|
|
|
Celtic tribes arrived on the island between 600-150 B.C. Invasions by Norsemen that began in the late 8th century were finally ended when King Brian BORU defeated the Danes in 1014. English invasions began in the 12th century and set off more than seven centuries of Anglo-Irish struggle marked by fierce rebellions and harsh repressions. A failed 1916 Easter Monday Rebellion touched off several years of guerrilla warfare that in 1921 resulted in independence from the UK for 26 southern counties; six northern (Ulster) counties remained part of the UK. In 1949, Ireland withdrew from the British Commonwealth; it joined the European Community in 1973. Irish governments have sought the peaceful unification of Ireland and have cooperated with Britain against terrorist groups. A peace settlement for Northern Ireland is gradually being implemented despite some difficulties. In 2006, the Irish and British governments developed and began to implement the St. Andrews Agreement, building on the Good Friday Agreement approved in 1998.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
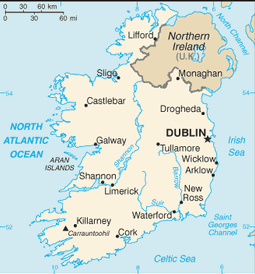
Western Europe, occupying five-sixths of the island of Ireland in the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Great Britain
|
|
|
|
|
53 00 N, 8 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 70,273 sq km
country comparison to the world: 120
land:
68,883 sq km
water:
1,390 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
total: 360 km
border countries:
UK 360 km
|
|
|
|
|
1,448 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive fishing zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
temperate maritime; modified by North Atlantic Current; mild winters, cool summers; consistently humid; overcast about half the time
|
|
|
|
|
mostly level to rolling interior plain surrounded by rugged hills and low mountains; sea cliffs on west coast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Carrauntoohil 1,041 m
|
|
|
|
|
natural gas, peat, copper, lead, zinc, silver, barite, gypsum, limestone, dolomite
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 16.82%
permanent crops:
0.03%
other:
83.15% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
46.8 cu km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.18 cu km/yr (23%/77%/0%)
per capita:
284 cu m/yr (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
water pollution, especially of lakes, from agricultural runoff
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on major air and sea routes between North America and northern Europe; over 40% of the population resides within 100 km of Dublin
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Ireland |
|
|
|
noun: Irishman(men), Irishwoman(women), Irish (collective plural)
adjective:
Irish
|
|
|
|
|
Irish 87.4%, other white 7.5%, Asian 1.3%, black 1.1%, mixed 1.1%, unspecified 1.6% (2006 census)
|
|
|
|
|
English (official, the language generally used), Irish (Gaelic or Gaeilge) (official, spoken mainly in areas along the western coast)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 87.4%, Church of Ireland 2.9%, other Christian 1.9%, other 2.1%, unspecified 1.5%, none 4.2% (2006 census)
|
|
|
|
|
4,722,028 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 21.3% (male 512,854/ female 491,801)
15-64 years:
66.9% (male 1,589,342/ female 1,568,149)
65 years and over:
11.9% (male 255,858/ female 304,024) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35.1 years
male:
34.8 years
female:
35.4 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.112% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
15.81 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
6.38 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
1.69 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 62% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.8% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
DUBLIN (capital) 1.084 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.84 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.81 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 202
male:
4.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.41 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 80.32 years
country comparison to the world: 26
male:
78.07 years
female:
82.69 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.01 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
7.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
3.187 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
5.17 beds/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 98% of population
total: 99% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 2% of population
