| Introduction ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
The Trucial States of the Persian Gulf coast granted the UK control of their defense and foreign affairs in 19th century treaties. In 1971, six of these states - Abu Dhabi, 'Ajman, Al Fujayrah, Ash Shariqah, Dubayy, and Umm al Qaywayn - merged to form the United Arab Emirates (UAE). They were joined in 1972 by Ra's al Khaymah. The UAE's per capita GDP is on par with those of leading West European nations. Its high oil revenues and its moderate foreign policy stance have allowed the UAE to play a vital role in the affairs of the region. For more than three decades, oil and global finance drove the UAE's economy. However, in 2008-09, the confluence of falling oil prices, collapsing real estate prices, and the international banking crisis hit the UAE especially hard. The UAE has essentially avoided the "Arab Spring" unrest seen elsewhere in the Middle East, though in March 2011, political activists and intellectuals signed a petition calling for greater public participation in governance that was widely circulated on the Internet. In an effort to stem potential further unrest, the government announced a multi-year, $1.6-billion infrastructure investment plan for the poorer northern Emirates.
|
|
|
|
|
| Geography ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
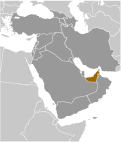
Middle East, bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf, between Oman and Saudi Arabia
|
|
|
|
|
24 00 N, 54 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 83,600 sq km
country comparison to the world: 115
land:
83,600 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Maine
|
|
|
|
|
total: 867 km
border countries:
Oman 410 km, Saudi Arabia 457 km
|
|
|
|
|
1,318 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
desert; cooler in eastern mountains
|
|
|
|
|
flat, barren coastal plain merging into rolling sand dunes of vast desert wasteland; mountains in east
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
Jabal Yibir 1,527 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0.77%
permanent crops:
2.27%
other:
96.96% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2,300 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.3 cu km/yr (23%/9%/68%)
per capita:
511 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
frequent sand and dust storms
|
|
|
|
|
lack of natural freshwater resources compensated by desalination plants; desertification; beach pollution from oil spills
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location along southern approaches to Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oil
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
noun: Emirati(s)
adjective:
Emirati
|
|
|
|
|
Emirati 19%, other Arab and Iranian 23%, South Asian 50%, other expatriates (includes Westerners and East Asians) 8% (1982)
note:
less than 20% are UAE citizens (1982)
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic (official), Persian, English, Hindi, Urdu
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (Islam - official) 96% (Shia 16%), other (includes Christian, Hindu) 4%
|
|
|
|
|
5,314,317 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
note:
estimate is based on the results of the 2005 census that included a significantly higher estimate of net immigration of non-citizens than previous estimates
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 20.5% (male 557,603/ female 532,303)
15-64 years:
78.5% (male 3,060,518/ female 1,113,867)
65 years and over:
0.9% (male 31,942/ female 18,084)
population pyramid: 
note:
73.9% of the population in the 15-64 age group is non-national (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 30.2 years
male:
32.1 years
female:
25 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.055% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
15.76 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
2.04 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 223
|
|
|
|
|
16.82 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 84% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
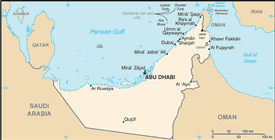
ABU DHABI (capital) 666,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
2.75 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.77 male(s)/female
total population:
2.19 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11.59 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 135
male:
13.54 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
9.55 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 76.71 years
country comparison to the world: 72
male:
74.12 years
female:
79.42 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.38 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
2.8% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
1.93 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 98% of population
rural: 95% of population
total: 97% of population
unimproved:
urban: 2% of population
rural: 5% of population
total: 3% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
33.7% (2000)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
1.2% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
77.9%
male:
76.1%
female:
81.7% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12.1%
country comparison to the world: 90
male:
7.9%
female:
21.8% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
| Government ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
conventional long form: United Arab Emirates
conventional short form:
none
local long form:
Al Imarat al Arabiyah al Muttahidah
local short form:
none
former:
Trucial Oman, Trucial States
abbreviation:
UAE
|
|
|
|
|
federation with specified powers delegated to the UAE federal government and other powers reserved to member emirates
|
|
|
|
|
name: Abu Dhabi
geographic coordinates:
24 28 N, 54 22 E
time difference:
UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
7 emirates (imarat, singular - imarah); Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi), 'Ajman, Al Fujayrah, Ash Shariqah (Sharjah), Dubayy (Dubai), Ra's al Khaymah, Umm al Qaywayn (Quwain)
|
|
|
|
|
