|
|
|
Following more than three centuries under Portuguese rule, Brazil gained its independence in 1822, maintaining a monarchical system of government until the abolition of slavery in 1888 and the subsequent proclamation of a republic by the military in 1889. Brazilian coffee exporters politically dominated the country until populist leader Getulio VARGAS rose to power in 1930. By far the largest and most populous country in South America, Brazil underwent more than a half century of populist and military government until 1985, when the military regime peacefully ceded power to civilian rulers. Brazil continues to pursue industrial and agricultural growth and development of its interior. Exploiting vast natural resources and a large labor pool, it is today South America's leading economic power and a regional leader, one of the first in the area to begin an economic recovery. Highly unequal income distribution and crime remain pressing problems.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
10 00 S, 55 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8,514,877 sq km
country comparison to the world: 5
land:
8,459,417 sq km
water:
55,460 sq km
note:
includes Arquipelago de Fernando de Noronha, Atol das Rocas, Ilha da Trindade, Ilhas Martin Vaz, and Penedos de Sao Pedro e Sao Paulo
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than the US
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16,885 km
border countries:
Argentina 1,261 km, Bolivia 3,423 km, Colombia 1,644 km, French Guiana 730 km, Guyana 1,606 km, Paraguay 1,365 km, Peru 2,995 km, Suriname 593 km, Uruguay 1,068 km, Venezuela 2,200 km
|
|
|
|
|
7,491 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
mostly tropical, but temperate in south
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat to rolling lowlands in north; some plains, hills, mountains, and narrow coastal belt
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Pico da Neblina 2,994 m
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, gold, iron ore, manganese, nickel, phosphates, platinum, tin, rare earth elements, uranium, petroleum, hydropower, timber
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 6.93%
permanent crops:
0.89%
other:
92.18% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
45,000 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
8,233 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 59.3 cu km/yr (20%/18%/62%)
per capita:
318 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
recurring droughts in northeast; floods and occasional frost in south
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation in Amazon Basin destroys the habitat and endangers a multitude of plant and animal species indigenous to the area; there is a lucrative illegal wildlife trade; air and water pollution in Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo, and several other large cities; land degradation and water pollution caused by improper mining activities; wetland degradation; severe oil spills
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
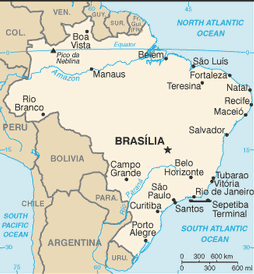
largest country in South America; shares common boundaries with every South American country except Chile and Ecuador
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Brazil |
|
|
|
noun: Brazilian(s)
adjective:
Brazilian
|
|
|
|
|
white 53.7%, mulatto (mixed white and black) 38.5%, black 6.2%, other (includes Japanese, Arab, Amerindian) 0.9%, unspecified 0.7% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Portuguese (official and most widely spoken language)
note:
less common languages include Spanish (border areas and schools), German, Italian, Japanese, English, and a large number of minor Amerindian languages
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic (nominal) 73.6%, Protestant 15.4%, Spiritualist 1.3%, Bantu/voodoo 0.3%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.2%, none 7.4% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Brazil's rapid fertility decline since the 1960s is the main factor behind the country's slowing population growth rate, aging population, and fast-paced demographic transition. Brasilia has not taken full advantage of its large working-age population to develop its human capital and strengthen its social and economic institutions. The current favorable age structure will begin to shift around 2025, with the labor force shrinking and the elderly starting to compose an increasing share of the total population. Well-funded public pensions have nearly wiped out poverty among the elderly, but limited social spending on children has restricted investment in education - a primary means of escaping poverty. Brazil's poverty and income inequality levels remain high despite improvements in the 2000s and continue to disproportionately affect the Northeast, North, and Center-West, women, and black, mixed race, and indigenous populations. Disparities in opportunities foster social exclusion and contribute to Brazil's high crime rate, particularly violent crime in cities and favelas.
