| Introduction ::Mauritania |
|
|
Independent from France in 1960, Mauritania annexed the southern third of the former Spanish Sahara (now Western Sahara) in 1976 but relinquished it after three years of raids by the Polisario guerrilla front seeking independence for the territory. Maaouya Ould Sid Ahmed TAYA seized power in a coup in 1984 and ruled Mauritania with a heavy hand for more than two decades. A series of presidential elections that he held were widely seen as flawed. A bloodless coup in August 2005 deposed President TAYA and ushered in a military council that oversaw a transition to democratic rule. Independent candidate Sidi Ould Cheikh ABDALLAHI was inaugurated in April 2007 as Mauritania's first freely and fairly elected president. His term ended prematurely in August 2008 when a military junta led by General Mohamed Ould Abdel AZIZ deposed him and ushered in a military council government. AZIZ was subsequently elected president in July 2009 and sworn in the following month. The country continues to experience ethnic tensions among its black population (Afro-Mauritanians) and white and black Moor (Arab-Berber) communities, and is having to confront a growing terrorism threat by al-Qa'ida in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM).
|
|
|
|
|
|
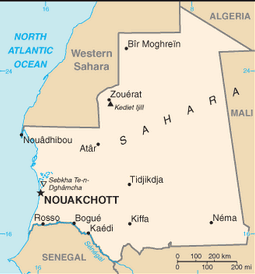
Northern Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara
|
|
|
|
|
20 00 N, 12 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,030,700 sq km
country comparison to the world: 29
land:
1,030,700 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than three times the size of New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,074 km
border countries:
Algeria 463 km, Mali 2,237 km, Senegal 813 km, Western Sahara 1,561 km
|
|
|
|
|
754 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
desert; constantly hot, dry, dusty
|
|
|
|
|
mostly barren, flat plains of the Sahara; some central hills
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Sebkhet Te-n-Dghamcha -5 m
highest point:
Kediet Ijill 915 m
|
|
|
|
|
iron ore, gypsum, copper, phosphate, diamonds, gold, oil, fish
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0.2%
permanent crops:
0.01%
other:
99.79% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
450 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
11.4 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.7 cu km/yr (9%/3%/88%)
per capita:
554 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dry, dust/sand-laden sirocco wind blows primarily in March and April; periodic droughts
|
|
|
|
|
overgrazing, deforestation, and soil erosion aggravated by drought are contributing to desertification; limited natural freshwater resources away from the Senegal, which is the only perennial river; locust infestation
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
most of the population is concentrated in the cities of Nouakchott and Nouadhibou and along the Senegal River in the southern part of the country
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,281,634 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 40.4% (male 665,314/female 660,352)
15-64 years:
56.2% (male 866,859/female 975,821)
65 years and over:
3.5% (male 48,075/female 65,213) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 19.5 years
male:
18.6 years
female:
20.4 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.349% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
33.23 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
8.83 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
-0.91 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 41% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.9% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NOUAKCHOTT (capital) 709,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.89 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.74 male(s)/female
total population:
0.93 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 60.42 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 34
male:
65.55 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
55.13 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 61.14 years
country comparison to the world: 184
male:
58.94 years
female:
63.41 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
0.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
14,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria and Rift Valley fever
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 52% of population
rural: 47% of population
total: 49% of population
unimproved:
urban: 48% of population
rural: 53% of population
total: 51% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 50% of population
rural: 9% of population
total: 26% of population
unimproved:
urban: 50% of population
rural: 91% of population
total: 74% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Mauritanian(s)
adjective:
Mauritanian
|
|
|
|
|
mixed Moor/black 40%, Moor 30%, black 30%
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 100%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic (official and national), Pulaar, Soninke, Wolof (all national languages), French, Hassaniya
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
51.2%
male:
59.5%
female:
43.4% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8 years
male:
8 years
female:
8 years (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Mauritania
conventional short form:
Mauritania
local long form:
Al Jumhuriyah al Islamiyah al Muritaniyah
local short form:
Muritaniyah
|
|
|
|
|
military junta
|
|
|
|
|
name: Nouakchott
geographic coordinates:
18 07 N, 16 02 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
13 regions (wilayas, singular - wilaya); Adrar, Assaba, Brakna, Dakhlet Nouadhibou, Gorgol, Guidimaka, Hodh ech Chargui, Hodh El Gharbi, Inchiri, Nouakchott, Tagant, Tiris Zemmour, Trarza
|
|
|
|
|
28 November 1960 (from France)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 28 November (1960)
|
|
|
|
|
12 July 1991
