|
|
A unified Thai kingdom was established in the mid-14th century. Known as Siam until 1939, Thailand is the only Southeast Asian country never to have been taken over by a European power. A bloodless revolution in 1932 led to a constitutional monarchy. In alliance with Japan during World War II, Thailand became a US treaty ally in 1954 after sending troops to Korea and fighting alongside the US in Vietnam. A military coup in September 2006 ousted then Prime Minister THAKSIN Chinnawat. December 2007 elections saw the pro-THAKSIN People's Power Party (PPP) emerge at the head of a coalition government that took office in February 2008. The anti-THAKSIN People's Alliance for Democracy (PAD, aka yellow-shirts) in May 2008 began street demonstrations against the new government, eventually occupying the prime minister's office in August and Bangkok's two international airports in November. After an early December 2008 court ruling that dissolved the ruling PPP and two other coalition parties for election violations, the Democrat Party formed a new coalition government and ABHISIT Wetchachiwa became prime minister. In October 2008 THAKSIN fled abroad in advance of an abuse of power conviction and has agitated his followers from abroad since then. THAKSIN supporters under the banner of the United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship (UDD, aka red-shirts) rioted in April 2009, shutting down an ASEAN meeting in Pattaya. Following a February 2010 court verdict confiscating half of THAKSIN's frozen assets, the UDD staged large protests between March and May 2010, and occupied several blocks of downtown Bangkok. Clashes between security forces and protesters, elements of which were armed, resulted in at least 92 deaths and an estimated $1.5 billion in arson-related property losses. These protests exposed major cleavages in the Thai body politic that continue to hamper the current government. The ABHISIT administration has announced a plan for a general election some time in 2011 ahead of its full term by the year-end. Since January 2004, thousands have been killed as separatists in Thailand's southern ethnic Malay-Muslim provinces increased the violence associated with their cause.
|
|
|
|
|
|
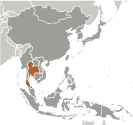
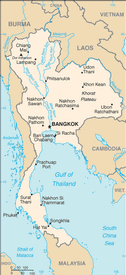
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, southeast of Burma
|
|
|
|
|
15 00 N, 100 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 513,120 sq km
country comparison to the world: 50
land:
510,890 sq km
water:
2,230 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than twice the size of Wyoming
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,863 km
border countries:
Burma 1,800 km, Cambodia 803 km, Laos 1,754 km, Malaysia 506 km
|
|
|
|
|
3,219 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; rainy, warm, cloudy southwest monsoon (mid-May to September); dry, cool northeast monsoon (November to mid-March); southern isthmus always hot and humid
|
|
|
|
|
central plain; Khorat Plateau in the east; mountains elsewhere
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
highest point:
Doi Inthanon 2,576 m
|
|
|
|
|
tin, rubber, natural gas, tungsten, tantalum, timber, lead, fish, gypsum, lignite, fluorite, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 27.54%
permanent crops:
6.93%
other:
65.53% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
64,150 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
409.9 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 82.75 cu km/yr (2%/2%/95%)
per capita:
1,288 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
land subsidence in Bangkok area resulting from the depletion of the water table; droughts
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution from vehicle emissions; water pollution from organic and factory wastes; deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by illegal hunting
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|
|
controls only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore
|
|
|
|
|
|
66,720,153 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 19.9% (male 6,779,723/female 6,466,625)
15-64 years:
70.9% (male 23,410,091/female 23,913,499)
65 years and over:
9.2% (male 2,778,012/female 3,372,203) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 34.2 years
male:
33.3 years
female:
35.2 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.566% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
12.95 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
7.29 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 34% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.8% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
BANGKOK (capital) 6.902 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.054 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.82 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16.39 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 108
male:
17.38 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
15.35 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 73.6 years
country comparison to the world: 113
male:
71.24 years
female:
76.08 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.66 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
530,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
28,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
animal contact disease:
rabies
water contact disease:
leptospirosis
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 99% of population
rural: 98% of population
total: 98% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1% of population
rural: 2% of population
total: 2% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 95% of population
rural: 96% of population
total: 96% of population
unimproved:
urban: 5% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 4% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Thai (singular and plural)
adjective:
Thai
|
|
|
|
|
Thai 75%, Chinese 14%, other 11%
|
|
|
|
|
Buddhist 94.6%, Muslim 4.6%, Christian 0.7%, other 0.1% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Thai, English (secondary language of the elite), ethnic and regional dialects
