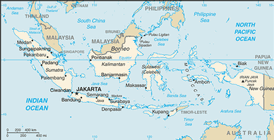
Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
5 00 S, 120 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,904,569 sq km
country comparison to the world: 15
land:
1,811,569 sq km
water:
93,000 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than three times the size of Texas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,830 km
border countries:
Timor-Leste 228 km, Malaysia 1,782 km, Papua New Guinea 820 km
|
|
|
|
|
54,716 km
|
|
|
|
|
measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines
territorial sea:
12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands
|
|
|
|
|
mostly coastal lowlands; larger islands have interior mountains
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Puncak Jaya 4,884 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, tin, natural gas, nickel, timber, bauxite, copper, fertile soils, coal, gold, silver
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 11.03%
permanent crops:
7.04%
other:
81.93% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
67,220 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
2,838 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 82.78 cu km/yr (8%/1%/91%)
per capita:
372 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
occasional floods; severe droughts; tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanoes; forest fires
volcanism:
Indonesia contains the most volcanoes of any country in the world - some 76 are historically active; significant volcanic activity occurs on Java, western Sumatra, the Sunda Islands, Halmahera Island, Sulawesi Island, Sangihe Island, and in the Banda Sea; Merapi (elev. 2,968 m), Indonesia's most active volcano and in eruption since 2010, has been deemed a "Decade Volcano" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Agung, Awu, Karangetang, Krakatau (Krakatoa), Makian, Raung, and Tambora
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; water pollution from industrial wastes, sewage; air pollution in urban areas; smoke and haze from forest fires
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
archipelago of 17,508 islands (6,000 inhabited); straddles equator; strategic location astride or along major sea lanes from Indian Ocean to Pacific Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Indonesia |
|
|
|
noun: Indonesian(s)
adjective:
Indonesian
|
|
|
|
|
Javanese 40.6%, Sundanese 15%, Madurese 3.3%, Minangkabau 2.7%, Betawi 2.4%, Bugis 2.4%, Banten 2%, Banjar 1.7%, other or unspecified 29.9% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects (of which the most widely spoken is Javanese)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 86.1%, Protestant 5.7%, Roman Catholic 3%, Hindu 1.8%, other or unspecified 3.4% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
248,645,008 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 27% (male 34,224,282/ female 33,022,222)
15-64 years:
66.6% (male 83,194,042/ female 82,385,050)
65 years and over:
6.4% (male 6,926,153/ female 8,893,259) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28.5 years
male:
28 years
female:
29.1 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.03% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
17.7 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
6.3 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|
|
-1.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 44% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.7% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
JAKARTA (capital) 9.121 million; Surabaya 2.509 million; Bandung 2.412 million; Medan 2.131 million; Semarang 1.296 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.78 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
220 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
total: 27 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 72
male:
31.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
22.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 71.62 years
country comparison to the world: 136
male:
69.07 years
female:
74.29 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.23 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
0.288 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 beds/1,000 population (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 67% of population
rural: 36% of population
total: 52% of population
unimproved:
urban: 33% of population
rural: 64% of population
total: 48% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
310,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
8,300 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
chikungunya, dengue fever, and malaria
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% (2001)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
19.6% (2007)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
2.8% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
90.4%
male:
94%
female:
86.8% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13 years
male:
13 years
female:
13 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22.2%
country comparison to the world: 41
male:
21.6%
female:
23% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Indonesia
conventional short form:
Indonesia
local long form:
Republik Indonesia
local short form:
Indonesia
former:
Netherlands East Indies, Dutch East Indies
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Jakarta
geographic coordinates:
6 10 S, 106 49 E
time difference:
UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note:
Indonesia is divided into three time zones
|
|
|
|
|