2 December 1971 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 2 December (1971)
|
|
|
|
|
2 December 1971; made permanent in 1996
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of Islamic law and civil law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
limited; note - rulers of the seven Emirates each select a proportion of voters for the Federal National Council (FNC) that together account for about 12 percent of the native Emirati population
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President KHALIFA bin Zayid Al-Nuhayyan (since 3 November 2004), ruler of Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi) (since 4 November 2004); Vice President and Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN RASHID Al-Maktum (since 5 January 2006)
head of government:
Prime Minister and Vice President MUHAMMAD BIN RASHID Al-Maktum (since 5 January 2006); Deputy Prime Ministers SAIF bin Zayid Al-Nuhayyan (since 11 May 2009) and MANSUR bin Zayid Al-Nuhayyan (since 11 May 2009)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
note:
there is also a Federal Supreme Council (FSC) composed of the seven emirate rulers; the FSC is the highest constitutional authority in the UAE; establishes general policies and sanctions federal legislation; meets four times a year; Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi) and Dubayy (Dubai) rulers have effective veto power
elections:
president and vice president elected by the FSC for five-year terms (no term limits) from among the seven FSC members; election last held 3 November 2004 upon the death of the UAE's Founding Father and first President ZAYID bin Sultan Al Nuhayyan (next election NA); prime minister and deputy prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
KHALIFA bin Zayid Al-Nuhayyan elected president by a unanimous vote of the FSC; MUHAMMAD bin Rashid Al-Maktum unanimously affirmed vice president after the 2006 death of his brother Sheikh MAKTUM bin Rashid Al-Maktum
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Federal National Council (FNC) or Majlis al-Ittihad al-Watani (40 seats; 20 members appointed by the rulers of the constituent states, 20 members elected to serve four-year terms);
elections:
last held on 24 September 2011 (next to be held in 2015); note - the electoral college was expanded from 6,689 voters in the December 2006 election to 129,274 in the September 2011 election; elections for candidates rather than party lists; 469 candidates including 85 women ran for 20 contested FNC seats
election results:
elected seats by emirate - Abu Dhabi 4, Dubai 4, Sharjah 3, Ras al-Khaimah 3, Ajman 2, Fujairah 2, Umm al-Quwain 2; note - number of appointed seats for each emirate are same as elected seats
|
|
|
|
|
Union Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president)
|
|
|
|
|
none; political parties are not allowed
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AfDB (nonregional member), AFESD, AMF, BIS, CAEU, CICA, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OIF (observer), OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Yusif bin Mani bin Said al-UTAYBA
chancery:
3522 International Court NW, Suite 400, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 243-2400
FAX:
[1] (202) 243-2432
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Michael H. CORBIN
embassy:
Embassies District, Plot 38 Sector W59-02, Street No. 4, Abu Dhabi
mailing address:
P. O. Box 4009, Abu Dhabi
telephone:
[971] (2) 414-2200
FAX:
[971] (2) 414-2603
consulate(s) general:
Dubai
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and black with a wider vertical red band on the hoist side; the flag incorporates all four Pan-Arab colors, which in this case represent fertility (green), neutrality (white), petroleum resources (black), and unity (red); red was the traditional color incorporated into all flags of the emirates before their unification
|
|
|
|
|
golden falcon
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Nashid al-watani al-imarati" (National Anthem of the UAE)
lyrics/music:
AREF Al Sheikh Abdullah Al Hassan/Mohamad Abdel WAHAB
note:
music adopted 1971, lyrics adopted 1996; Mohamad Abdel WAHAB also composed the music for the anthem of Tunisia
|
|
|
|
|
| Economy ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
The UAE has an open economy with a high per capita income and a sizable annual trade surplus. Successful efforts at economic diversification have reduced the portion of GDP based on oil and gas output to 25%. Since the discovery of oil in the UAE more than 30 years ago, the country has undergone a profound transformation from an impoverished region of small desert principalities to a modern state with a high standard of living. The government has increased spending on job creation and infrastructure expansion and is opening up utilities to greater private sector involvement. In April 2004, the UAE signed a Trade and Investment Framework Agreement with Washington and in November 2004 agreed to undertake negotiations toward a Free Trade Agreement with the US; however, those talks have not moved forward. The country's Free Trade Zones - offering 100% foreign ownership and zero taxes - are helping to attract foreign investors. The global financial crisis, tight international credit, and deflated asset prices constricted the economy in 2009. UAE authorities tried to blunt the crisis by increasing spending and boosting liquidity in the banking sector. The crisis hit Dubai hardest, as it was heavily exposed to depressed real estate prices. Dubai lacked sufficient cash to meet its debt obligations, prompting global concern about its solvency. The UAE Central Bank and Abu Dhabi-based banks bought the largest shares. In December 2009 Dubai received an additional $10 billion loan from the emirate of Abu Dhabi. Dependence on oil, a large expatriate workforce, and growing inflation pressures are significant long-term challenges. The UAE's strategic plan for the next few years focuses on diversification and creating more opportunities for nationals through improved education and increased private sector employment.
|
|
|
|
|
$271.2 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
$260.7 billion (2011 est.)