Brazil has traditionally been a net recipient of immigrants, with its southeast being the prime destination. After the importation of African slaves was outlawed in the mid-19th century, Brazil sought Europeans (Italians, Portuguese, Spaniards, and Germans) and later Asians (Japanese) to work in agriculture, especially coffee cultivation. Recent immigrants come mainly from Argentina, Chile, and Andean countries (many are unskilled illegal migrants) or are returning Brazilian nationals. Since Brazil's economic downturn in the 1980s, emigration to the United States, Europe, and Japan has been rising but is negligible relative to Brazil's total population. The majority of these emigrants are well-educated and middle-class. Fewer Brazilian peasants are emigrating to neighboring countries to take up agricultural work.
|
|
|
|
|
199,321,413 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 24.7% (male 25,066,889/ female 24,125,185)
15-64 years:
68.2% (male 67,365,021/ female 68,597,919)
65 years and over:
7.1% (male 6,007,524/ female 8,158,875) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 29.6 years
male:
28.8 years
female:
30.5 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.86% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
15.2 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
6.5 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
-0.09 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 87% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Sao Paulo 19.96 million; Rio de Janeiro 11.836 million; Belo Horizonte 5.736 million; Porto Alegre 4.034 million; BRASILIA (capital) 3.789 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.74 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
56 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
total: 20.5 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 93
male:
23.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
16.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 72.79 years
country comparison to the world: 124
male:
69.24 years
female:
76.53 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.82 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
9% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
1.72 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4 beds/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 87% of population
rural: 37% of population
total: 80% of population
unimproved:
urban: 13% of population
rural: 63% of population
total: 20% of population
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
11.1% (2003)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
2.2% (2007)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
5% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
88.6%
male:
88.4%
female:
88.8% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14 years
male:
14 years
female:
14 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.8%
country comparison to the world: 65
male:
13.9%
female:
23.1% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Federative Republic of Brazil
conventional short form:
Brazil
local long form:
Republica Federativa do Brasil
local short form:
Brasil
|
|
|
|
|
federal republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Brasilia
geographic coordinates:
15 47 S, 47 55 W
time difference:
UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins third Sunday in October; ends last Sunday in February
note:
Brazil is divided into three time zones, including one for the Fernando de Noronha Islands
|
|
|
|
|
26 states (estados, singular - estado) and 1 federal district* (distrito federal); Acre, Alagoas, Amapa, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceara, Distrito Federal*, Espirito Santo, Goias, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Para, Paraiba, Parana, Pernambuco, Piaui, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondonia, Roraima, Santa Catarina, Sao Paulo, Sergipe, Tocantins
|
|
|
|
|
7 September 1822 (from Portugal)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 7 September (1822)
|
|
|
|
|
5 October 1988
|
|
|
|
|
civil law; note - a new civil law code was enacted in 2002 replacing the 1916 code
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
voluntary between 16 to under 18 years of age and over 70; compulsory 18 to 70 years of age; note - military conscripts do not vote by law
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Dilma ROUSSEFF (since 1 January 2011); Vice President Michel TEMER (since 1 January 2011); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Dilma ROUSSEFF (since 1 January 2011); Vice President Michel TEMER (since 1 January 2011)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a single four-year term; election last held on 3 October 2010 with runoff on 31 October 2010 (next to be held on 5 October 2014 and, if necessary, a runoff election on 2 November 2014)
election results:
Dilma ROUSSEFF (PT) elected president in a runoff election; percent of vote - Dilma ROUSSEFF 56.01%, Jose SERRA (PSDB) 43.99%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral National Congress or Congresso Nacional consists of the Federal Senate or Senado Federal (81 seats; 3 members from each state and federal district elected according to the principle of majority to serve eight-year terms; one-third and two-thirds of members elected every four years, alternately) and the Chamber of Deputies or Camara dos Deputados (513 seats; members are elected by proportional representation to serve four-year terms)