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
92.6%
male:
94.9%
female:
90.5% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
13 years (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
4.1% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Thailand
conventional short form:
Thailand
local long form:
Ratcha Anachak Thai
local short form:
Prathet Thai
former:
Siam
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Bangkok
geographic coordinates:
13 45 N, 100 31 E
time difference:
UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
76 provinces (changwat, singular and plural); Amnat Charoen, Ang Thong, Buriram, Chachoengsao, Chai Nat, Chaiyaphum, Chanthaburi, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Chon Buri, Chumphon, Kalasin, Kamphaeng Phet, Kanchanaburi, Khon Kaen, Krabi, Krung Thep Mahanakhon (Bangkok), Lampang, Lamphun, Loei, Lop Buri, Mae Hong Son, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Nayok, Nakhon Pathom, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nakhon Sawan, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Nan, Narathiwat, Nong Bua Lamphu, Nong Khai, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Pattani, Phangnga, Phatthalung, Phayao, Phetchabun, Phetchaburi, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Phrae, Phuket, Prachin Buri, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ranong, Ratchaburi, Rayong, Roi Et, Sa Kaeo, Sakon Nakhon, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram, Sara Buri, Satun, Sing Buri, Sisaket, Songkhla, Sukhothai, Suphan Buri, Surat Thani, Surin, Tak, Trang, Trat, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani, Uthai Thani, Uttaradit, Yala, Yasothon
|
|
|
|
|
1238 (traditional founding date; never colonized)
|
|
|
|
|
Birthday of King PHUMIPHON (BHUMIBOL), 5 December (1927)
|
|
|
|
|
24 August 2007
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system with common law influences
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: King PHUMIPHON Adunyadet, also spelled BHUMIBOL Adulyadej (since 9 June 1946)
head of government:
Prime Minister ABHISIT Wechachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva (since 17 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SANAN Kachornprasat, also spelled SANAN Kachornparsart (since 7 February 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SUTHEP Thueaksuban, also spelled SUTHEP Thaugsuban (since 22 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister TRAIRONG Suwannakhiri (since 18 January 2010)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
note:
there is also a Privy Council advising the king
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; according to 2007 constitution, the prime minister elected from among members of House of Representatives; following national elections for House of Representatives, the leader of the party positioned to organize a majority coalition usually becomes prime minister by appointment by the king; the prime minister limited to two four-year terms
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral National Assembly or Rathasapha consisted of the Senate or Wuthisapha (150 seats; 76 members elected by popular vote representing 76 provinces, 74 appointed by judges and independent government bodies; members serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Sapha Phuthaen Ratsadon (480 seats; 400 members elected from 157 multi-seat constituencies and 80 elected on proportional party-list basis of 10 per eight zones or groupings of provinces; members serve four-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held on 2 March 2008 (next to be held in March 2014); House of Representatives - last election held on 23 December 2007 (next to be held on 3 July 2011)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PPP 233, DP 164, TNP 34, Motherland 24, Middle Way 11, Unity 9, Royalist People's 5; following the PPP's dissolution in December 2008, most of the party's seats were assumed by its successor, the Phuea Thai Party
note:
74 senators were appointed on 19 February 2008 by a seven-member committee headed by the chief of the Constitutional Court; 76 senators were elected on 2 March 2008; elections to the Senate are non-partisan; registered political party members are disqualified from being senators
|
|
|
|
|
Constitutional Court, Supreme Court of Justice, and Supreme Administrative Court; all judges are appointed by the king; the king's appointments to the Constitutional Courtare made upon the advice of the Senate; the nine Constitutional Court judges are drawn from the Supreme Court of Justice and Supreme Administrative Court as well as from among substantive experts in law and social sciences outside the judiciary
|
|
|
|
|
Chat Thai Phattana Party or CP (Thai Nation Development Party) [CHUMPON Silpa-archa]; Democrat Party or DP (Prachathipat Party) [ABHISIT Wetchachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva]; Motherland Party (Phuea Phaendin Party) [CHANCHAI Chairungrueng]; Phuea Thai Party (For Thais Party) or PTP [YONGYUTH Wichaidit]; Phumjai (Bhumjai) Thai Party or PJT (Thai Pride) [CHAWARAT Chanvirakun]; Royalist People's Party (Pracharaj) [SANOH Thienthong]; Ruam Jai Thai Party (Thai Unity Party) [WANNARAT Channukun]
|
|
|
|
|
People's Alliance for Democracy or PAD; United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship or UDD
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, BIS, CICA, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE (partner), PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Kittiphong Na RANONG
chancery:
1024 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Suite 401, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 944-3600
FAX:
[1] (202) 944-3611
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Kristie A. KENNEY
embassy:
120-122 Wireless Road, Bangkok 10330
mailing address:
APO AP 96546
telephone:
[66] (2) 205-4000
FAX:
[66] (2) 254-2990, 205-4131
consulate(s) general:
Chiang Mai
|
|
|
|
|
