| Introduction ::Bangladesh |
|
|
|
Muslim conversions and settlement in the region now referred to as Bangladesh began in the 10th century, primarily from Arab and Persian traders and preachers. Europeans began to set up trading posts in the area in the 16th century. Eventually the area known as Bengal, primarily Hindu in the western section and mostly Muslim in the eastern half, became part of British India. Partition in 1947 resulted in an eastern wing of Pakistan in the Muslim-majority area, which became East Pakistan. Calls for greater autonomy and animosity between the eastern and western wings of Pakistan led to a Bengali independence movement. That movement, led by the Awami League (AL), won independence for Bangladesh in 1971, with India's assistance and after the death of at least 300,000 civilians. The post-independence, AL government faced daunting challenges and in 1975 was overthrown by the military, triggering a series of military coups that resulted in a military-backed government and subsequent creation of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). That government also ended in a coup in 1981, followed by military-backed rule until democratic elections in 1991. The BNP and AL have alternated in power since then, with the exception of a military-backed, emergency caretaker regime that suspended parliamentary elections planned for January 2007 in an effort to reform the political system and root out corruption. That government returned the country to fully democratic rule in December 2008 with the election of the AL and Prime Minister Sheikh HASINA. With the help of international development assistance, Bangladesh has made great progress in food security since independence, and the economy has grown at an average of about 6 percent over the last two decades.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Southern Asia, bordering the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and India
|
|
|
|
|
24 00 N, 90 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 143,998 sq km
country comparison to the world: 95
land:
130,168 sq km
water:
13,830 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Iowa
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,246 km
border countries:
Burma 193 km, India 4,053 km
|
|
|
|
|
580 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
18 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
up to the outer limits of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; mild winter (October to March); hot, humid summer (March to June); humid, warm rainy monsoon (June to October)
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat alluvial plain; hilly in southeast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Keokradong 1,230 m
|
|
|
|
|
natural gas, arable land, timber, coal
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 55.39%
permanent crops:
3.08%
other:
41.53% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
50,500 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
1,210.6 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 79.4 cu km/yr (3%/1%/96%)
per capita:
560 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
droughts; cyclones; much of the country routinely inundated during the summer monsoon season
|
|
|
|
|
many people are landless and forced to live on and cultivate flood-prone land; waterborne diseases prevalent in surface water; water pollution, especially of fishing areas, results from the use of commercial pesticides; ground water contaminated by naturally occurring arsenic; intermittent water shortages because of falling water tables in the northern and central parts of the country; soil degradation and erosion; deforestation; severe overpopulation
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
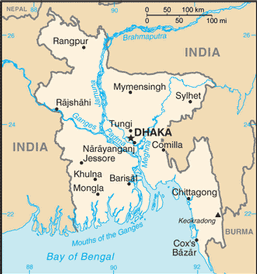
most of the country is situated on deltas of large rivers flowing from the Himalayas: the Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna to eventually empty into the Bay of Bengal
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Bangladesh |
|
|
|
noun: Bangladeshi(s)
adjective:
Bangladeshi
|
|
|
|
|
Bengali 98%, other 2% (includes tribal groups, non-Bengali Muslims) (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
Bangla (official, also known as Bengali), English
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 89.5%, Hindu 9.6%, other 0.9% (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
161,083,804 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 33.6% (male 27,489,425/ female 26,705,051)
15-64 years:
61.6% (male 47,035,450/ female 52,164,097)
65 years and over:
4.8% (male 3,763,528/ female 3,926,253) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23.6 years
male:
23.1 years
female:
24.1 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.579% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
22.53 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
5.71 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
-1.04 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 28% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
3.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
DHAKA (capital) 14.251 million; Chittagong 4.816 million; Khulna 1.636 million; Rajshahi 853,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.96 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
240 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
total: 48.99 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 45
male:
51.48 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
46.39 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 70.06 years
country comparison to the world: 148
male:
68.21 years
female:
71.98 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.55 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
0.295 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 beds/1,000 population (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 56% of population
rural: 52% of population
total: 53% of population
unimproved:
urban: 44% of population
rural: 48% of population
total: 47% of population
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