elections:
Federal Senate - last held on 3 October 2010 for two-thirds of the Senate (next to be held in October 2014 for one-third of the Senate); Chamber of Deputies - last held on 3 October 2010 (next to be held in October 2014)
election results:
Federal Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PMDB 20, PT 13, PSDB 10, DEM (formerly PFL) 7, PTdoB 6, PP 5, PDT 4, PR 4, PSB 4, PPS 1, PRB 1, other 3; Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PT 87, PMDB 80, PSDB 53, DEM (formerly PFL) 43, PP 41, PR 41, PSB 34, PDT 28, PTdoB 21, PSC 17, PCdoB 15, PV 15, PPS 12, other 18
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Federal Tribunal or STF (11 ministers are appointed for life by the president and confirmed by the Senate); Superior Tribunal of Justice or STJ; Superior Electoral Tribunal or TSE; Regional Federal Tribunals (judges are appointed for life); note - though appointed "for life," judges, like all federal employees, have a mandatory retirement age of 70
|
|
|
|
|
Brazilian Democratic Movement Party or PMDB [Michel TEMER]; Brazilian Labor Party or PTB [Roberto JEFFERSON]; Brazilian Renewal Labor Party or PRTB [Jose Levy FIDELIX da Cruz]; Brazilian Republican Party or PRB [Vitor Paulo DOS SANTOS]; Brazilian Social Democracy Party or PSDB [Sergio GUERRA]; Brazilian Socialist Party or PSB [Eduardo Henrique Accioly CAMPOS]; Christian Labor Party or PTC [Daniel TOURINHO]; Communist Party of Brazil or PCdoB [Jose Renato RABELO]; Democratic Labor Party or PDT [Carlos Roberto LUPI]; the Democrats or DEM [Jose AGRIPINO] (formerly Liberal Front Party or PFL); Freedom and Socialism Party or PSOL [Ivan VALENTE]; Green Party or PV [Jose Luiz PENNA]; Humanist Party of Solidarity or PHS [Philippe GUEDON]; Labor Party of Brazil or PTdoB [Luis Henrique de Oliveira RESENDE]; National Mobilization Party or PMN [Celso BRANT]; Party of the Republic or PR [Sergio Victor TAMER]; Popular Socialist Party or PPS [Roberto Joao PEREIRA FREIRE]; Progressive Party or PP [Francisco DORNELLES]; Social Christian Party or PSC [Vitor Jorge Abdala NOSSEIS]; Social Democracy Party or PSD [Gilberto KASSAB]; Workers' Party or PT [Rui FALCAO]
|
|
|
|
|
Landless Workers' Movement or MST
other:
industrial federations; labor unions and federations; large farmers' associations; religious groups including evangelical Christian churches and the Catholic Church
|
|
|
|
|
AfDB (nonregional member), BIS, BRICS, CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, CPLP, FAO, FATF, G-15, G-20, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, LAS (observer), Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS, OECD (Enhanced Engagement, OPANAL, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mauro Luiz Iecker VIEIRA
chancery:
3006 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 238-2805
FAX:
[1] (202) 238-2827
consulate(s) general:
Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Thomas A. SHANNON
embassy:
Avenida das Nacoes, Quadra 801, Lote 3, Distrito Federal Cep 70403-900, Brasilia
mailing address:
Unit 7500, DPO, AA 34030
telephone:
[55] (61) 3312-7000
FAX:
[55] (61) 3225-9136
consulate(s) general:
Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo
consulate(s):
Recife
|
|
|
|
|
green with a large yellow diamond in the center bearing a blue celestial globe with 27 white five-pointed stars; the globe has a white equatorial band with the motto ORDEM E PROGRESSO (Order and Progress); the current flag was inspired by the banner of the former Empire of Brazil (1822-1889); on the imperial flag, the green represented the House of Braganza of Pedro I, the first Emperor of Brazil, while the yellow stood for the Habsburg Family of his wife; on the modern flag the green represents the forests of the country and the yellow rhombus its mineral wealth; the blue circle and stars, which replaced the coat of arms of the original flag, depict the sky over Rio de Janeiro on the morning of 15 November 1889 - the day the Republic of Brazil was declared; the number of stars has changed with the creation of new states and has risen from an original 21 to the current 27 (one for each state and the Federal District)
|
|
|
|
|
Southern Cross constellation
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Hino Nacional Brasileiro" (Brazilian National Anthem)
lyrics/music:
Joaquim Osorio Duque ESTRADA/Francisco Manoel DA SILVA
note:
