|
|
Poland is an ancient nation that was conceived near the middle of the 10th century. Its golden age occurred in the 16th century. During the following century, the strengthening of the gentry and internal disorders weakened the nation. In a series of agreements between 1772 and 1795, Russia, Prussia, and Austria partitioned Poland among themselves. Poland regained its independence in 1918 only to be overrun by Germany and the Soviet Union in World War II. It became a Soviet satellite state following the war, but its government was comparatively tolerant and progressive. Labor turmoil in 1980 led to the formation of the independent trade union "Solidarity" that over time became a political force and by 1990 had swept parliamentary elections and the presidency. A "shock therapy" program during the early 1990s enabled the country to transform its economy into one of the most robust in Central Europe, but Poland still faces the lingering challenges of high unemployment, underdeveloped and dilapidated infrastructure, and a poor rural underclass. Poland joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004. With its transformation to a democratic, market-oriented country largely completed, Poland is an increasingly active member of Euro-Atlantic organizations.
|
|
|
|
|
|
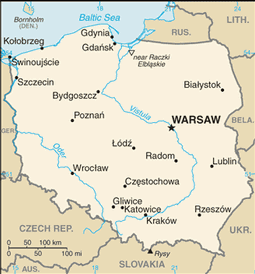
Central Europe, east of Germany
|
|
|
|
|
52 00 N, 20 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 312,685 sq km
country comparison to the world: 69
land:
304,255 sq km
water:
8,430 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,047 km
border countries:
Belarus 605 km, Czech Republic 615 km, Germany 456 km, Lithuania 91 km, Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast) 432 km, Slovakia 420 km, Ukraine 428 km
|
|
|
|
|
440 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
defined by international treaties
|
|
|
|
|
temperate with cold, cloudy, moderately severe winters with frequent precipitation; mild summers with frequent showers and thundershowers
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat plain; mountains along southern border
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: near Raczki Elblaskie -2 m
highest point:
Rysy 2,499 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal, sulfur, copper, natural gas, silver, lead, salt, amber, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 40.25%
permanent crops:
1%
other:
58.75% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1,160 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
63.1 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11.73 cu km/yr (13%/79%/8%)
per capita:
304 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding
|
|
|
|
|
situation has improved since 1989 due to decline in heavy industry and increased environmental concern by post-Communist governments; air pollution nonetheless remains serious because of sulfur dioxide emissions from coal-fired power plants, and the resulting acid rain has caused forest damage; water pollution from industrial and municipal sources is also a problem, as is disposal of hazardous wastes; pollution levels should continue to decrease as industrial establishments bring their facilities up to EU code, but at substantial cost to business and the government
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Kyoto Protocol, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94
|
|
|
|
|
historically, an area of conflict because of flat terrain and the lack of natural barriers on the North European Plain
|
|
|
|
|
|
38,441,588 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 14.7% (male 2,910,324/female 2,748,546)
15-64 years:
71.6% (male 13,698,363/female 13,834,779)
65 years and over:
13.7% (male 2,004,550/female 3,245,026) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 38.5 years
male:
36.8 years
female:
40.3 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.062% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
|
|
|
|
|
10.01 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
10.17 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
-0.47 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 61% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
-0.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
WARSAW (capital) 1.71 million; Krakow 756,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.061 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.62 male(s)/female
total population:
0.94 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6.54 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 170
male:
