|
|
Macedonia gained its independence peacefully from Yugoslavia in 1991. Greece's objection to the new state's use of what it considered a Hellenic name and symbols delayed international recognition, which occurred under the provisional designation of "the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia." In 1995, Greece lifted a 20-month trade embargo and the two countries agreed to normalize relations. The United States began referring to Macedonia by its constitutional name, Republic of Macedonia, in 2004 and negotiations continue between Greece and Macedonia to resolve the name issue. Some ethnic Albanians, angered by perceived political and economic inequities, launched an insurgency in 2001 that eventually won the support of the majority of Macedonia's Albanian population and led to the internationally-brokered Ohrid Framework Agreement, which ended the fighting by establishing a set of new laws enhancing the rights of minorities. Fully implementing the Framework Agreement and stimulating economic growth and development continue to be challenges for Macedonia, although progress has been made on both fronts over the past several years.
|
|
|
|
|
|
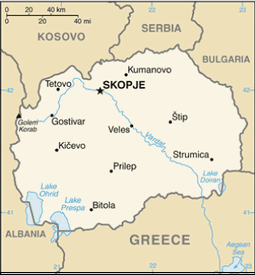
Southeastern Europe, north of Greece
|
|
|
|
|
41 50 N, 22 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25,713 sq km
country comparison to the world: 149
land:
25,433 sq km
water:
280 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Vermont
|
|
|
|
|
total: 766 km
border countries:
Albania 151 km, Bulgaria 148 km, Greece 246 km, Kosovo 159 km, Serbia 62 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
warm, dry summers and autumns; relatively cold winters with heavy snowfall
|
|
|
|
|
mountainous territory covered with deep basins and valleys; three large lakes, each divided by a frontier line; country bisected by the Vardar River
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Vardar River 50 m
highest point:
Golem Korab (Maja e Korabit) 2,764 m
|
|
|
|
|
low-grade iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, chromite, manganese, nickel, tungsten, gold, silver, asbestos, gypsum, timber, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 22.01%
permanent crops:
1.79%
other:
76.2% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1,280 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
6.4 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.27
per capita:
1,118 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
high seismic risks
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution from metallurgical plants
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; major transportation corridor from Western and Central Europe to Aegean Sea and Southern Europe to Western Europe
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,077,328 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 18.5% (male 198,643/female 184,775)
15-64 years:
70% (male 733,601/female 720,103)
65 years and over:
11.6% (male 103,620/female 136,586) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35.8 years
male:
34.8 years
female:
36.9 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.248% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
11.87 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
8.91 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
-0.48 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 59% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
SKOPJE (capital) 480,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.077 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.08 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.76 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8.54 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 157
male:
8.76 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
8.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 75.14 years
country comparison to the world: 88
male:
72.61 years
female:
77.87 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.58 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 99% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 1% of population
total: 0% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 92% of population
rural: 82% of population
total: 89% of population
unimproved:
urban: 8% of population
rural: 18% of population
total: 11% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Macedonian(s)
adjective:
Macedonian
|
|
|
|
|
Macedonian 64.2%, Albanian 25.2%, Turkish 3.9%, Roma (Gypsy) 2.7%, Serb 1.8%, other 2.2% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Macedonian Orthodox 64.7%, Muslim 33.3%, other Christian 0.37%, other and unspecified 1.63% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Macedonian (official) 66.5%, Albanian (official) 25.1%, Turkish 3.5%, Roma 1.9%, Serbian 1.2%, other 1.8% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
96.1%
male:
98.2%
female:
94.1% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13 years
male:
13 years
female:
13 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Macedonia
conventional short form:
Macedonia
local long form:
Republika Makedonija
local short form:
Makedonija
note:
the provisional designation used by the UN, EU, and NATO is the "former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM)
former:
People's Republic of Macedonia, Socialist Republic of Macedonia
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Skopje
geographic coordinates:
42 00 N, 21 26 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
84 municipalities (opstini, singular - opstina); Aerodrom (Skopje), Aracinovo, Berovo, Bitola, Bogdanci, Bogovinje, Bosilovo, Brvenica, Butel (Skopje), Cair (Skopje), Caska, Centar (Skopje), Centar Zupa, Cesinovo, Cucer Sandevo, Debar, Debarca, Delcevo, Demir Hisar, Demir Kapija, Dojran, Dolneni, Dorce Petrov (Gjorce Petrov) (Skopje), Drugovo, Gazi Baba (Skopje), Gevgelija, Gostivar, Gradsko, Ilinden, Jegunovce, Karbinci, Karpos (Skopje), Kavadarci, Kicevo, Kisela Voda (Skopje), Kocani, Konce, Kratovo, Kriva Palanka, Krivogastani, Krusevo, Kumanovo, Lipkovo, Lozovo, Makedonska Kamenica, Makedonski Brod, Mavrovo i Rostusa, Mogila, Negotino, Novaci, Novo Selo, Ohrid, Oslomej, Pehcevo, Petrovec, Plasnica, Prilep, Probistip, Radovis, Rankovce, Resen, Rosoman, Saraj (Skopje), Sopiste, Staro Nagoricane, Stip, Struga, Strumica, Studenicani, Suto Orizari (Skopje), Sveti Nikole, Tearce, Tetovo, Valandovo, Vasilevo, Veles, Vevcani, Vinica, Vranestica, Vrapciste, Zajas, Zelenikovo, Zelino, Zrnovci