total: 1% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
6,900 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
13% (2002)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
4.9% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18 years
male:
18 years
female:
18 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24.3%
country comparison to the world: 33
male:
30.9%
female:
17.3% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Ireland
local long form:
none
local short form:
Eire
|
|
|
|
|
republic, parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Dublin
geographic coordinates:
53 19 N, 6 14 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
29 counties and 5 cities*; Carlow, Cavan, Clare, Cork, Cork*, Donegal, Dublin*, Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown, Fingal, Galway, Galway*, Kerry, Kildare, Kilkenny, Laois, Leitrim, Limerick, Limerick*, Longford, Louth, Mayo, Meath, Monaghan, North Tipperary, Offaly, Roscommon, Sligo, South Dublin, South Tipperary, Waterford, Waterford*, Westmeath, Wexford, Wicklow
|
|
|
|
|
6 December 1921 (from the UK by treaty)
|
|
|
|
|
Saint Patrick's Day, 17 March
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 1 July 1937 by plebiscite; effective 29 December 1937
|
|
|
|
|
common law system based on the English model but substantially modified by customary law; judicial review of legislative acts in Supreme Court
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Michael D. HIGGINS (since 29 October 2011)
head of government:
Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Enda KENNY (since 9 March 2011)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president with previous nomination by the prime minister and approval of the lower house of Parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 29 October 2011 (next scheduled for October 2018); prime minister (taoiseach) nominated by the House of Representatives (Dail Eireann) and appointed by the president
election results:
Michael D. HIGGINS elected president; percent of vote - Michael D. HIGGINS 39.6%, Sean GALLAGHER 28.5%, Martin MCGUINNESS 13.7%, Gay MITCHELL 6.4%, David NORRIS 6.2%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Parliament or Oireachtas consists of the Senate or Seanad Eireann (60 seats; 49 members elected by the universities and from candidates put forward by five vocational panels, 11 are nominated by the prime minister; members serve five-year terms) and the lower house of Parliament or Dail Eireann (166 seats; members elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve five-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held in 27 April 2011 (next to be held 2016); House of Representatives - last held on 25 February 2011 (next to be held probably in 2016)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Fine Gael 19, Fianna Fail 14, Labor Party 12, Sinn Fein 3, independents 12; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - Fine Gael 45.8%, Labor Party 22.3%, Fianna Fail 12.0%, Sinn Fein 8.4%, United Left Alliance 3.0%, New Vision 0.6%, independents 7.8%; seats by party - Fine Gael 76, Labor Party 37, Fianna Fail 20, Sinn Fein 14, United Left Alliance 5, New Vision 1, independents 13; note - after November 2009 disbandment of the Progressive Democrats, the two members of the Senate continued as independent DPs
note:
on 8 November 2008, delegates voted to disband the Progressive Democrats, and in November 2009 it officially stopped operating as a political party
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (Court of Final Appeal) (judges appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister and cabinet); Courts of First Instance (includes High Court)
|
|
|
|
|
Fianna Fail [Michael MARTIN]; Fine Gael [Enda KENNY]; Green Party [Eamon RYAN]; Labor Party [Eamon GILMORE]; New Vision; Sinn Fein [Gerry ADAMS]; Socialist Party [Joe HIGGINS]; The Workers' Party [Michael FINNEGAN]; United Left Alliance
|
|
|
|
|
Families Acting for Innocent Relatives or FAIR [Brian MCCONNELL] (seek compensation for victims of violence); Families Against Intimidation and Terror or FAIT (oppose terrorism); Gaeltacht Civil Rights Campaign (Coiste Cearta Sibhialta na Gaeilge) or CCSG (encourages the use of the Irish language and campaigns for greater civil rights in Irish speaking areas); Iona Institute [David QUINN] (a conservative Catholic think tank); Irish Anti-War Movement [Richard BOYD BARRETT] (campaigns against wars around the world); Irish Republican Army or IRA (terrorist group); Keep Ireland Open (environmental group); Midland Railway Action Group or MRAG [Willie ALLEN] (transportation promoters); Peace and Neutrality Alliance [Roger COLE] (campaigns to protect Irish neutrality); Rail Users Ireland (formerly the Platform 11 - transportation promoters); 32 Country Sovereignty Movement or 32CSM (supports a fully sovereign Ireland); Ulster Defence Association or UDA (terrorist group)