7.25 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
5.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 76.05 years
country comparison to the world: 76
male:
72.1 years
female:
80.25 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
|
|
|
|
|
0.1%; 0.1% note - no country specific models provided (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
27,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne disease:
tickborne encephalitis
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 96% of population
rural: 80% of population
total: 90% of population
unimproved:
urban: 4% of population
rural: 20% of population
total: 10% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Pole(s)
adjective:
Polish
|
|
|
|
|
Polish 96.7%, German 0.4%, Belarusian 0.1%, Ukrainian 0.1%, other and unspecified 2.7% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 89.8% (about 75% practicing), Eastern Orthodox 1.3%, Protestant 0.3%, other 0.3%, unspecified 8.3% (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
Polish (official) 97.8%, other and unspecified 2.2% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.8%
male:
99.8%
female:
99.7% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
15 years
female:
16 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
4.9% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Poland
conventional short form:
Poland
local long form:
Rzeczpospolita Polska
local short form:
Polska
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Warsaw
geographic coordinates:
52 15 N, 21 00 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
16 provinces (wojewodztwa, singular - wojewodztwo); Dolnoslaskie (Lower Silesia), Kujawsko-Pomorskie (Kuyavia-Pomerania), Lodzkie, Lubelskie (Lublin), Lubuskie (Lubusz), Malopolskie (Lesser Poland), Mazowieckie (Masovia), Opolskie, Podkarpackie (Subcarpathia), Podlaskie, Pomorskie (Pomerania), Slaskie (Silesia), Swietokrzyskie, Warminsko-Mazurskie (Warmia-Masuria), Wielkopolskie (Greater Poland), Zachodniopomorskie (West Pomerania)
|
|
|
|
|
11 November 1918 (republic proclaimed); notable earlier dates: A.D. 966 (adoption of Christianity, traditional founding date), 1 July 1569 (Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth created)
|
|
|
|
|
Constitution Day, 3 May (1791)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted by the National Assembly 2 April 1997; passed by national referendum 25 May 1997; effective 17 October 1997
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; changes gradually being introduced as part of broader democratization process; limited judicial review of legislative acts, but rulings of the Constitutional Tribunal are final
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Bronislaw KOMOROWSKI (since 6 August 2010)
head of government:
Prime Minister Donald TUSK (since 16 November 2007); Deputy Prime Minister Waldemar PAWLAK (since 16 November 2007)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers responsible to the prime minister and the Sejm; the prime minister proposes, the president appoints, and the Sejm approves the Council of Ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 20 June and 4 July 2010 (next to be held in 2015); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president and confirmed by the Sejm
election results:
Bronislaw KOMOROWSKI elected president; percent of popular vote - Bronislaw KOMOROWSKI 53%, Jaroslaw KACZYNSKI 47%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral legislature consists of an upper house, the Senate or Senat (100 seats; members elected by a majority vote on a provincial basis to serve four-year terms), and a lower house, the Sejm (460 seats; members elected under a complex system of proportional representation to serve four-year terms); the designation of National Assembly or Zgromadzenie Narodowe is only used on those rare occasions when the two houses meet jointly
elections:
Senate - last held on 21 October 2007 (next to be held by October 2011); Sejm - last held on 21 October 2007 (next to be held by October 2011)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PO 60, PiS 39, independents 1; Sejm - percent of vote by party - PO 41.5%, PiS 32.1%, LiD 13.2%, PSL 8.9%, other 4.3%; seats by party - PO 209, PiS 166, LiD 53, PSL 31, German minorities 1; note - seats by party as of December 2010 - PO 203, PiS 147, SLD 44, PSL 31, PJN 17, SDPL 4, DKP-SD 3, German minorities 1, independents 9, vacant 1
note:
one seat is assigned to ethnic minority parties in the Sejm only