music adopted 1890, lyrics adopted 1922; the anthem's music, composed in 1822, was used unofficially for many years before it was adopted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characterized by large and well-developed agricultural, mining, manufacturing, and service sectors, Brazil's economy outweighs that of all other South American countries, and Brazil is expanding its presence in world markets. Since 2003, Brazil has steadily improved its macroeconomic stability, building up foreign reserves, and reducing its debt profile by shifting its debt burden toward real denominated and domestically held instruments. In 2008, Brazil became a net external creditor and two ratings agencies awarded investment grade status to its debt. After strong growth in 2007 and 2008, the onset of the global financial crisis hit Brazil in 2008. Brazil experienced two quarters of recession, as global demand for Brazil's commodity-based exports dwindled and external credit dried up. However, Brazil was one of the first emerging markets to begin a recovery. In 2010, consumer and investor confidence revived and GDP growth reached 7.5%, the highest growth rate in the past 25 years. Rising inflation led the authorities to take measures to cool the economy; these actions and the deteriorating international economic situation slowed growth to 2.7% in 2011, and 1.5% in 2012. Despite slower growth, in 2011 Brazil overtook the United Kingdom as the world's seventh largest economy in terms of GDP. Unemployment is at historic lows and Brazil's traditionally high level of income inequality has declined for each of the last 14 years. Brazil's historically high interest rates have made it an attractive destination for foreign investors. Large capital inflows over the past several years have contributed to the appreciation of the currency, hurting the competitiveness of Brazilian manufacturing and leading the government to intervene in foreign exchanges markets and raise taxes on some foreign capital inflows. President Dilma ROUSSEFF has retained the previous administration's commitment to inflation targeting by the central bank, a floating exchange rate, and fiscal restraint. In an effort to boost growth, in 2012 the administration implemented a series of more expansionary monetary and fiscal policies that have failed to stimulate much growth.
|
|
|
|
|
$2.362 trillion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$2.331 trillion (2011 est.)
$2.269 trillion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$2.425 trillion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
2.7% (2011 est.)
7.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$12,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$12,000 (2011 est.)
$11,700 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 5.4%
industry:
27.4%
services:
67.2% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
107.1 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 20%
industry:
14%
services:
66% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.2% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
21.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 0.8%
highest 10%:
42.9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
51.9 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 16
60.7 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
18.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $911.4 billion
expenditures:
$846.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
37.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
2.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
54.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
54.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
6.6% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.25% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
11% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
39.4% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
43.88% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$158.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$152.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.878 trillion (30 November 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
$1.826 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.537 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
$2.247 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.229 trillion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 10
$1.546 trillion (31 December 2010)
$1.167 trillion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, soybeans, wheat, rice, corn, sugarcane, cocoa, citrus; beef
|
|
|
|
|
-0.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
-$65.13 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
-$52.48 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$256 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$256 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
transport equipment, iron ore, soybeans, footwear, coffee, autos
|
|
|
|
|
China 17.3%, US 10.1%, Argentina 8.9%, Netherlands 5.3% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$238.8 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$226.2 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, electrical and transport equipment, chemical products, oil, automotive parts, electronics
|
|
|
|
|
US 15.1%, China 14.5%, Argentina 7.5%, Germany 6.7%, South Korea 4.5% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$371.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$352 billion (31 December 2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$405.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$382.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$595.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
$539.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$176.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$171.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
reals (BRL) per US dollar -
2.1 (2012 est.)
1.675 (2011 est.)
1.7592 (2010 est.)