30 provinces (provinsi-provinsi, singular - provinsi), 2 special regions* (daerah-daerah istimewa, singular - daerah istimewa), and 1 special capital city district** (daerah khusus ibukota); Aceh*, Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jakarta Raya**, Jambi, Jawa Barat (West Java), Jawa Tengah (Central Java), Jawa Timur (East Java), Kalimantan Barat (West Kalimantan), Kalimantan Selatan (South Kalimantan), Kalimantan Tengah (Central Kalimantan), Kalimantan Timur (East Kalimantan), Kepulauan Bangka Belitung (Bangka Belitung Islands), Kepulauan Riau (Riau Islands), Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara (North Maluku), Nusa Tenggara Barat (West Nusa Tenggara), Nusa Tenggara Timur (East Nusa Tenggara), Papua, Papua Barat (West Papua), Riau, Sulawesi Barat (West Sulawesi), Sulawesi Selatan (South Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tengah (Central Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tenggara (Southeast Sulawesi), Sulawesi Utara (North Sulawesi), Sumatera Barat (West Sumatra), Sumatera Selatan (South Sumatra), Sumatera Utara (North Sumatra), Yogyakarta*
note:
following the implementation of decentralization beginning on 1 January 2001, regencies and municipalities have become the key administrative units responsible for providing most government services
|
|
|
|
|
17 August 1945 (declared); 27 December 1949 (recognized by the Netherlands); note - in August 2005 the Netherlands announced that it had recognized de facto Indonesian independence on 17 August 1945
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 17 August (1945)
|
|
|
|
|
August 1945; abrogated by Federal Constitution of 1949 and Provisional Constitution of 1950, restored 5 July 1959; series of amendments concluded in 2002
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on the Roman-Dutch model and influenced by customary law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
17 years of age; universal and married persons regardless of age
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO (since 20 October 2004); Vice President BOEDIONO (since 20 October 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO (since 20 October 2004); Vice President BOEDIONO (since 20 October 2009)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected for five-year terms (eligible for a second term) by direct vote of the citizenry; election last held on 8 July 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO elected president; percent of vote - Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO 60.8%, MEGAWATI Sukarnoputri 26.8%, Jusuf KALLA 12.4%
|
|
|
|
|
People's Consultative Assembly (Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat or MPR) is the upper house; it consists of members of the DPR and DPD and has role in inaugurating and impeaching the president and in amending the constitution but does not formulate national policy; House of Representatives or Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat (DPR) (560 seats, members elected to serve five-year terms), formulates and passes legislation at the national level; House of Regional Representatives (Dewan Perwakilan Daerah or DPD), constitutionally mandated role includes providing legislative input to DPR on issues affecting regions (132 members, four from each of Indonesia's 30 provinces, two special regions, and one special capital city district)
elections:
last held on 9 April 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party - PD 20.9%, GOLKAR 14.5%, PDI-P 14.0%, PKS 7.9%, PAN 6.0%, PPP 5.3%, PKB 4.9%, GERINDRA 4.5%, HANURA 3.8%, others 18.2%; seats by party - PD 148, GOLKAR 107, PDI-P 94, PKS 57, PAN 46, PPP 37, PKB 28, GERINDRA 26, HANURA 17
note:
29 other parties received less than 2.5% of the vote so did not obtain any seats; because of election rules, the number of seats won does not always follow the percentage of votes received by parties
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Mahkamah Agung is the final court of appeal but does not have the power of judicial review (justices are appointed by the president from a list of candidates selected by the legislature); in March 2004 the Supreme Court assumed administrative and financial responsibility for the lower court system from the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights; Constitutional Court or Mahkamah Konstitusi (invested by the president on 16 August 2003) has the power of judicial review, jurisdiction over the results of a general election, and reviews actions to dismiss a president from office; Labor Court under supervision of Supreme Court began functioning in January 2006; anti-corruption courts have jurisdiction over corruption cases brought by the independent Corruption Eradication Commission
|
|
|
|
|
Democrat Party or PD [Anas URBANINGRUM]; Functional Groups Party or GOLKAR [Aburizal BAKRIE]; Great Indonesia Movement Party or GERINDRA [SUHARDI]; Indonesia Democratic Party-Struggle or PDI-P [MEGAWATI Sukarnoputri]; National Awakening Party or PKB [Muhaiman ISKANDAR]; National Mandate Party or PAN [Hatta RAJASA]; People's Conscience Party or HANURA [WIRANTO]; Prosperous Justice Party or PKS [Luthfi Hasan ISHAQ]; United Development Party or PPP [Suryadharma ALI]
|
|
|
|
|
Commission for the "Disappeared" and Victims of Violence or KontraS; Indonesia Corruption Watch or ICW; Indonesian Forum for the Environment or WALHI; Islamic Defenders Front or FPI; People's Democracy Fortress or Bendera
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, D-8, EAS, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-11, G-15, G-20, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OECD (Enhanced Engagement, OIC, OPCW, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Dino Patti DJALAL
chancery:
2020 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone:
[1] (202) 775-5200
FAX:
[1] (202) 775-5365
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Scot A. MARCIEL
embassy:
Jalan Medan Merdeka Selatan 3-5, Jakarta 10110