6,300 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever and malaria are high risks in some locations
water contact disease:
leptospirosis
animal contact disease:
rabies
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
41.3% (2007)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
56.8%
male:
61.3%
female:
52.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8 years
male:
8 years
female:
8 years (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9.3%
country comparison to the world: 106
male:
8%
female:
13.6% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: People's Republic of Bangladesh
conventional short form:
Bangladesh
local long form:
Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh
local short form:
Bangladesh
former:
East Bengal, East Pakistan
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Dhaka
geographic coordinates:
23 43 N, 90 24 E
time difference:
UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
7 divisions; Barisal, Chittagong, Dhaka, Khulna, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Sylhet
|
|
|
|
|
16 December 1971 (from West Pakistan)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 26 March (1971); Victory Day; note - March 1971 is the date of the Awami League's declaration of an independent Bangladesh, and 16 December, known as Victory Day, memorializes the military victory over Pakistan and the official creation of the state of Bangladesh
|
|
|
|
|
enacted 4 November 1972; effective 16 December 1972; suspended following coup of 24 March 1982; restored 10 November 1986; amended many times
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of mostly English common law and Islamic law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Zillur RAHMAN (since 12 February 2009)
head of government:
Prime Minister Sheikh HASINA Wajed (since 6 January 2009)
cabinet:
Cabinet selected by the prime minister and appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by National Parliament for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); last election held on 11 February 2009 (next must be held by 2014)
election results:
Zillur RAHMAN declared president-elect by the Election Commission on 11 February 2009 (sworn in on 12 February); he ran unopposed as president
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Parliament or Jatiya Sangsad; 300 seats (45 reserved for women) elected by popular vote from single territorial constituencies; members serve five-year terms
elections:
last held on 29 December 2008; note - general elections must be held within 90 days of the expiration of the Parliament or by 24 January 2014 or earlier if Parliament is dissolved before its term expires
election results:
percent of vote by party - AL 49%, BNP 33.2%, JP 7%, JIB 4.6%, other 6.2%; seats by party - AL 230, BNP 30, JP 27, JIB 2, other 11
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (the chief justices and other judges are appointed by the president)
|
|
|
|
|
Awami League or AL [Sheikh HASINA]; Communist Party of Bangladesh or CPB [Manjurul A. KHAN]; Bangladesh Nationalist Party or BNP [Khaleda ZIA]; Bikalpa Dhara Bangladesh or BDB [Badrudozza CHOWDHURY]; Islami Oikya Jote or IOJ [multiple leaders]; Jamaat-e-Islami Bangladesh or JIB [Matiur Rahman NIZAMI]; Jatiya Party or JP (Ershad faction) [Hussain Mohammad ERSHAD]; Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Oli AHMED]
|
|
|
|
|
Advocacy to End Gender-based Violence through the MoWCA (Ministry of Women's and Children's Affairs); Ain o Salish Kendro (Law and Order Center); Bangladesh Rural Advancement Committee or BRAC; Bangladesh Center for Worker Solidarity; Federation of Bangladesh Chambers of Commerce and Industry; Odikhar (Human Rights)
other:
associations of madrassa teachers; business associations, including those intended to promote international trade; development and advocacy NGOs associated with the Grameen Bank; environmentalists; Islamist groups; labor rights advocacy groups; nongovernmental organizations focused on poverty, alleviation, and socioeconomic international trade; religious leaders; tribal groups and advocacy organizations; union leaders
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CICA (observer), CP, D-8, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Akramul QADER
chancery:
3510 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 244-0183
FAX:
[1] (202) 244-7830/2771
consulate(s) general:
Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Dan W. MOZENA
embassy:
Madani Avenue, Baridhara, Dhaka 1212
mailing address:
G. P. O. Box 323, Dhaka 1000
telephone:
[880] (2) 885-5500
FAX:
[880] (2) 882-3744
|
|
|
|
|
green field with a large red disk shifted slightly to the hoist side of center; the red disk represents the rising sun and the sacrifice to achieve independence; the green field symbolizes the lush vegetation of Bangladesh
|
|
|
|
|
Bengal tiger
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Amar Shonar Bangla" (My Golden Bengal)
lyrics/music:
Rabindranath TAGORE
note:
adopted 1971; Rabindranath TAGORE, a Nobel laureate, also wrote India's national anthem
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In real terms Bangladesh's economy has grown 5.8% per year since 1996 despite political instability, poor infrastructure, corruption, insufficient power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms. Bangladesh remains a poor, overpopulated, and inefficiently-governed nation. Although more than half of GDP is generated through the service sector, 45% of Bangladeshis are employed in the agriculture sector with rice as the single-most-important product. Bangladesh's growth was resilient during the 2008-09 global financial crisis and recession. Garment exports, totaling $12.3 billion in FY09 and remittances from overseas Bangladeshis, totaling $11 billion in FY10, accounted for almost 12% of GDP.
|
|
|
|
|
$305.5 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
$288.1 billion (2011 est.)
$270.5 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$118.7 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
6.5% (2011 est.)
6.4% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
$1,900 (2011 est.)