2 (2009)
1.8644 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
489.5 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
438.3 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
1.257 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
36.63 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
106.2 million kW (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
17.1% of total installed capacity (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% of total installed capacity (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
74.7% of total installed capacity (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
6.3% of total installed capacity (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
2.633 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
533,200 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
412,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
26 billion bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
2.008 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
2.594 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
164,300 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
325,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
24.07 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
26.7 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
12.6 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
416.9 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
453.9 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.026 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
244.358 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: good working system including an extensive microwave radio relay system and a domestic satellite system with 64 earth stations
domestic:
fixed-line connections have remained relatively stable in recent years and stand at about 20 per 100 persons; less expensive mobile-cellular technology has been a major driver in expanding telephone service to the lower-income segments of the population with mobile-cellular teledensity roughly 120 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 55; landing point for a number of submarine cables, including Americas-1, Americas-2, Atlantis-2, GlobeNet, South America-1, South American Crossing/Latin American Nautilus, and UNISUR that provide direct connectivity to South and Central America, the Caribbean, the US, Africa, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic Ocean region east), connected by microwave relay system to Mercosur Brazilsat B3 satellite earth station (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
state-run Radiobras operates a radio and a TV network; more than 1,000 radio stations and more than 100 TV channels operating - mostly privately owned; private media ownership highly concentrated (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.br
|
|
|
|
|
26.577 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
75.982 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,105 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
total: 713
over 3,047 m:
7
2,438 to 3,047 m:
28
1,524 to 2,437 m:
174
914 to 1,523 m:
449
under 914 m:
55 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,392
1,524 to 2,437 m:
91
914 to 1,523 m:
1,648
under 914 m:
1,653 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
13 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate/gas 62 km; gas 13,514 km; liquid petroleum gas 352 km; oil 3,729 km; refined products 4,684 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28,538 km
country comparison to the world: 10
broad gauge:
5,627 km 1.600-m gauge (467 km electrified)
standard gauge:
194 km 1.440-m gauge
narrow gauge:
22,717 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,580,964 km
country comparison to the world: 4
paved:
212,798 km
unpaved:
1,368,166 km
note:
does not include urban roads (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
50,000 km (most in areas remote from industry and population) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
total: 109
country comparison to the world: 50
by type:
bulk carrier 18, cargo 16, chemical tanker 7, container 13, liquefied gas 11, petroleum tanker 39, roll on/roll off 5
foreign-owned:
27 (Chile 1, Denmark 3, Germany 6, Greece 1, Norway 3, Spain 12, Turkey 1)
registered in other countries:
36 (Argentina 1, Bahamas 1, Ghana 1, Liberia 20, Marshall Islands 1, Panama 3, Singapore 9) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
cargo ports (tonnage): Ilha Grande (Gebig), Paranagua, Rio Grande, Santos, Sao Sebastiao, Tubarao
container ports (TEUs):
Santos (2,677,839), Itajai (693,580)
oil terminals:
DTSE/Gegua oil terminal, Guaiba Island terminal, Guamare oil terminal
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports that the territorial and offshore waters in the Atlantic Ocean remain a significant risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; 2010 saw an 80% increase in attacks over 2009; numerous commercial vessels were attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; crews were robbed and stores or cargoes stolen
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brazilian Army (Exercito Brasileiro, EB), Brazilian Navy (Marinha do Brasil (MB), includes Naval Air and Marine Corps (Corpo de Fuzileiros Navais)), Brazilian Air Force (Forca Aerea Brasileira, FAB) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
21-45 years of age for compulsory military service; conscript service obligation - 9 to 12 months; 17-45 years of age for voluntary service; an increasing percentage of the ranks are "long-service" volunteer professionals; women were allowed to serve in the armed forces beginning in early 1980s when the Brazilian Army became the first army in South America to accept women into career ranks; women serve in Navy and Air Force only in Women's Reserve Corps (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 53,350,703
females age 16-49:
53,433,918 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 38,993,989
females age 16-49:
44,841,661 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 1,733,168
female:
1,672,477 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Brazil |
|
|
|
uncontested boundary dispute between Brazil and Uruguay over Braziliera/Brasiliera Island in the Quarai/Cuareim River leaves the tripoint with Argentina in question; smuggling of firearms and narcotics continues to be an issue along the Uruguay-Brazil border; Colombian-organized illegal narcotics and paramilitary activities penetrate Brazil's border region with Venezuela
|
|
|
|
|
second-largest consumer of cocaine in the world; illicit producer of cannabis; trace amounts of coca cultivation in the Amazon region, used for domestic consumption; government has a large-scale eradication program to control cannabis; important transshipment country for Bolivian, Colombian, and Peruvian cocaine headed for Europe; also used by traffickers as a way station for narcotics air transshipments between Peru and Colombia; upsurge in drug-related violence and weapons smuggling; important market for Colombian, Bolivian, and Peruvian cocaine; illicit narcotics proceeds are often laundered through the financial system; significant illicit financial activity in the Tri-Border Area (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|