| Introduction ::Turkmenistan |
|
|
Eastern Turkmenistan for centuries formed part of the Persian province of Khurasan; in medieval times Merv (today known as Mary) was one of the great cities of the Islamic world and an important stop on the Silk Road. Annexed by Russia between 1865 and 1885, Turkmenistan became a Soviet republic in 1924. It achieved independence upon the dissolution of the USSR in 1991. Extensive hydrocarbon/natural gas reserves could prove a boon to this underdeveloped country once extraction and delivery projects are expanded. The Turkmen Government is actively working to diversify its gas export routes beyond the still dominant Russian pipeline network. In 2010, new gas export pipelines that carry Turkmen gas to China and to northern Iran began operating, effectively ending the Russian monopoly on Turkmen gas exports. President for Life Saparmurat NYYAZOW died in December 2006, and Turkmenistan held its first multi-candidate presidential election in February 2007. Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW, a deputy cabinet chairman under NYYAZOW, emerged as the country's new president.
|
|
|
|
|
|
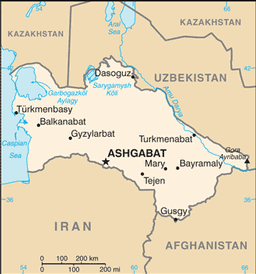
Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea, between Iran and Kazakhstan
|
|
|
|
|
40 00 N, 60 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 488,100 sq km
country comparison to the world: 52
land:
469,930 sq km
water:
18,170 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than California
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,736 km
border countries:
Afghanistan 744 km, Iran 992 km, Kazakhstan 379 km, Uzbekistan 1,621 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km; note - Turkmenistan borders the Caspian Sea (1,768 km)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
subtropical desert
|
|
|
|
|
flat-to-rolling sandy desert with dunes rising to mountains in the south; low mountains along border with Iran; borders Caspian Sea in west
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Vpadina Akchanaya -81 m
note:
Sarygamysh Koli is a lake in northern Turkmenistan with a water level that fluctuates above and below the elevation of Vpadina Akchanaya (the lake has dropped as low as -110 m)
highest point:
Gora Ayribaba 3,139 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, sulfur, salt
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 4.51%
permanent crops:
0.14%
other:
95.35% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
18,000 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
60.9 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24.65 cu km/yr (2%/1%/98%)
per capita:
5,104 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
contamination of soil and groundwater with agricultural chemicals, pesticides; salination, water logging of soil due to poor irrigation methods; Caspian Sea pollution; diversion of a large share of the flow of the Amu Darya into irrigation contributes to that river's inability to replenish the Aral Sea; desertification
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; the western and central low-lying desolate portions of the country make up the great Garagum (Kara-Kum) desert, which occupies over 80% of the country; eastern part is plateau
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,997,503 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 27.5% (male 696,749/female 679,936)
15-64 years:
68.4% (male 1,692,885/female 1,724,019)
65 years and over:
4.1% (male 88,590/female 115,324) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25.3 years
male:
24.9 years
female:
25.8 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.138% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
19.54 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
6.24 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
-1.92 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 50% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
ASHGABAT (capital) 637,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.77 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 42.34 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 58
male:
50.42 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
33.85 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 68.52 years
country comparison to the world: 151
male:
65.57 years
female:
71.63 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.16 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2004 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 97% of population
rural: 72% of population
total: 83% of population
unimproved:
urban: 3% of population
rural: 28% of population
total: 17% of population (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 99% of population
rural: 97% of population
total: 98% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1% of population
rural: 3% of population
total: 2% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Turkmen(s)
adjective:
Turkmen
|
|
|
|
|
Turkmen 85%, Uzbek 5%, Russian 4%, other 6% (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 89%, Eastern Orthodox 9%, unknown 2%
|
|
|
|
|
Turkmen (official) 72%, Russian 12%, Uzbek 9%, other 7%
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
98.8%
male:
99.3%
female:
98.3% (1999 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Turkmenistan |
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Turkmenistan
local long form:
none
local short form:
Turkmenistan
former:
Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
|
|
|
|
|
defines itself as a secular democracy and a presidential republic; in actuality displays authoritarian presidential rule, with power concentrated within the presidential administration
|
|
|
|
|
name: Ashgabat (Ashkhabad)
geographic coordinates:
37 57 N, 58 23 E
time difference:
UTC+5 (10 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
5 provinces (welayatlar, singular - welayat) and 1 independent city*: Ahal Welayaty (Anew), Ashgabat*, Balkan Welayaty (Balkanabat), Dashoguz Welayaty, Lebap Welayaty (Turkmenabat), Mary Welayaty