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of Islamic and French civil law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Mohamed Ould Abdel AZIZ (since 5 August 2009); note - AZIZ, who deposed democratically elected President Sidi Ould Cheikh ABDELLAHI in a coup and installed himself as President of the High State Council on 6 August 2008, retired from the military and stepped down from the Presidency in April 2009 to run for president; he was elected president in an election held on 18 July 2009
head of government:
Prime Minister Moulaye Ould Mohamed LAGHDAF (since 14 August 2008)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
following the August 2008 coup, the High State Council planned to hold a new presidential election in June 2009; the election was subsequently rescheduled to 18 July 2009 following the Dakar Accords, which brought Mauritania back to constitutional rule; under Mauritania's constitution, the president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held on 18 July 2009 (next to be held by 2014)
election results:
percent of vote - Mohamed Ould Abdel AZIZ 52.6%, Messaoud Ould BOULKHEIR 16.3%, Ahmed Ould DADDAH 13.7%, other 17.4%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral legislature consists of the Senate or Majlis al-Shuyukh (56 seats; 53 members elected by municipal leaders and 3 members elected for Mauritanians abroad to serve six-year terms; a portion of seats up for election every two years) and the National Assembly or Al Jamiya Al Wataniya (95 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held in November 2009; National Assembly - last held on 19 November and 3 December 2006 (next to be held in 2011)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CPM (Coalition of Majority Parties) 45, COD 7, RNRD-TAWASSOUL 4; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CPM 63 (UPR 50, PRDR 7, UDP 3, HATEM-PMUC 2, RD 1), COD 27 (RFD 9, UFP 6, APP 6, PNDD-ADIL 6), RNRD-TAWASSOUL 4, FP 1
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme; Court of Appeals; lower courts
|
|
|
|
|
Alternative or El-Badil [Mohamed Yahdhi Ould MOCTAR HACEN]; Coalition of Majority Parties or CPM (parties supporting the regime including PRDR, UPR, RD, HATEM-PMUC, UCD); Coordination of Democratic Opposition or COD (coalition of opposition political parties opposed to the government including APP, RFD, UFP, PNDD-ADIL, Alternative or El-Badil); Democratic Renewal or RD [Moustapha Ould ABDEIDARRAHMANE]; Mauritanian Party for Unity and Change or HATEM-PMUC [Saleh Ould HANENA]; National Pact for Democracy and Development or PNDD-ADIL [Yahya Ould Ahmed Ould WAGHEF] (independents formerly supporting President Abdellahi); National Rally for Freedom, Democracy and Equality or RNDLE; National Rally for Reform and Development or RNRD-TAWASSOUL [Mohamed Jamil MANSOUR] (moderate Islamists); Popular Front or FP [Ch'bih Ould CHEIKH MALAININE]; Popular Progressive Alliance or APP [Messoud Ould BOULKHEIR]; Rally of Democratic Forces or RFD [Ahmed Ould DADDAH]; Republican Party for Democracy and Renewal or PRDR [Mintata Mint HDEID]; Socialist and Democratic Unity Party or PUDS; Union for Democracy and Progress or UDP [Naha Mint MOUKNASS]; Union for the Republic or UPR; Union of Democratic Center or UCD [Cheikh Sid'Ahmed Ould BABA]; Union of the Forces for Progress or UFP [Mohamed Ould MAOULOUD];
|
|
|
|
|
General Confederation of Mauritanian Workers or CGTM [Abdallahi Ould MOHAMED, secretary general]; Independent Confederation of Mauritanian Workers or CLTM [Samory Ould BEYE]; Mauritanian Workers Union or UTM [Mohamed Ely Ould BRAHIM, secretary general]
other:
Arab nationalists; Ba'thists; Islamists
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, CAEU, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mohamed Lemine El HAYCEN
chancery:
2129 Leroy Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 232-5700 through 5701
FAX:
[1] (202) 319-2623
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mark M. BOULWARE
embassy:
288 Rue Abdallaye, Rue 42-100 (between Presidency building and Spanish Embassy), Nouakchott
mailing address:
BP 222, Nouakchott
telephone:
[222] 525-2660 through 2663
FAX:
[222] 525-1592
|
|
|
|
|
green with a yellow five-pointed star above a yellow, horizontal crescent; the closed side of the crescent is down; the crescent, star, and color green are traditional symbols of Islam; the gold color stands for the sands of the Sahara
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Hymne National de la Republique Islamique de Mauritanie" (National Anthem of the Islamic Republic of Mauritania)
lyrics/music:
Baba Ould CHEIKH/traditional, arranged by Tolia NIKIPROWETZKY
note:
adopted 1960; the unique rhythm of the Mauritanian anthem makes it particularly challenging to sing
|
|
|
|
|
|
Half the population still depends on agriculture and livestock for a livelihood, even though many of the nomads and subsistence farmers were forced into the cities by recurrent droughts in the 1970s and 1980s. Mauritania has extensive deposits of iron ore, which account for nearly 40% of total exports. The nation's coastal waters are among the richest fishing areas in the world but overexploitation by foreigners threatens this key source of revenue. The country's first deepwater port opened near Nouakchott in 1986. Before 2000, drought and economic mismanagement resulted in a buildup of foreign debt. In February 2000, Mauritania qualified for debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative and nearly all of its foreign debt has since been forgiven. A new investment code approved in December 2001 improved the opportunities for direct foreign investment. Mauritania and the IMF agreed to a three-year Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF) arrangement in 2006. Mauritania made satisfactory progress, but the IMF, World Bank, and other international actors suspended assistance and investment in Mauritania after the August 2008 coup. Since the presidential election in July 2009, donors have resumed assistance. Oil prospects, while initially promising, have largely failed to materialize, and the government has placed a priority on attracting private investment to spur economic growth. The Government also emphasizes reduction of poverty, improvement of health and education, and privatization of the economy.
|
|
|
|
|
$6.655 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
$6.358 billion (2009 est.)