note:
the 10 municipalities followed by Skopje in parentheses collectively constitute the larger Skopje Municipality
|
|
|
|
|
8 September 1991 (referendum by registered voters endorsed independence from Yugoslavia)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 8 September (1991); also known as National Day
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 17 November 1991, effective 20 November 1991; amended November 2001, 2005 and in 2009
note:
amended November 2001 by a series of new constitutional amendments strengthening minority rights, in 2005 with amendments related to the judiciary, and in 2009 with amendments related to the threshold required to elect the president
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Gjorge IVANOV (since 12 May 2009)
head of government:
Prime Minister Nikola GRUEVSKI (since 26 August 2006)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers elected by the majority vote of all the deputies in the Assembly; note - current cabinet formed by the government coalition parties VMRO-DPMNE, BDI/DUI, and several small parties
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); two-round election: first round held on 22 March 2009, second round held on 5 April 2009 (next to be held in March 2014); prime minister elected by the Assembly following legislative elections
election results:
Gjorge IVANOV elected president on second-round ballot; percent of vote - Gjorge IVANOV 63.1%, Ljubomir FRCKOSKI 36.9%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Assembly or Sobranie (120 seats; members elected by popular vote from party lists based on the percentage of the overall vote the parties gain in each of six electoral districts; members serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 1 June and 15 June 2008 (next to be held by July 2012)
election results:
percent of vote by party - VMRO-DPMNE-led block 49%, SDSM-led block 24%, BDI/DUI 13%, PDSh/DPA 8%, other 6%; seats by party - VMRO-DPMNE-led block 63, SDSM-led block 27, BDI/DUI 18, PDSh/DPA 11, PEI 1
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court; Constitutional Court; Judicial Council
note:
the Judicial Council appoints the judges
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Alliance or DS [Pavle TRAJANOV]; Democratic Party of Serbs in Macedonia [Ivan STOILJKOVIC]; Democratic Party of the Albanians or PDSh/DPA [Menduh THACI]; Democratic Party of Turks in Macedonia [Kenan HASIPI]; Democratic Union for Integration or BDI/DUI [Ali AHMETI]; Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization--Democratic Party for Macedonian National Unity (VMRO-DPMNE) [Nikola GRUEVSKI]; Liberal Democratic Party or LDP; Liberal Party [Borce STOJANOVSKI]; Movement for Reconstruction of Macedonia or DOM [Liljana POPOVSKA]; New Alternative [Gjorgji OROVCANEC]; New Democracy or DR [Imer SELMANI]; New Social-Democratic Party or NSDP [Tito PETKOVSKI]; Party for Democratic Action in Macedonia or SDAM [Avdija PEPIC]; Party for European Future or PEI [Fijat CANOSKI]; Social-Democratic Union of Macedonia or SDSM [Branko CRVENKOVSKI]; Socialist Party or SP [Ljubisav IVANOV-DZINGO]; Union of Roma of Macedonia [Amdi BAJRAM]; United for Macedonia or OM [Ljube BOSKOVSKI]; VMRO-Macedonian [Borislav STOJMENOV]
|
|
|
|
|
Federation of Free Trade Unions [Rasko MISHKOSKI]; Federation of Trade Unions [Zivko MITREVSKI]; Trade Union of Education, Science and Culture [Yakim NEDELKOV]
|
|
|
|
|
BIS, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, EU (candidate country), FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Zoran JOLEVSKI
chancery:
2129 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 667-0501
FAX:
[1] (202) 667-2131
consulate(s) general:
Southfield (Michigan), Chicago
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Philip T. REEKER
embassy:
Str. Samolilova, Nr. 21, 1000 Skopje
mailing address:
American Embassy Skopje, US Department of State, 7120 Skopje Place, Washington, DC 20521-7120 (pouch)
telephone:
[389] 2 310-2000
FAX:
[389] 2 310-2499
|
|
|
|
|
a yellow sun (the Sun of Liberty) with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field; the red and yellow colors have long been associated with Macedonia
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Denes Nad Makedonija" (Today Over Macedonia)
lyrics/music:
Vlado MALESKI/Todor SKALOVSKI
note:
adopted 1991; the song, written in 1943, previously served as the anthem of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia while part of Yugoslavia
|
|
|
|
|
|
Having a small, open economy makes Macedonia vulnerable to economic developments in Europe and dependent on regional integration and progress toward EU membership for continued economic growth. At independence in September 1991, Macedonia was the least developed of the Yugoslav republics, producing a mere 5% of the total federal output of goods and services. The collapse of Yugoslavia ended transfer payments from the central government and eliminated advantages from inclusion in a de facto free trade area. An absence of infrastructure, UN sanctions on the downsized Yugoslavia, and a Greek economic embargo over a dispute about the country's constitutional name and flag hindered economic growth until 1996. Since then, Macedonia has maintained macroeconomic stability with low inflation, but it has so far lagged the region in attracting foreign investment and creating jobs, despite making extensive fiscal and business sector reforms. Official unemployment remains high at 31.7%, but may be overstated based on the existence of an extensive gray market, estimated to be more than 20% of GDP, that is not captured by official statistics. In the wake of the global economic downturn, Macedonia has experienced decreased foreign direct investment, lowered credit, and a large trade deficit. However, as a result of conservative fiscal policies and a sound financial system, in 2010 the country received slightly improved credit ratings. Macroeconomic stability also was maintained by a prudent monetary policy, which kept the domestic currency at the pegged level against the euro, while interest rates were falling. As a result, GDP growth was modest, but positive, in 2010.