note:
administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)
|
|
|
|
|
27 October 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 27 October (1991)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 26 September 2008
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system with Islamic law influences
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW (since 14 February 2007); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW (since 14 February 2007)
cabinet:
Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held on 11 February 2007 (next to be held in February 2012)
election results:
Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW elected president; percent of vote - Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW 89.2%, Amanyaz ATAJYKOW 3.2%, other candidates 7.6%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral parliament known as the National Assembly (Mejlis) (125 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 14 December 2008 (next to be held in December 2013)
election results:
100% of elected officials are members of either the Democratic Party of Turkmenistan or its pseudo-civil society parent organization, the Revival Movement, and are preapproved by the president
note:
in 26 September 2008, a new constitution of Turkmenistan abolished a second, 2,507-member legislative body known as the People's Council and expanded the number of deputies in the National Assembly from 65 to 125; the powers formerly held by the People's Council were divided up between the president and the National Assembly
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president)
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Party of Turkmenistan or DPT [Gurbanguly BERDIMUHAMEDOW is chairman; Kasymguly BABAYEW is DPT Political Council First Secretary]
note:
formal opposition parties are outlawed; unofficial, small opposition movements exist abroad; the three most prominent opposition groups-in-exile are the National Democratic Movement of Turkmenistan (NDMT), the Republican Party of Turkmenistan, and the Watan (Fatherland) Party; the NDMT was led by former Foreign Minister Boris SHIKHMURADOV until his arrest and imprisonment in the wake of the 25 November 2002 attack on President NYYAZOW's motorcade
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, CIS (associate member, has not ratified the 1993 CIS charter although it participates in meetings), EAPC, EBRD, ECO, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Meret Bairamovich ORAZOW
chancery:
2207 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 588-1500
FAX:
[1] (202) 588-0697
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Eileen A. MALLOY
embassy:
No. 9 1984 Street (formerly Pushkin Street), Ashgabat, Turkmenistan 744000
mailing address:
7070 Ashgabat Place, Washington, DC 20521-7070
telephone:
[993] (12) 35-00-45
FAX:
[993] (12) 39-26-14
|
|
|
|
|
green field with a vertical red stripe near the hoist side, containing five tribal guls (designs used in producing carpets) stacked above two crossed olive branches; five white stars and a white crescent moon appear in the upper corner of the field just to the fly side of the red stripe; the green color and crescent moon represent Islam; the five stars symbolize the regions or welayats of Turkmenistan; the guls reflect the national identity of Turkmenistan where carpet-making has long been a part of traditional nomadic life
note:
the flag of Turkmenistan is the most intricate of all national flags
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Garassyz, Bitarap Turkmenistanyn" (Independent, Neutral, Turkmenistan State Anthem)
lyrics/music:
collective/Veli MUKHATOV
note:
adopted 1997, lyrics revised 2008; following the death of the President Saparmurat NYYAZOW, the lyrics were altered to eliminate references to the former president
|
|
|
|
|
|
Turkmenistan is largely a desert country with intensive agriculture in irrigated oases and sizeable gas and oil resources. The two largest crops are cotton, most of which is produced for export, and wheat, which is domestically consumed. Although agriculture accounts for roughly 10% of GDP, it continues to employ nearly half of the country's workforce. With an authoritarian ex-Communist regime in power and a tribally based social structure, Turkmenistan has taken a cautious approach to economic reform, hoping to use gas and cotton export revenues to sustain its inefficient economy. Privatization goals remain limited. From 1998-2005, Turkmenistan suffered from the continued lack of adequate export routes for natural gas and from obligations on extensive short-term external debt. At the same time, however, total exports rose by an average of roughly 15% per year from 2003-08, largely because of higher international oil and gas prices. New pipelines to China and Iran, that began operation in early 2010, have given Turkmenistan additional export routes for its gas, although these new routes have not offset the sharp drop in export revenue since early 2009 from decreased gas exports to Russia. Overall prospects in the near future are discouraging because of widespread internal poverty, endemic corruption, a poor educational system, government misuse of oil and gas revenues, and Ashgabat's reluctance to adopt market-oriented reforms. In the past, Turkmenistan's economic statistics were state secrets. The new government has established a State Agency for Statistics, but GDP numbers and other figures are subject to wide margins of error. In particular, the rate of GDP growth is uncertain. Since his election, President BERDIMUHAMEDOW unified the country's dual currency exchange rate, ordered the redenomination of the manat, reduced state subsidies for gasoline, and initiated development of a special tourism zone on the Caspian Sea. Although foreign investment is encouraged, numerous bureaucratic obstacles impede international business activity.
|
|
|
|
|
$36.9 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
$33.79 billion (2009 est.)