$6.437 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$3.799 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
-1.2% (2009 est.)
3.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2,100 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
$2,000 (2009 est.)
$2,100 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 12.5%
industry:
46.7%
services:
40.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.318 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 50%
industry:
10%
services:
40% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
30% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
20% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
40% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.5%
highest 10%:
29.5% (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
39 (2000)
country comparison to the world: 66
37.3 (1995)
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $770 million
expenditures:
$770 million (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.3% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 28
12% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
dates, millet, sorghum, rice, corn; cattle, sheep
|
|
|
|
|
fish processing, oil production, mining of iron ore, gold, and copper
note:
gypsum deposits have never been exploited
|
|
|
|
|
2% (2000 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
415.3 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
386.2 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
16,510 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
20,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
30,620 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
20,610 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
100 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
28.32 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
$-184 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
$1.395 billion (2006)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
iron ore, fish and fish products, gold, copper, petroleum
|
|
|
|
|
China 42.06%, Italy 9.71%, Japan 7.57%, Cote d'Ivoire 6.16%, Spain 5.63%, Netherlands 4.32% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.475 billion (2006)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, petroleum products, capital goods, foodstuffs, consumer goods
|
|
|
|
|
France 14.3%, Netherlands 10.33%, China 9.94%, Brazil 5.58%, Belgium 4.87%, Germany 4.04%, Spain 4.02% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
ouguiyas (MRO) per US dollar -
261.5 (2010 est.)
262.4 (2009)
238.2 (2008)
258.6 (2007)
271.3 (2006)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Mauritania |
|
|
74,500 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
2.182 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: limited system of cable and open-wire lines, minor microwave radio relay links, and radiotelephone communications stations; mobile-cellular services expanding rapidly
domestic:
Mauritel, the national telecommunications company, was privatized in 2001 but remains the monopoly provider of fixed-line services; fixed-line teledensity 2 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular network coverage extends mainly to urban areas with a teledensity of 70 per 100 persons; mostly cable and open-wire lines; a domestic satellite telecommunications system links Nouakchott with regional capitals
international:
country code - 222; satellite earth stations - 3 (1 Intelsat - Atlantic Ocean, 2 Arabsat); fiber-optic and Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) cables for Internet access (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
broadcast media state-owned; 1 state-run TV and 1 state-run radio network; Television de Mauritanie, the state-run TV station, has an additional 6 regional TV stations that provide local programming (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.mr
|
|
|
|
|
23 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 216
|
|
|
|
|
75,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Mauritania |
|
|
28 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 19
1,524 to 2,437 m:
9
914 to 1,523 m:
8
under 914 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
728 km
standard gauge:
728 km 1.435-m gauge (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11,066 km
country comparison to the world: 133
paved:
2,966 km
unpaved:
8,100 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
(some is navigation possible on the Senegal River) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Nouadhibou, Nouakchott
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mauritanian Armed Forces: Army, Mauritanian Navy (Marine Mauritanienne; includes naval infantry), Islamic Air Force of Mauritania (Force Aerienne Islamique de Mauritanie, FAIM) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age (est.); conscript service obligation - 2 years; majority of servicemen believed to be volunteers; service in Air Force and Navy is voluntary (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 718,713
females age 16-49:
804,622 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 480,042
females age 16-49:
581,473 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 36,116
female:
36,826 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Mauritania |
|
|
Mauritanian claims to Western Sahara remain dormant
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Mauritania is a source and destination country for children trafficked for forced labor and sexual exploitation; slavery-related practices, rooted in ancestral master-slave relationships, continue to exist in isolated parts of the country; Mauritanian boys called talibe are trafficked within the country by religious teachers for forced begging; children are also trafficked by street gangs within the country that force them to steal, beg, and sell drugs; girls are trafficked internally for domestic servitude and sexual exploitation; women and children from neighboring states are trafficked into Mauritania for purposes of forced begging, domestic servitude, and sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 3 - the Government of Mauritania does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government did not show evidence of overall progress in prosecuting and punishing trafficking offenders, protecting trafficking victims, or preventing new incidents of trafficking during the past year; progress that the previous government demonstrated in 2007 through enactment of strengthened anti-slavery legislation and deepened political will to eliminate slavery and trafficking has stalled; law enforcement efforts to address human trafficking including traditional slavery practices decreased (2009)
|
|
|
|
|