five horizontal bands of red (top), white, blue (double width), white, and red; the red color symbolizes the nation and the blood of life; white represents religion and the purity of Buddhism; blue stands for the monarchy
note:
similar to the flag of Costa Rica but with the blue and red colors reversed
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Phleng Chat Thai" (National Anthem of Thailand)
lyrics/music:
LUANG Saranuprapan/PHRA Jenduriyang
note:
music adopted 1932, lyrics adopted 1939; by law, people are required to stand for the national anthem at 0800 and 1800 every day; the anthem is played in schools, offices, theaters, and on television and radio during this time; "Phleng Sansasoen Phra Barami" (A Salute to the Monarch) serves as the royal anthem and is played in the presence of the royal family and during certain state ceremonies
|
|
|
|
|
|
With a well-developed infrastructure, a free-enterprise economy, generally pro-investment policies, and strong export industries, Thailand enjoyed solid growth from 2000 to 2007 - averaging more than 4% per year - as it recovered from the Asian financial crisis of 1997-98. Thai exports - mostly machinery and electronic components, agricultural commodities, and jewelry - continue to drive the economy, accounting for more than half of GDP. The global financial crisis of 2008-09 severely cut Thailand's exports, with most sectors experiencing double-digit drops. In 2009, the economy contracted 2.2%. In 2010, Thailand's economy expanded 7.6%, its fastest pace since 1995, as exports rebounded from their depressed 2009 level. Antigovernment protests during March-May and the country's polarized political situation had - at most - a temporary impact on business and consumer confidence. Although tourism was hit hard during the protests, its quick recovery helped boost consumer confidence to new highs. Moreover, business and investor sentiment remained buoyant as Thailand's stock market grew almost 5% during the three-month period. The economy probably will continue to experience high grow well into 2011.
|
|
|
|
|
$586.9 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$544.4 billion (2009 est.)
$557.4 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$318.9 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
-2.3% (2009 est.)
2.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8,700 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
$8,200 (2009 est.)
$8,400 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 10.4%
industry:
45.6%
services:
44% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
38.7 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 42.4%
industry:
19.7%
services:
37.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
1.5% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
9.6% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.6%
highest 10%:
33.7% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
43 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 47
42 (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
24.9% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $56.33 billion
expenditures:
$56.87 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
42.3% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
44.9% of GDP (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
3.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
-0.9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.75% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 131
1.25% (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
6.1% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 134
5.96% (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$38 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
$34.26 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$354.5 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$309.7 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$336 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$292.4 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$138.2 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 39
$102.6 billion (31 December 2008)
$196 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, cassava (tapioca), rubber, corn, sugarcane, coconuts, soybeans
|
|
|
|
|
tourism, textiles and garments, agricultural processing, beverages, tobacco, cement, light manufacturing such as jewelry and electric appliances, computers and parts, integrated circuits, furniture, plastics, automobiles and automotive parts; world's second-largest tungsten producer and third-largest tin producer
|
|
|
|
|
14.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
148.2 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
134.4 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
846 million kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.313 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
380,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
356,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
269,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
1.695 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
430 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
28.76 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
37.31 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
8.55 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
342 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
$12.29 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$21.86 billion (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$191.3 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$151.9 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
textiles and footwear, fishery products, rice, rubber, jewelry, automobiles, computers and electrical appliances
|
|
|
|
|
US 10.9%, China 10.6%, Japan 10.3%, Hong Kong 6.2%, Australia 5.6%, Malaysia 5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$156.9 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$118 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
capital goods, intermediate goods and raw materials, consumer goods, fuels