$31.85 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$27.96 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
9.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
6.1% (2009 est.)
14.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$7,500 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
$6,900 (2009 est.)
$6,600 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 10.2%
industry:
30%
services:
59.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.3 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 48.2%
industry:
14%
services:
37.8% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
60% (2004 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
30% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.6%
highest 10%:
31.7% (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
40.8 (1998)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
12.4% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $1.97 billion
expenditures:
$1.878 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
10% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$573 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
$469.5 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.053 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
$912.3 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.089 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
$1.811 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
cotton, grain; livestock
|
|
|
|
|
natural gas, oil, petroleum products, textiles, food processing
|
|
|
|
|
7.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
15.5 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
13 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
2.5 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
197,700 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
120,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
38,360 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|
|
600 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
34 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
20 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
14 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
7.504 trillion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
$3.081 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
$1.065 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.672 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
$6.737 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
gas, crude oil, petrochemicals, textiles, cotton fiber
|
|
|
|
|
Ukraine 22.3%, Turkey 10.27%, Hungary 6.75%, UAE 6.25%, Poland 6.16%, Afghanistan 5.79%, Iran 5.17% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.888 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
$4.109 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, chemicals, foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
China 18.03%, Turkey 16.49%, Russia 16.45%, Germany 5.91%, UAE 5.81%, Ukraine 5.67%, US 5.41%, France 4.32% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$10.81 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
$9.551 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
$1.4 billion (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Turkmen manat (TMM) per US dollar -
2.85 (2010)
2.85 (2009)
14,250 (2008)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Turkmenistan |
|
|
478,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: telecommunications network remains underdeveloped and progress toward improvement is slow; strict government control and censorship inhibits liberalization and modernization
domestic:
Turkmentelekom, in cooperation with foreign partners, has installed high speed fiber-optic lines and has upgraded most of the country's telephone exchanges and switching centers with new digital technology; mobile telephone usage is expanding with Russia's Mobile Telesystems (MTS) the primary service provider; combined fixed-line and mobile teledensity is about 40 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 993; linked by fiber-optic cable and microwave radio relay to other CIS republics and to other countries by leased connections to the Moscow international gateway switch; an exchange in Ashgabat switches international traffic through Turkey via Intelsat; satellite earth stations - 1 Orbita and 1 Intelsat (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
broadcast media is government controlled and censored; 4 state-owned TV and 4 state-owned radio networks; satellite dishes and programming provide an alternative to the state-run media; officials sometimes limit access to satellite TV by seizing satellite dishes (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.tm
|
|
|
|
|
794 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
80,400 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Turkmenistan |
|
|
27 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
10
1,524 to 2,437 m:
9
914 to 1,523 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
under 914 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 7,352 km; oil 1,457 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,980 km
country comparison to the world: 55
broad gauge:
2,980 km 1.520-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 58,592 km
country comparison to the world: 75
paved:
47,577 km
unpaved:
11,015 km (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
1,300 km (Amu Darya and Kara Kum canal are important inland waterways) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9
country comparison to the world: 118
by type:
cargo 4, petroleum tanker 4, refrigerated cargo 1
foreign-owned:
1 (Turkey 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Turkmenbasy
|
|
|
|
|
|
Army, Navy, Air and Air Defense Forces (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-30 years of age for compulsory military service; 2-year conscript service obligation (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,380,794
females age 16-49:
1,387,211 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,066,649
females age 16-49:
1,185,538 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 53,829
female:
52,988 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Turkmenistan |
|
|
cotton monoculture in Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan creates water-sharing difficulties for Amu Darya river states; field demarcation of the boundaries with Kazakhstan commenced in 2005, but Caspian seabed delimitation remains stalled with Azerbaijan, Iran, and Kazakhstan due to Turkmenistan's indecision over how to allocate the sea's waters and seabed; bilateral talks continue with Azerbaijan on dividing the seabed and contested oilfields in the middle of the Caspian
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 11,173 (Tajikistan); less than 1,000 (Afghanistan) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
transit country for Afghan narcotics bound for Russian and Western European markets; transit point for heroin precursor chemicals bound for Afghanistan
|
|
|
|
|