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the National Council of the Judiciary for an indefinite period); Constitutional Tribunal (judges are chosen by the Sejm for nine-year terms)
|
|
|
|
|
Civic Platform or PO [Donald TUSK, chairman; Tomasz TOMCZYKIEWICZ, parliamentary caucus leader]; Democratic Caucus of the Democratic Party (SD) or DKP SD [Bogdan LIS, parliamentary caucus leader]; Democratic Left Alliance or SLD [Grzegorz NAPIERALSKI, chairman, parliamentary caucus leader]; Democratic Party or PD [Brygida KUZNIAK, chairwoman]; Democratic Party or SD [Pawel PISKORSKI, chairman]; German Minority of Lower Silesia or MNSO [Ryszard GALLA, representative]; Law and Justice or PiS [Jaroslaw KACZYNSKI, chairman; Mariusz BLASZCZAK, parliamentary caucus leader]; League of Polish Families or LPR [Witold BALAZAK, chairman]; Poland Comes First or PJN [Joanna KLUZIK-ROSTKOWSKA, chairwoman, parliamentary caucus leader]; Polish People's Party or PSL [Waldemar PAWLAK, chairman; Stanislaw ZELICHOWSKI, parliamentary caucus leader]; Samoobrona or SO [Andrzej LEPPER, chairman]; Social Democratic Party of Poland or SDPL [Wojciech FILEMONOWICZ, chairman; Marek BOROWSKI, parliamentary caucus leader]; Union of Labor or UP [Waldemar WITKOWSKI, chairman]
|
|
|
|
|
All Poland Trade Union Alliance or OPZZ (trade union) [Jan GUZ]; Roman Catholic Church [Cardinal Stanislaw DZIWISZ, Archbishop Jozef MICHALIK]; Solidarity Trade Union [Piotr DUDA]
|
|
|
|
|
Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Robert KUPIECKI
chancery:
2640 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-3800 through 3802
FAX:
[1] (202) 328-6271
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Lee FEINSTEIN
embassy:
Aleje Ujazdowskie 29/31 00-540 Warsaw
mailing address:
American Embassy Warsaw, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-5010 (pouch)
telephone:
[48] (22) 504-2000
FAX:
[48] (22) 504-2688
consulate(s) general:
Krakow
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red; colors derive from the Polish emblem - a white eagle on a red field
note:
similar to the flags of Indonesia and Monaco which are red (top) and white
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Mazurek Dabrowskiego" (Dabrowski's Mazurka)
lyrics/music:
Jozef WYBICKI/traditional
note:
adopted 1927; the anthem, commonly known as "Jeszcze Polska nie zginela" (Poland Has Not Yet Perished), was written in 1797; the lyrics resonate strongly with Poles because they reflect the numerous occasions in which the nation's lands have been occupied
|
|
|
|
|
|
Poland has pursued a policy of economic liberalization since 1990 and today stands out as a success story among transition economies. It is the only country in the European Union to maintain positive GDP growth through the 2008-2009 economic downturn. GDP per capita is still much below the EU average, but is similar to that of the three Baltic states. Since 2004, EU membership and access to EU structural funds have provided a major boost to the economy. Unemployment fell rapidly to 6.4% in October 2008, but climbed back to 11.8% for the year 2010, exceeding the EU average by more than 2%. Inflation reached a low of about 2.6% in 2010 due to the global economic slowdown but has since climbed and is expected to remain around 3%, and close to the upper limit of the National Bank of Poland's target rate. Poland's economic performance could improve over the longer term if the country addresses some of the remaining deficiencies in its road and rail infrastructure and its business environment. An inefficient commercial court system, a rigid labor code, bureaucratic red tape, burdensome tax system, and persistent low-level corruption keep the private sector from performing up to its full potential. Rising demands to fund health care, education, and the state pension system caused the public sector budget deficit to rise to 7.9% of GDP in 2010. The PO/PSL coalition government, which came to power in November 2007, has planned to reduce the budget deficit in 2011 and has also announced its intention to enact business-friendly reforms, increase workforce participation, reduce public sector spending growth, lower taxes, and accelerate privatization. The government has moved slowly on most major reforms, but has sped up privatization.
|
|
|
|
|
$721.3 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$694.8 billion (2009 est.)
$683.5 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$468.5 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
1.7% (2009 est.)
5.1% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$18,800 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
$18,100 (2009 est.)