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 18.7%, China 12.7%, Malaysia 6.4%, US 6.3%, UAE 5%, Singapore 4.3%, South Korea 4.1% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$176.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
$138.4 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$82.5 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
$70.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$117.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
$109.6 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$20.3 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
$18.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
baht per US dollar -
31.663 (2010)
34.286 (2009)
33.37 (2008)
34.52 (2007)
37.882 (2006)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Thailand |
|
|
7.024 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
83.057 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: high quality system, especially in urban areas like Bangkok
domestic:
fixed line system provided by both a government owned and commercial provider; wireless service expanding rapidly
international:
country code - 66; connected to major submarine cable systems providing links throughout Asia, Australia, Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean, 1 Pacific Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
6 terrestrial TV stations in Bangkok broadcast nationally via relay stations - 2 of the networks are owned by the military, the other 4 are government-owned or controlled, leased to private enterprise, and are all required to broadcast government-produced news programs twice a day; multi-channel satellite and cable TV subscription services are available; radio frequencies have been allotted for more than 500 government and commercial radio stations; many small community radio stations operate with low-power transmitters (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.th
|
|
|
|
|
1.335 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
17.483 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Thailand |
|
|
105 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
total: 64
over 3,047 m:
8
2,438 to 3,047 m:
11
1,524 to 2,437 m:
24
914 to 1,523 m:
15
under 914 m:
6 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
13
under 914 m:
27 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 1,889 km; liquid petroleum gas 85 km; refined products 1,099 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,071 km
country comparison to the world: 42
standard gauge:
29 km 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge:
4,042 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 180,053 km (includes 450 km of expressways) (2006)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 km (3,701 km navigable by boats with drafts up to 0.9 m) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
total: 382
country comparison to the world: 27
by type:
bulk carrier 30, cargo 116, chemical tanker 23, container 19, liquefied gas 36, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 10, petroleum tanker 120, refrigerated cargo 27
foreign-owned:
15 (China 1, Hong Kong 1, Japan 2, Malaysia 3, Singapore 1, Taiwan 1, UK 6)
registered in other countries:
41 (Bahamas 4, Panama 6, Singapore 30, Tuvalu 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Bangkok, Laem Chabang, Map Ta Phut, Prachuap Port, Si Racha
|
|
|
|
|
|
Royal Thai Army (Kongthap Bok Thai, RTA), Royal Thai Navy (Kongthap Ruea Thai, RTN, includes Royal Thai Marine Corps), Royal Thai Air Force (Kongthap Agard Thai, RTAF) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
21 years of age for compulsory military service; 18 years of age for voluntary military service; males register at 18 years of age; 2-year conscript service obligation (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 17,689,921
females age 16-49:
17,754,795 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 13,308,372
females age 16-49:
14,182,567 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 533,424
female:
509,780 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.8% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Thailand |
|
|
separatist violence in Thailand's predominantly Muslim southern provinces prompt border closures and controls with Malaysia to stem terrorist activities; Southeast Asian states have enhanced border surveillance to check the spread of avian flu; talks continue on completion of demarcation with Laos but disputes remain over several islands in the Mekong River; despite continuing border committee talks, Thailand must deal with Karen and other ethnic rebels, refugees, and illegal cross-border activities, and as of 2006, over 116,000 Karen, Hmong, and other refugees and asylum seekers from Burma; Cambodia and Thailand dispute sections of boundary; in 2011 Thailand and Cambodia resorted to arms in the dispute over the location of the boundary on the precipice surmounted by Preah Vihear temple ruins, awarded to Cambodia by ICJ decision in 1962 and part of a planned UN World Heritage site; Thailand is studying the feasibility of jointly constructing the Hatgyi Dam on the Salween river near the border with Burma; in 2004, international environmentalist pressure prompted China to halt construction of 13 dams on the Salween River that flows through China, Burma, and Thailand; 140,000 mostly Karen refugees fleeing civil strife, political upheaval and economic stagnation in Burma live in remote camps in Thailand near the border
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 132,241 (Burma) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
a minor producer of opium, heroin, and marijuana; transit point for illicit heroin en route to the international drug market from Burma and Laos; eradication efforts have reduced the area of cannabis cultivation and shifted some production to neighboring countries; opium poppy cultivation has been reduced by eradication efforts; also a drug money-laundering center; minor role in methamphetamine production for regional consumption; major consumer of methamphetamine since the 1990s despite a series of government crackdowns
|
|
|
|
|