|
|
|
Greenland, the world's largest island, is about 81% ice capped. Vikings reached the island in the 10th century from Iceland; Danish colonization began in the 18th century, and Greenland was made an integral part of Denmark in 1953. It joined the European Community (now the EU) with Denmark in 1973 but withdrew in 1985 over a dispute centered on stringent fishing quotas. Greenland was granted self-government in 1979 by the Danish parliament; the law went into effect the following year. Greenland voted in favor of increased self-rule in November 2008 and acquired greater responsibility for internal affairs when the Act on Greenland Self Government was signed into law in June 2009. Denmark, however, continues to exercise control of Greenland's foreign affairs, security, and financial policy in consultation with Greenland's Home Rule Government.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
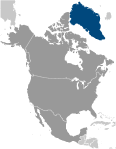
Northern North America, island between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada
|
|
|
|
|
72 00 N, 40 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,166,086 sq km
country comparison to the world: 12
land:
2,166,086 sq km (410,449 sq km ice-free, 1,755,637 sq km ice-covered)
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than three times the size of Texas
|
|
|
|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|
|
44,087 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 3 nm
exclusive fishing zone:
200 nm or agreed boundaries or median line
continental shelf:
200 nm or agreed boundaries or median line
|
|
|
|
|
arctic to subarctic; cool summers, cold winters
|
|
|
|
|
flat to gradually sloping icecap covers all but a narrow, mountainous, barren, rocky coast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Gunnbjorn Fjeld 3,700 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal, iron ore, lead, zinc, molybdenum, diamonds, gold, platinum, niobium, tantalite, uranium, fish, seals, whales, hydropower, possible oil and gas
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0%
permanent crops:
0%
other:
100% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
continuous permafrost over northern two-thirds of the island
|
|
|
|
|
protection of the arctic environment; preservation of the Inuit traditional way of life, including whaling and seal hunting
|
|
|
|
|
dominates North Atlantic Ocean between North America and Europe; sparse population confined to small settlements along coast; close to one-quarter of the population lives in the capital, Nuuk; world's second largest ice cap
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Greenland |
|
|
|
noun: Greenlander(s)
adjective:
Greenlandic
|
|
|
|
|
Inuit 89%, Danish and other 11% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
Greenlandic (East Inuit) (official), Danish (official), English
|
|
|
|
|
Evangelical Lutheran, traditional Inuit spiritual beliefs
|
|
|
|
|
57,695 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 21.9% (male 6,420/ female 6,229)
15-64 years:
70.2% (male 21,559/ female 18,949)
65 years and over:
7.9% (male 2,376/ female 2,162) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 33.7 years
male:
35 years
female:
32.2 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.038% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
|
|
|
|
|
14.58 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
8.22 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
-5.98 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 84% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NUUK (capital) 15,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.14 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.1 male(s)/female
total population:
1.11 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9.83 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 146
male:
11.23 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
8.37 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 71.25 years
country comparison to the world: 141
male:
68.6 years
female:
74.04 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.11 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
100 (1999)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
100%
male:
100%
female:
100% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Greenland
local long form:
none
local short form:
Kalaallit Nunaat
|
|
|
|
|
part of the Kingdom of Denmark; self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark since 1979
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy within a constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
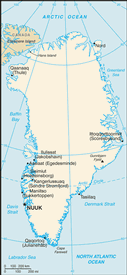
name: Nuuk (Godthab)
geographic coordinates:
64 11 N, 51 45 W
time difference:
UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note:
Greenland is divided into four time zones
|
|
|
|
|
4 municipalities (kommuner, singular kommune); Kujalleq, Qaasuitsup, Qeqqata, Sermersooq
note:
the North and East Greenland National Park (Avannaarsuani Tunumilu Nuna Allanngutsaaliugaq) and the Thule Air Base in Pituffik (in northwest Greenland) are two unincorporated areas; the national park's 972,000 sq km - about 46% of the island - make it the largest national park in the world and also the most northerly
|
|
|
|
|
none (extensive self-rule as part of the Kingdom of Denmark; foreign affairs is the responsibility of Denmark, but Greenland actively participates in international agreements relating to Greenland)
|
|
|
|
|
June 21 (longest day)
|
|
|
|
|
(June 2009) Act on Greenland Self Government
|
|
|
|
|
the laws of Denmark, where applicable, apply
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II of Denmark (since 14 January 1972), represented by High Commissioner Mikaela ENGELL (since April 2011)
head of government:
Prime Minister Kuupik KLEIST (since 12 June 2009)
cabinet:
Home Rule Government elected by the Parliament (Landsting) on the basis of the strength of parties
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; high commissioner appointed by the monarch; prime minister elected by parliament (usually the leader of the majority party)
election results:
Kuupik KLEIST elected prime minister
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Parliament or Inatsisartut (Landsting) (31 seats; members elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 2 June 2009 (next to be held by 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - Inuit Community 43.7%, Forward Party 26.5%, Democratic Party 12.7%, Solidarity Party 10.9%; Candidate List 3.8%, other 2.4%; seats by party - Inuit Community 14, Forward Party 9, Democratic Party 4, Solidarity Party 3, Candidate List 1
note:
two representatives were elected to the Danish Parliament or Folketing on 15 September 2011 (next to be held by September 2015); percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Siumut 1, Inuit Ataqatigiit 1 (2013)
|
|
|
|
|
High Court or Eggartuussisuuneqarfia (Landsret) (appeals can be made to the Ostre Landsret or Eastern Division of the High Court or Supreme Court in Copenhagen)
|
|
|
|
|
Candidate List (Kattusseqatigiit) [Anthon FREDERIKSEN]; Democratic Party (Demokraatit) [Jens B. FREDERIKSEN]; Forward Party (Siumut) [Aleqa HAMMOND]; Inuit Community (Inuit Ataqatigiit) or IA [Kuupik KLEIST]; Solidarity Party (Atassut) [Gerhardt PETERSEN]
|
|
|
|
|
conservationists; environmentalists
|
|
|
|
|
Arctic Council, NC, NIB, UPU
|
|
|
|
|
none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)
|
|
|
|
|