|
|
|
|
|
$20 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
$19.86 billion (2009 est.)
$20.04 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars; Macedonia has a large informal sector
|
|
|
|
|
$9.108 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
-0.9% (2009 est.)
5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$9,700 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
$9,600 (2009 est.)
$9,700 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 8.7%
industry:
22.1%
services:
69.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
949,300 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 19.9%
industry:
22.1%
services:
58% (September 2010)
|
|
|
|
|
31.7% (3rd quarter, 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
32.2% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
28.7% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.4%
highest 10%:
29.6% (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
39 (2003)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
23.2% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $2.772 billion
expenditures:
$3.011 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
34.2% of GDP (November 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
31.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
-0.8% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.5% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 55
6.5% (31 December 2008)
note:
series discontinued in January 2010. Discount rate was replaced by a referent rate for calculating the penalty rate: 4.0% (31 December 2010)
|
|
|
|
|
8.2% (30 November 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
9.3% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.146 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
$1.224 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.134 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
$4.858 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.001 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$4.055 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.647 billion (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 92
$2.859 billion (31 December 2009)
$823.5 million (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
grapes, tobacco, vegetables, fruits; milk, eggs
|
|
|
|
|
food processing, beverages, textiles, chemicals, iron, steel, cement, energy, pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
|
|
4% (November 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
6.819 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
8.189 billion kWh (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.37 billion kWh (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2010)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
18,200 bbl/day (2010)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
8,594 bbl/day (2010)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
18,200 bbl/day (2009)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
117.4 million cu m (2010)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
117.4 million cu m (2010)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
$-328 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
$-645.6 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.171 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
$2.686 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
food, beverages, tobacco; textiles, miscellaneous manufactures, iron and steel
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 20.31%, Greece 13.09%, Italy 11.08%, Bulgaria 10.61%, Croatia 7.74% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.113 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
$4.842 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, automobiles, chemicals, fuels, food products
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 15.11%, Greece 14.88%, Bulgaria 9.08%, Italy 7.68%, Turkey 7.59%, Slovenia 6.26%, Hungary 4.31% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.217 billion (30 November 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$2.292 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.485 billion (30 September 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$5.5 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.739 billion (31 October 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$3.554 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2010)
$564 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Macedonian denars (MKD) per US dollar -
46.434 (2010)
44.1 (2009)
41.414 (2008)
44.732 (2007)
48.978 (2006)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Macedonia |
|
|
442,200 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
1.943 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: competition from the mobile-cellular segment of the telecommunications market has led to a drop in fixed-line telephone subscriptions
domestic:
combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership about 115 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 389 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
public television broadcaster operates 3 national channels and a satellite network; 5 privately-owned TV channels broadcast nationally using terrestrial transmitters and about 15 broadcast on national level via satellite; roughly 75 local commercial TV stations broadcasting; large number of cable operators offering domestic and international programming; public radio broadcaster operates over multiple stations; 3 privately-owned radio stations broadcast nationally; about 70 local commercial radio stations functioning (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
.mk
|
|
|
|
|
60,533 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
1.057 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Macedonia |
|
|
14 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
under 914 m:
8 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
3 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 268 km; oil 120 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 699 km
country comparison to the world: 100
standard gauge:
699 km 1.435-m gauge (234 km electrified) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13,736 km (includes 216 km of expressways) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
|
Army of the Republic of Macedonia (ARM): Joint Operational Command, with subordinate Air Wing (Makedonsko Voeno Vozduhoplovstvo, MVV); Special Operations Regiment; Logistic Support Command; Training Command (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 532,196
females age 16-49:
511,964 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 443,843
females age 16-49:
426,251 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 16,144
female:
14,920 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Macedonia |
|
|
Kosovo and Macedonia completed demarcation of their boundary in September 2008; Greece continues to reject the use of the name Macedonia or Republic of Macedonia
|
|
|
|
|
IDPs: fewer than 1,000 (ethnic conflict in 2001) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
major transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and hashish; minor transit point for South American cocaine destined for Europe; although not a financial center and most criminal activity is thought to be domestic, money laundering is a problem due to a mostly cash-based economy and weak enforcement
|
|
|
|
|