$247.8 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$361.9 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
5.2% (2011 est.)
1.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$49,000 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
$48,500 (2011 est.)
$47,500 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0.8%
industry:
56.1%
services:
43.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.337 million
country comparison to the world: 86
note:
expatriates account for about 85% of the work force (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 7%
industry:
15%
services:
78% (2000 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% (2001)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
19.5% (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
28.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $130.3 billion
expenditures:
$113.8 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
36% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
40.4% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
45.9% of GDP (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
0.9% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$80.53 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
$71.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$234.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
$224.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$313.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
$293.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$93.77 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 42
$104.7 billion (31 December 2010)
$109.6 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
dates, vegetables, watermelons; poultry, eggs, dairy products; fish
|
|
|
|
|
3.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
$26.76 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
$30.65 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$300.6 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$281.6 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil 45%, natural gas, reexports, dried fish, dates
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 16.2%, India 13.5%, Iran 10.9%, South Korea 5.6%, Thailand 5.5%, Singapore 4.4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$220.3 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$202.1 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food
|
|
|
|
|
India 19.8%, China 13.7%, US 8.1%, Germany 4.6% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$43.77 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
$37.27 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$158.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$156.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$91.56 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$83.36 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$58.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$55.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Emirati dirhams (AED) per US dollar -
3.673 (2012 est.)
3.673 (2011 est.)
3.6725 (2010 est.)
3.673 (2009)
3.6725 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
| Energy ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
83.31 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
74.12 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
23.25 million kW (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|
|
3.087 million bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
2.036 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
97.8 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
346,900 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
572,100 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
452,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
377,300 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
51.28 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
60.54 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
7.65 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
16.91 billion cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
6.089 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
199.4 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
1.825 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
11.727 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modern fiber-optic integrated services; digital network with rapidly growing use of mobile-cellular telephones; key centers are Abu Dhabi and Dubai
domestic:
microwave radio relay, fiber optic and coaxial cable
international:
country code - 971; linked to the international submarine cable FLAG (Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe); landing point for both the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cable networks; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat; tropospheric scatter to Bahrain; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia
|
|
|
|
|
except for the many organizations now operating in Dubai's Media Free Zone, most TV and radio stations remain government-owned; widespread use of satellite dishes provides access to pan-Arab and other international broadcasts (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.ae
|
|
|
|
|
337,804 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
3.449 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
42 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25
over 3,047 m:
12
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
4
under 914 m:
2 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
5 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
5 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 458 km; refined products 212 km; gas 2,352 km; liquid petroleum gas 220 km; oil 1,437 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,080 km
country comparison to the world: 157
paved:
4,080 km (includes 253 km of expressways) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 61
country comparison to the world: 65
by type:
bulk carrier 3, cargo 13, chemical tanker 8, container 7, liquefied gas 1, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 24, roll on/roll off 4
foreign-owned:
13 (Greece 3, Kuwait 10)
registered in other countries:
253 (Bahamas 23, Barbados 1, Belize 3, Cambodia 2, Comoros 8, Cyprus 3, Georgia 2, Gibraltar 5, Honduras 1, Hong Kong 1, India 4, Iran 2, Jordan 2, Liberia 37, Malta 1, Marshall Islands 12, Mexico 1, Netherlands 4, North Korea 2, Panama 83, Papua New Guinea 6, Philippines 1, Saint Kitts and Nevis 8, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 3, Saudi Arabia 6, Sierra Leone 1, Singapore 10, Tanzania 3, Togo 1, UK 8, Vanuatu 1, unknown 8) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Al Fujayrah, Mina' Jabal 'Ali (Dubai), Khor Fakkan (Khawr Fakkan), Mubarraz Island, Mina' Rashid (Dubai), Mina' Saqr (Ra's al Khaymah)
|
|
|
|
|
| Military ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
United Arab Emirates Armed Forces: Critical Infrastructure Coastal Patrol Agency (CNIA), Land Forces, Navy, Air Force and Air Defense, Border and Coast Guard Directorate (BCGD) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; 18 years of age for officers and women; no conscription; 16-22 years of age for candidates for the UAE Naval College (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,676,928 (includes non-nationals)
females age 16-49:
981,649 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,229,366
females age 16-49:
842,759 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 27,439
female:
24,419 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::United Arab Emirates |
|
|
|
boundary agreement was signed and ratified with Oman in 2003 for entire border, including Oman's Musandam Peninsula and Al Madhah enclaves, but contents of the agreement and detailed maps showing the alignment have not been published; Iran and UAE dispute Tunb Islands and Abu Musa Island, which Iran occupies
|
|
|
|
|
the UAE is a drug transshipment point for traffickers given its proximity to Southwest Asian drug-producing countries; the UAE's position as a major financial center makes it vulnerable to money laundering; anti-money-laundering controls improving, but informal banking remains unregulated
|
|
|
|
|
|