none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red with a large disk slightly to the hoist side of center - the top half of the disk is red, the bottom half is white; the design represents the sun reflecting off a field of ice; the colors are the same as those of the Danish flag and symbolize Greenland's links to the Kingdom of Denmark
|
|
|
|
|
polar bear
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Nunarput utoqqarsuanngoravit" ("Our Country, Who's Become So Old" also translated as "You Our Ancient Land")
lyrics/music:
Henrik LUND/Jonathan PETERSEN
note:
adopted 1916; the government also recognizes "Nuna asiilasooq" as a secondary anthem
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The economy remains critically dependent on exports of shrimp and fish, income from resource exploration and extraction, and on a substantial subsidy from the Danish Government. The subsidy is budgeted to be about $650 million in 2012, approximately 56% of government revenues in 2012 for the year. The public sector, including publicly owned enterprises and the municipalities, plays the dominant role in Greenland's economy. Greenland's real GDP contracted about 1% in 2009 as a result of the global economic slowdown, but is estimated to have grown 2% in 2010 and 3% in 2011. The relative ease with which Greenland has weathered the economic crisis is due to increased hydrocarbon and mineral exploration and extraction activities, a high level of construction activity in the Nuuk area and the increasing price of fish and shrimp. During the last decade the Greenland Home Rule Government (GHRG) pursued conservative fiscal and monetary policies, but public pressure has increased for better schools, health care and retirement systems. The Greenlandic economy has benefited from increasing catches and exports of shrimp, Greenland halibut and, more recently, crabs. Due to Greenland's continued dependence on exports of fish - which accounted for 89% of exports in 2010 - the economy remains very sensitive to foreign developments. International consortia are increasingly active in exploring for hydrocarbon resources off Greenland's western coast, and international studies indicate the potential for oil and gas fields in northern and northeastern Greenland. In May 2007 a US aluminum producer concluded a memorandum of understanding with the Greenland Home Rule Government to build an aluminum smelter and a power generation facility, which takes advantage of Greenland's abundant hydropower potential. Within the area of mining, olivine sand continues to be produced and gold production has resumed in south Greenland, while rare-earth and iron ore mineral projects have been proposed or planned elsewhere on the island. Tourism also offers another avenue of economic growth for Greenland, with increasing numbers of cruise lines now operating in Greenland's western and southern waters during the peak summer tourism season.
|
|
|
|
|
$2.133 billion (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
$2.071 billion (2010 est.)
$2.03 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.16 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
2% (2010 est.)
-1.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$37,400 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$36,600 (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 4%
industry:
29%
services:
67% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
33,670 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 4%
industry:
29%
services:
67% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.9% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
4.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
9.2% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $1.72 billion
expenditures:
$1.68 billion (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
79.6% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
2.8% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
1.7% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
forage crops, garden and greenhouse vegetables; sheep, reindeer; fish
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$384.3 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 176
$358 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
fish and fish products 89%, metals 10% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Denmark 63.3%, Japan 12%, China 6.4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$814.2 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 181
$726 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, petroleum products
|
|
|
|
|
Denmark 58.1%, Sweden 19.7%, UK 10.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$36.4 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 194
$58 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar -
5.847 (2011)
5.6241 (2011)
5.6241 (2010)
5.361 (2009)
5.0236 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
276.6 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
|
|
|
|
|
239.4 million kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
|
|
|
|
|
137,000 kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
3,897 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
1,034 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
5,376 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
|
|
|
|
|
555,600 Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Greenland |
|
|
|
19,900 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 190
|
|
|
|
|
58,700 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 199
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: adequate domestic and international service provided by satellite, cables and microwave radio relay; totally digital since 1995
domestic:
microwave radio relay and satellite
international:
country code - 299; satellite earth stations - 15 (12 Intelsat, 1 Eutelsat, 2 Americom GE-2 (all Atlantic Ocean)) (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
the Greenland Broadcasting Company provides public radio and TV services throughout the island with a broadcast station and a series of repeaters; a few private local TV and radio stations; Danish public radio rebroadcasts are available (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.gl
|
|
|
|
|
15,645 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
36,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 179
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Greenland |
|
|
|
15 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
6 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
2 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
note: although there are short roads in towns, there are no roads between towns; inter-urban transport takes place either by sea or air (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
registered in other countries: 1 (Denmark 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
Sisimiut
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
no regular military forces
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 15,280 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 10,765
females age 16-49:
11,399 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 488
female:
478 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
defense is the responsibility of Denmark
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Greenland |
|
|
|
managed dispute between Canada and Denmark over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Canada's Ellesmere Island and Greenland; Denmark (Greenland) and Norway have made submissions to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental shelf (CLCS) and Russia is collecting additional data to augment its 2001 CLCS submission
|
|
|
|
|
|