mailing address:
Unit 8129, Box 1, FPO AP 96520
telephone:
[62] (21) 3435-9000
FAX:
[62] (21) 385-7189
consulate general:
Surabaya
presence post:
Medan
consular agent:
Bali
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white; the colors derive from the banner of the Majapahit Empire of the 13th-15th centuries; red symbolizes courage, white represents purity
note:
similar to the flag of Monaco, which is shorter; also similar to the flag of Poland, which is white (top) and red
|
|
|
|
|
garuda (mythical bird)
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Indonesia Raya" (Great Indonesia)
lyrics/music:
Wage Rudolf SOEPRATMAN
note:
adopted 1945
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indonesia, a vast polyglot nation, grew an estimated 6.1% and 6.4% in 2010 and 2011, respectively. The government made economic advances under the first administration of President YUDHOYONO (2004-09), introducing significant reforms in the financial sector, including tax and customs reforms, the use of Treasury bills, and capital market development and supervision. During the global financial crisis, Indonesia outperformed its regional neighbors and joined China and India as the only G20 members posting growth in 2009. The government has promoted fiscally conservative policies, resulting in a debt-to-GDP ratio of less than 25%, a fiscal deficit below 3%, and historically low rates of inflation. Fitch and Moody's upgraded Indonesia's credit rating to investment grade in December 2011. Indonesia still struggles with poverty and unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, corruption, a complex regulatory environment, and unequal resource distribution among regions. The government in 2013 faces the ongoing challenge of improving Indonesia's insufficient infrastructure to remove impediments to economic growth, labor unrest over wages, and reducing its fuel subsidy program in the face of high oil prices.
|
|
|
|
|
$1.212 trillion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$1.143 trillion (2011 est.)
$1.074 trillion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$894.9 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
6.5% (2011 est.)
6.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$4,700 (2011 est.)
$4,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 14.3%
industry:
46.9%
services:
38.8% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
119.5 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 38.3%
industry:
12.8%
services:
48.9% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.7% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
6.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.3%
highest 10%:
29.9% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
36.8 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 78
39.4 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
33.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $139.2 billion
expenditures:
$160.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
15.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
|
|
|
|
|
-2.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
24.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
24.1% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
5.4% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.37% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 57
6.46% (31 December 2009)
note:
this figure represents the 3-month SBI rate; the Bank of Indonesia has not employed the one-month SBI since September 2010
|
|
|
|
|
11.9% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
12.4% (31 December 2011 est.)
note:
these figures represent the average annualized rate on working capital loans
|
|
|
|
|
$90.24 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
$79.73 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$355.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$317.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$323 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$307.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$390.1 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 24
$360.4 billion (31 December 2010)
$178.2 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, cassava (manioc), peanuts, rubber, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, copra; poultry, beef, pork, eggs
|
|
|
|
|
4.1% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
-$20.73 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
$2.069 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$199.1 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$201.5 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
oil and gas, electrical appliances, plywood, textiles, rubber
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 16.6%, China 11.3%, Singapore 9.1%, US 8.1%, South Korea 8.1%, India 6.6%, Malaysia 5.4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$185 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$166.1 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels, foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
China 14.8%, Singapore 14.6%, Japan 11%, South Korea 7.3%, US 6.1%, Thailand 5.9%, Malaysia 5.9% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$104.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$110.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$187.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$190.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$125.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$104.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$48.57 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
$40.57 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Indonesian rupiah (IDR) per US dollar -
9,348.3 (2012 est.)
8,770.43 (2011 est.)
9,090.4 (2010 est.)