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Michael COLLINS
chancery:
2234 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 462-3939
FAX:
[1] (202) 232-5993
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires John HENNESSEY-NILAND
embassy:
42 Elgin Road, Ballsbridge, Dublin 4
mailing address:
use embassy street address
telephone:
[353] (1) 668-8777
FAX:
[353] (1) 668-9946
|
|
|
|
|
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), white, and orange; officially the flag colors have no meaning, but a common interpretation is that the green represents the Irish nationalist (Gaelic) tradition of Ireland; orange represents the Orange tradition (minority supporters of William of Orange); white symbolizes peace (or a lasting truce) between the green and the orange
note:
similar to the flag of Cote d'Ivoire, which is shorter and has the colors reversed - orange (hoist side), white, and green; also similar to the flag of Italy, which is shorter and has colors of green (hoist side), white, and red
|
|
|
|
|
harp
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Amhran na bhFiann" (The Soldier's Song)
lyrics/music:
Peadar KEARNEY [English], Liam O RINN [Irish]/Patrick HEENEY and Peadar KEARNEY
note:
adopted 1926; instead of "Amhran na bhFiann," the song "Ireland's Call" is often used in athletic events where citizens of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland compete as a unified team
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ireland is a small, modern, trade-dependent economy. Ireland was among the initial group of 12 EU nations that began circulating the euro on 1 January 2002. GDP growth averaged 6% in 1995-2007, but economic activity has dropped sharply since the onset of the world financial crisis, with GDP falling by over 3% in 2008, nearly 7% in 2009, and less than 1% in 2010. Ireland entered into a recession in 2008 for the first time in more than a decade, with the subsequent collapse of its domestic property and construction markets. Property prices rose more rapidly in Ireland in the decade up to 2007 than in any other developed economy. Since their 2007 peak, average house prices have fallen 47%. In the wake of the collapse of the construction sector and the downturn in consumer spending and business investment, the export sector, dominated by foreign multinationals, has become a key component of Ireland's economy. Agriculture, once the most important sector, is now dwarfed by industry and services. In 2008 the COWEN government moved to guarantee all bank deposits, recapitalize the banking system, and establish partly-public venture capital funds in response to the country's economic downturn. In 2009, in continued efforts to stabilize the banking sector, the Irish Government established the National Asset Management Agency (NAMA) to acquire problem commercial property and development loans from Irish banks. Faced with sharply reduced revenues and a burgeoning budget deficit, the Irish Government introduced the first in a series of draconian budgets in 2009. In addition to across-the-board cuts in spending, the 2009 budget included wage reductions for all public servants. These measures were not sufficient. In 2010, the budget deficit reached 32.4% of GDP - the world's largest deficit, as a percentage of GDP - because of additional government support for the banking sector. In late 2010, the former COWEN Government agreed to a $112 billion loan package from the EU and IMF to help Dublin further increase the capitalization of its banking sector and avoid defaulting on its sovereign debt. Since entering office in March 2011, the KENNY government has intensified austerity measures to try to meet the deficit targets under Ireland's EU-IMF program. Ireland achieved moderate growth of 1.4% in 2011 and cut the budget deficit to 9.1% of GDP. Although the recovery slowed in 2012 because of weaker EU demand for Irish exports, Dublin managed to trim the deficit to about 8.5% of GDP.
|
|
|
|
|
$191.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$190.1 billion (2011 est.)
$187.5 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$204.7 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.7% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
1.4% (2011 est.)
-0.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$41,700 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$41,500 (2011 est.)