$17,800 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 4%
industry:
32%
services:
64% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
17 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17.4%
industry:
29.2%
services:
53.4% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
11.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
11% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
17% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3%
highest 10%:
27.2% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
34.9 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 87
31.6 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
19.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $91.23 billion
expenditures:
$128.4 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
53.6% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
49.8% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
3.5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 114
1.75% (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
5.99% (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
5.72% (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$138.7 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$124.6 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$251.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$229.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$288.7 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
$264.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$135.3 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 42
$90.23 billion (31 December 2008)
$207.3 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
potatoes, fruits, vegetables, wheat; poultry, eggs, pork, dairy
|
|
|
|
|
machine building, iron and steel, coal mining, chemicals, shipbuilding, food processing, glass, beverages, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
6.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
149.1 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
129.3 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
9.703 billion kWh (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
8.48 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
34,140 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
|
|
|
|
|
545,400 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
65,280 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
553,900 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
96.38 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
5.842 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
16.33 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
40 million cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
9.954 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
164.8 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
$-12.33 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
$-9.598 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$160.8 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$142.1 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment 37.8%, intermediate manufactured goods 23.7%, miscellaneous manufactured goods 17.1%, food and live animals 7.6%
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 26.06%, Italy 6.84%, France 6.78%, UK 6.38%, Czech Republic 5.85%, Netherlands 4.14% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$167.4 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
$146.4 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment 38%, intermediate manufactured goods 21%, chemicals 15%, minerals, fuels, lubricants, and related materials 9%
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 28.08%, Russia 8.65%, Italy 6.5%, Netherlands 5.59%, China 5.27%, France 4.6%, Czech Republic 4.05% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$99.76 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$79.58 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$252.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$239.6 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$198.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$182.8 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$30.71 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
$26.21 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
zlotych (PLN) per US dollar -
3.0718 (2010)
3.1214 (2009)
2.3 (2008)
2.81 (2007)
3.1032 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.556 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
44.553 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modernization of the telecommunications network has accelerated with market-based competition; fixed-line service, dominated by the former state-owned company, is dwarfed by the growth in mobile-cellular services
domestic:
mobile-cellular service available since 1993 and provided by three nation-wide networks with a fourth provider beginning operations in late 2006; coverage is generally good with some gaps in the east; fixed-line service lags in rural areas
international:
country code - 48; international direct dialing with automated exchanges; satellite earth station - 1 with access to Intelsat, Eutelsat, Inmarsat, and Intersputnik (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
state-run public television operates 2 national channels supplemented by 16 regional channels and several niche channels; privately-owned entities operate several national TV broadcast networks and a number of special interest channels; large number of privately-owned channels broadcasting locally; roughly half of all households are linked to either satellite or cable TV systems providing access to foreign television networks; state-run public radio operates 5 national networks and 17 regional radio stations; 2 privately-owned national radio networks, several commercial stations broadcasting to multiple cities, and a large number of privately-owned local radio stations (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.pl
|
|
|
|
|
10.51 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
22.452 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
|
129 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
total: 86
over 3,047 m:
4
2,438 to 3,047 m:
30
1,524 to 2,437 m:
39
914 to 1,523 m:
7
under 914 m:
6 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 43
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
16
under 914 m:
21 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
7 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 13,860 km; oil 1,384 km; refined products 777 km; unknown 35 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22,314 km
country comparison to the world: 12
broad gauge:
633 km 1.524-m gauge
standard gauge:
21,681 km 1.435-m gauge (11,769 km electrified) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 423,997 km
country comparison to the world: 15
paved:
295,356 km (includes 765 km of expressways)
unpaved:
128,641 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
3,997 km (navigable rivers and canals) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
country comparison to the world: 115
by type:
cargo 6, chemical tanker 3, passenger/cargo 1
registered in other countries:
104 (Antigua and Barbuda 2, Bahamas 32, Cyprus 20, Liberia 13, Malta 22, Norway 2, Panama 3, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1, Slovakia 2, Vanuatu 7) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Gdansk, Gdynia, Swinoujscie, Szczecin
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polish Armed Forces: Land Forces, Navy, Air and Air Defense Aviation Forces, Special Forces (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-28 years of age for male voluntary or compulsory military service; service obligation shortened from 12 to 9 months in 2005; conscription is to end in 2012; only soldiers who have completed their conscript service are allowed to volunteer for professional service; as of April 2004, women are only allowed to serve as officers and noncommissioned officers; reserve obligation to age 50 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 9,531,855
females age 16-49:
9,298,593 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 7,817,556
females age 16-49:
7,766,361 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 221,889
female:
211,172 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.71% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Poland |
|
|
as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Poland has implemented the strict Schengen border rules to restrict illegal immigration and trade along its eastern borders with Belarus and Ukraine
|
|
|
|
|
despite diligent counternarcotics measures and international information sharing on cross-border crimes, a major illicit producer of synthetic drugs for the international market; minor transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and Latin American cocaine to Western Europe
|
|
|
|
|