10,389.9 (2009)
9,698.9 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
156 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
131.5 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
|
|
|
|
|
32.8 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
81.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
14.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
3.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
982,900 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
293,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
324,900 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
4 billion bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
935,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
1.322 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
142,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
407,700 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
82.8 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
41.35 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
41.25 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
|
|
|
|
|
3.994 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
389.4 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Indonesia |
|
|
|
38.618 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
249.8 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: domestic service includes an interisland microwave system, an HF radio police net, and a domestic satellite communications system; international service good
domestic:
coverage provided by existing network has been expanded by use of over 200,000 telephone kiosks many located in remote areas; mobile-cellular subscribership growing rapidly
international:
country code - 62; landing point for both the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cable networks that provide links throughout Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
mixture of about a dozen national TV networks - 2 public broadcasters, the remainder private broadcasters - each with multiple transmitters; more than 100 local TV stations; widespread use of satellite and cable TV systems; public radio broadcaster operates 6 national networks as well as regional and local stations; overall, more than 700 radio stations with more than 650 privately-operated (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.id
|
|
|
|
|
1.344 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
20 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Indonesia |
|
|
|
676 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
total: 185
over 3,047 m:
4
2,438 to 3,047 m:
22
1,524 to 2,437 m:
51
914 to 1,523 m:
71
under 914 m:
37 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 491
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
24
under 914 m:
462 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
76 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 812 km; condensate/gas 73 km; gas 7,165 km; oil 5,984 km; oil/gas/water 12 km; refined products 617 km; water 44 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,042 km
country comparison to the world: 35
narrow gauge:
5,042 km 1.067-m gauge (565 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 437,759 km
country comparison to the world: 14
paved:
258,744 km
unpaved:
179,015 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
21,579 km (2011)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,340
country comparison to the world: 8
by type:
bulk carrier 105, cargo 618, chemical tanker 69, container 120, liquefied gas 28, passenger 49, passenger/cargo 77, petroleum tanker 244, refrigerated cargo 6, roll on/roll off 12, specialized tanker 1, vehicle carrier 11
foreign-owned:
69 (China 1, France 1, Greece 1, Japan 8, Jordan 1, Malaysia 1, Norway 3, Singapore 46, South Korea 2, Taiwan 1, UK 2, US 2)
registered in other countries:
95 (Bahamas 2, Cambodia 2, China 2, Hong Kong 10, Liberia 4, Marshall Islands 1, Mongolia 2, Panama 10, Singapore 60, Tuvalu 1, unknown 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Banjarmasin, Belawan, Kotabaru, Krueg Geukueh, Palembang, Panjang, Sungai Pakning, Tanjung Perak, Tanjung Priok
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Strait of Malacca and South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; 2010 saw the highest levels of armed robbery against ships since 2007; 40 commercial vessels were attacked, boarded, or hijacked both at anchor or while underway; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia; crews have been murdered or cast adrift
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indonesian Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, TNI): Army (TNI-Angkatan Darat (TNI-AD)), Navy (TNI-Angkatan Laut (TNI-AL); includes marines (Korps Marinir, KorMar), naval air arm), Air Force (TNI-Angkatan Udara (TNI-AU)), National Air Defense Command (Kommando Pertahanan Udara Nasional (Kohanudnas)) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for selective compulsory and voluntary military service; 2-year conscript service obligation, with reserve obligation to age 45 (officers); Indonesian citizens only (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 65,847,171
females age 16-49:
63,228,017 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 54,264,299
females age 16-49:
53,274,361 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 2,263,892
female:
2,191,267 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Indonesia |
|
|
|
Indonesia has a stated foreign policy objective of establishing stable fixed land and maritime boundaries with all of its neighbors; three stretches of land borders with Timor-Leste have yet to be delimited, two of which are in the Oecussi exclave area, and no maritime or Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) boundaries have been established between the countries; many refugees from Timor-Leste who left in 2003 still reside in Indonesia and refuse repatriation; all borders between Indonesia and Australia have been agreed upon bilaterally, but a 1997 treaty that would settle the last of their maritime and EEZ boundary has yet to be ratified by Indonesia's legislature; Indonesian groups challenge Australia's claim to Ashmore Reef; Australia has closed parts of the Ashmore and Cartier Reserve to Indonesian traditional fishing and placed restrictions on certain catches
; land and maritime negotiations with Malaysia are ongoing, and disputed areas include the controversial Tanjung Datu and Camar Wulan border area in Borneo and the maritime boundary in the Ambalat oil block in the Celebes Sea; Indonesia and Singapore continue to work on finalizing their 1973 maritime boundary agreement by defining unresolved areas north of Indonesia's Batam Island; Indonesian secessionists, squatters, and illegal migrants create repatriation problems for Papua New Guinea; maritime delimitation talks continue with Palau; EEZ negotiations with Vietnam are ongoing, and the two countries in Fall 2011 agreed to work together to reduce illegal fishing along their maritime boundary
|
|
|
|
|
IDPs: 180,000 (government offensives against rebels in Aceh; most IDPs in Aceh, Central Kalimantan, Central Sulawesi Provinces, and Maluku) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
illicit producer of cannabis largely for domestic use; producer of methamphetamine and ecstasy
|
|
|
|
|
|