$1,800 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17.3%
industry:
28.6%
services:
54.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
77 million
country comparison to the world: 7
note:
extensive export of labor to Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Oman, Qatar, and Malaysia; workers' remittances were $10.9 billion in FY09/10 (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 45%
industry:
30%
services:
25% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
5% (2011 est.)
note:
about 40% of the population is underemployed; many participants in the labor force work only a few hours a week, at low wages
|
|
|
|
|
31.51% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 4%
highest 10%:
27% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
33.2 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 97
33.6 (1996)
|
|
|
|
|
25.1% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $13.98 billion
expenditures:
$19.62 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
-4.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
32% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
33.9% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
10.7% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
5% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
13.3% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
13.25% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$14.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
$13.19 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$66.84 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$66.14 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$80.81 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$68.57 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$23.55 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 65
$15.68 billion (31 December 2010)
$7.068 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, jute, tea, wheat, sugarcane, potatoes, tobacco, pulses, oilseeds, spices, fruit; beef, milk, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
7.4% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
-$941.9 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
$243.6 million (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$25.79 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
$24.56 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
garments, knitwear, agricultural products, frozen food (fish and seafood), jute and jute goods, leather
|
|
|
|
|
US 19.4%, Germany 16.5%, UK 10%, France 7.3%, Italy 4.4%, Spain 4.2%, Netherlands 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$35.06 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
$32.58 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, chemicals, iron and steel, textiles, foodstuffs, petroleum products, cement
|
|
|
|
|
China 18.2%, India 13.5%, Malaysia 4.9% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$10.19 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
$9.192 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$36.21 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
$33.84 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$7.849 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$6.85 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$93.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
$92.9 million (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
taka (BDT) per US dollar -
82.17 (2012 est.)
74.152 (2011 est.)
69.649 (2010 est.)
69.04 (2009)
68.554 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 July - 30 June
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.7 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
34.83 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
5.819 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
95.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
4% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
0.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
5,200 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
26,460 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
28 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
24,790 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
108,900 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
2,928 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
77,340 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
20.13 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
20.13 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
183.7 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
56.74 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Bangladesh |
|
|
|
977,700 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
84.369 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: inadequate for a modern country; introducing digital systems; trunk systems include VHF and UHF microwave radio relay links, and some fiber-optic cable in cities
domestic:
fixed-line teledensity remains only about 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone subscribership has been increasing rapidly and now exceeds 50 telephones per 100 persons
international:
country code - 880; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-4 fiber-optic submarine cable system that provides links to Europe, the Middle East, and Asia; satellite earth stations - 6; international radiotelephone communications and landline service to neighboring countries (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
state-owned Bangladesh Television (BTV) operates 1 terrestrial TV station, 3 radio networks, and about 10 local stations; 8 private satellite TV stations and 3 private radio stations also broadcasting; foreign satellite TV stations are gaining audience share in the large cities; several international radio broadcasters are available (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.bd
|
|
|
|
|
71,164 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
617,300 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Bangladesh |
|
|
|
18 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
6
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
4 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
under 914 m:
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
3 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 2,714 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,622 km
country comparison to the world: 64
broad gauge:
946 km 1.676-m gauge
narrow gauge:
1,676 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21,269 km
country comparison to the world: 105
paved:
1,063 km
unpaved:
20,206 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
8,370 km (includes up to 3,060 km of main cargo routes; the network is reduced to 5,200 km in the dry season) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
total: 62
country comparison to the world: 64
by type:
bulk carrier 25, cargo 28, chemical tanker 1, container 5, petroleum tanker 3
foreign-owned:
8 (China 1, Singapore 7)
registered in other countries:
10 (Comoros 1, Hong Kong 1, Panama 5, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1, Sierra Leone 1, Singapore 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Chittagong, Mongla Port
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial waters of Bangladesh remain a high risk for armed robbery against ships; attacks against vessels increased in 2010 for the second consecutive year; 23 commercial vessels were attacked both at anchor and while underway; crews were robbed and stores or cargoes stolen
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bangladesh Defense Force: Bangladesh Army (Sena Bahini), Bangladesh Navy (Noh Bahini, BN), Bangladesh Air Force (Biman Bahini, BAF) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
17-19 years of age for voluntary enlisted military service; Bangladeshi birth and 10th grade education required; intial obligation 15 years (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 36,520,491 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 30,486,086
females age 16-49:
35,616,093 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 1,606,963
female:
1,689,442 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Bangladesh |
|
|
|
Bangladesh referred its maritime boundary claims with Burma and India to the International Tribunal on the Law of the Sea; Prime Minister Singh's September 2011 visit to Bangladesh resulted in the signing of a Protocol to the 1974 Land Boundary Agreement between India and Bangladesh, which had called for the settlement of longstanding boundary disputes over undemarcated areas and the exchange of territorial enclaves, but which had never been implemented; Bangladesh struggles to accommodate 29,000 Rohingya, Burmese Muslim minority from Arakan State, living as refugees in Cox's Bazar; Burmese border authorities are constructing a 200 km (124 mi) wire fence designed to deter illegal cross-border transit and tensions from the military build-up along border
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 229,644 (Burma) (2011)
IDPs:
undetermined (land conflicts, religious persecution) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
transit country for illegal drugs produced in neighboring countries
|
|
|
|
|
|