$41,900 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2%
industry:
29%
services:
69% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.104 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 5%
industry:
19%
services:
76% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
14.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
14.4% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.9%
highest 10%:
27.2% (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
33.9 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 92
35.9 (1987)
|
|
|
|
|
9.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $71.57 billion
expenditures:
$88.97 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
35% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
-8.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
118% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
108.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
2.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 122
1.75% (31 December 2010)
note:
this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
3.81% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$118.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$118.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|
|
$291.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$260 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$892.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$983.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$35.36 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 56
$33.72 billion (31 December 2010)
$29.88 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
barley, potatoes, wheat; beef, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
$3.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$2.484 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$113.6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
$118.1 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, computers, chemicals, medical devices, pharmaceuticals; food products, animal products
|
|
|
|
|
US 22.3%, UK 16.1%, Belgium 15.5%, Germany 7%, France 5.7%, Switzerland 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$63.1 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$67.18 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
data processing equipment, other machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum and petroleum products, textiles, clothing
|
|
|
|
|
UK 39.8%, US 13%, Germany 7.8%, Netherlands 5.8% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.703 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
$2.115 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.352 trillion (30 September 2011)
country comparison to the world: 10
$2.283 trillion (31 December 2010)
|
|
|
|
|
$260.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$243.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$338.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$324.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7838 (2012 est.)
0.7185 (2011 est.)
755 (2010 est.)
0.7198 (2009 est.)
0.6827 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.35 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
26.1 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
242 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
732 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
7.401 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
75.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
3.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
17.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
53,560 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
55,340 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
144,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
17,480 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
166,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
346 million cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
4.981 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
|
|
|
|
|
4.633 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
9.911 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
40.48 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.047 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
4.906 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modern digital system using cable and microwave radio relay
domestic:
system privatized but dominated by former state monopoly operator; increasing levels of broadband access particularly in urban areas
international:
country code - 353; landing point for the Hibernia-Atlantic submarine cable with links to the US, Canada, and UK; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
publicly-owned broadcaster Radio Telefis Eireann (RTE) operates 2 TV stations; commercial TV stations are available; about 75% of households utilize multi-channel satellite and TV services that provide access to a wide range of stations; RTE operates 4 national radio stations and has launched digital audio broadcasts on several stations; a number of commercial broadcast stations operate at the national, regional, and local levels (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.ie
|
|
|
|
|
1.387 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
3.042 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
5
under 914 m:
5 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
21 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 1,888 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,237 km
country comparison to the world: 54
broad gauge:
1,872 km 1.600-m gauge (37 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
1,365 km 0.914-m gauge (operated by the Irish Peat Board to transport peat to power stations and briquetting plants) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 96,036 km
country comparison to the world: 45
paved:
96,036 km (includes 1,224 km of expressways) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
956 km (pleasure craft only) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
total: 31
country comparison to the world: 84
by type:
cargo 28, chemical tanker 2, container 1
foreign-owned:
5 (France 2, Spain 1, US 2)
registered in other countries:
33 (Bahamas 3, Bermuda 1, Cambodia 1, Cyprus 3, Isle of Man 1, Kazakhstan 1, Malta 4, Marshall Islands 6, Netherlands 8, Panama 1, Russia 1, Slovakia 1, Sweden 1, UK 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Cork, Dublin, Shannon Foynes, Waterford
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Irish Defense Forces (Oglaigh na h-Eireannn), Permanent Defence Force: Army, Naval Service, Air Corps (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
17-25 years of age for male and female voluntary military service (17-27 years of age for the Naval Service); enlistees 16 years of age can be recruited for apprentice specialist positions; 17-35 years of age for the Reserve Defense Forces (RDF); maximum obligation 12 years (5 years IDF, 7 years RDF); EU citizenship or 5-year residence in Ireland required (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,179,125
females age 16-49:
1,163,728 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 977,631
females age 16-49:
965,900 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 28,564
female:
27,197 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.9% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Ireland |
|
|
|
Ireland, Iceland, and the UK dispute Denmark's claim that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for and consumer of hashish from North Africa to the UK and Netherlands and of European-produced synthetic drugs; increasing consumption of South American cocaine; minor transshipment point for heroin and cocaine destined for Western Europe; despite recent legislation, narcotics-related money laundering - using bureaux de change, trusts, and shell companies involving the offshore financial community - remains a concern
|
|
|
|
|
|