|
|
Guinea has had a history of authoritarian rule since gaining its independence from France in 1958. Lansana CONTE came to power in 1984 when the military seized the government after the death of the first president, Sekou TOURE. Guinea did not hold democratic elections until 1993 when Gen. CONTE (head of the military government) was elected president of the civilian government. He was reelected in 1998 and again in 2003, though all the polls were marred by irregularities. History repeated itself in December 2008 when following President CONTE's death, Capt. Moussa Dadis CAMARA led a military coup, seizing power and suspending the constitution. His unwillingness to yield to domestic and international pressure to step down led to heightened political tensions that culminated in September 2009 when presidential guards opened fire on an opposition rally killing more than 150 people, and in early December 2009 when CAMARA was wounded in an assassination attempt and evacuated to Morocco and subsequently to Burkina Faso. A transitional government led by General Sekouba KONATE held democratic elections in 2010 and Alpha CONDE was elected president in the country's first free and fair elections since independence.
|
|
|
|
|
|
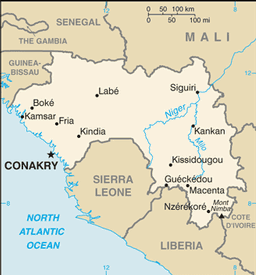
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea-Bissau and Sierra Leone
|
|
|
|
|
11 00 N, 10 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 245,857 sq km
country comparison to the world: 78
land:
245,717 sq km
water:
140 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Oregon
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,399 km
border countries:
Cote d'Ivoire 610 km, Guinea-Bissau 386 km, Liberia 563 km, Mali 858 km, Senegal 330 km, Sierra Leone 652 km
|
|
|
|
|
320 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds
|
|
|
|
|
generally flat coastal plain, hilly to mountainous interior
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mont Nimba 1,752 m
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, iron ore, diamonds, gold, uranium, hydropower, fish, salt
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 4.47%
permanent crops:
2.64%
other:
92.89% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
950 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
226 cu km (1987)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.51 cu km/yr (8%/2%/90%)
per capita:
161 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; inadequate supplies of potable water; desertification; soil contamination and erosion; overfishing, overpopulation in forest region; poor mining practices have led to environmental damage
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
the Niger and its important tributary the Milo have their sources in the Guinean highlands
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,601,009 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 42.5% (male 2,278,048/female 2,229,602)
15-64 years:
54% (male 2,860,845/female 2,860,004)
65 years and over:
3.5% (male 164,051/female 208,459) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18.6 years
male:
18.3 years
female:
18.8 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.645% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
36.9 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
10.45 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 35% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
4.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
CONAKRY (capital) 1.597 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.78 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 61.03 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 31
male:
64.29 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
57.68 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 58.11 years
country comparison to the world: 191
male:
56.63 years
female:
59.64 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.1 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
79,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
4,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria and yellow fever
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
aerosolized dust or soil contact disease:
Lassa fever
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 89% of population
rural: 61% of population
total: 71% of population
unimproved:
urban: 11% of population
rural: 39% of population
total: 29% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 34% of population
rural: 11% of population
total: 19% of population
unimproved:
urban: 66% of population
rural: 89% of population
total: 81% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Guinean(s)
adjective:
Guinean
|
|
|
|
|
Peuhl 40%, Malinke 30%, Soussou 20%, smaller ethnic groups 10%
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 85%, Christian 8%, indigenous beliefs 7%
|
|
|
|
|
French (official)
note:
each ethnic group has its own language
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
29.5%
male:
42.6%
female:
18.1% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9 years
male:
10 years
female:
7 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Guinea
conventional short form:
Guinea
local long form:
Republique de Guinee
local short form:
Guinee
former:
French Guinea
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Conakry
geographic coordinates:
9 33 N, 13 42 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
33 prefectures and 1 special zone (zone special)*; Beyla, Boffa, Boke, Conakry*, Coyah, Dabola, Dalaba, Dinguiraye, Dubreka, Faranah, Forecariah, Fria, Gaoual, Gueckedou, Kankan, Kerouane, Kindia, Kissidougou, Koubia, Koundara, Kouroussa, Labe, Lelouma, Lola, Macenta, Mali, Mamou, Mandiana, Nzerekore, Pita, Siguiri, Telimele, Tougue, Yomou
|
|
|
|
|
2 October 1958 (from France)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 2 October (1958)
|
|
|
|
|
7 May 2010 (Loi Fundamentale)
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on the French model
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Alpha CONDE (since 21 December 2010)
head of government:
Prime Minister Mohamed Said FOFANA (since 24 December 2010)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); candidate must receive a majority of the votes cast to be elected president; election last held on 27 June 2010 with a runoff election held on 7 November 2010
election results:
Alpha CONDE elected president in a runoff election; percent of vote Alpha CONDE 52.5%, Cellou Dalein DIALLO 47.5%
|
|
|
|
|
the legislature was dissolved by junta leader Moussa Dadis CAMARA in December 2008 and in February 2010, the Transition Government appointed a 155 member National Transition Council (CNT) that has since acted in the legislature's place
elections:
last held on 30 June 2002
|
|
|
|
|
Constitutional Court; Court of First Instance or Tribunal de Premiere Instance; Court of Appeal or Cour d'Appel; Supreme Court or Cour Supreme
|
|
|
|
|
Rally for the Guinean People or RPG [Alpha CONDE]; Union of Democratic Forces of Guinea or UFDG [Cellou Dalein DIALLO]; Union of Republican Forces or UFR [Sidya TOURE]
note:
Listed are the three most popular parties in first round voting for president in 2010; overall, there are more than 130 registered parties
|
|
|
|
|
National Confederation of Guinean Workers-Labor Union of Guinean Workers or CNTG-USTG Alliance (includes National Confederation of Guinean Workers or CNTG and Labor Union of Guinean Workers or USTG); Syndicate of Guinean Teachers and Researchers or SLECG
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU (suspended), ECOWAS (suspended), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mory Karamoko KABA
chancery:
2112 Leroy Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 986-4300
FAX:
[1] (202) 483-8688
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Patricia Newton MOLLER
embassy:
Koloma, Conakry, east of Hamdallaye Circle
mailing address:
B. P. 603, Transversale No. 2, Centre Administratif de Koloma, Commune de Ratoma, Conakry
telephone:
[224] 65-10-40-00
FAX:
[224] 65-10-42-97
|
|
|
|
|
three equal vertical bands of red (hoist side), yellow, and green; red represents the people's sacrifice for liberation and work; yellow stands for the sun, for the riches of the earth, and for justice; green symbolizes the country's vegetation and unity
note:
uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the colors from left to right are the reverse of those on the flags of neighboring Mali and Senegal
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Liberte" (Liberty)
lyrics/music:
unknown/Fodeba KEITA
note:
adopted 1958
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guinea is a poor country that possesses major mineral, hydropower, and agricultural resources. The country has almost half of the world's bauxite reserves and significant iron ore, gold, and diamond reserves. However, Guinea has been unable to profit from this potential, as rampant corruption, dilapidated electricity and other degraded infrastructure, and political uncertainty have drained investor confidence. In the time since a 2008 coup following the death of long-term President Lansana CONTE, international donors, including the G-8, the IMF, and the World Bank, have significantly curtailed their development programs. Throughout 2009, policies of the ruling military junta severely weakened the economy. The junta leaders spent and printed money at an accelerated rate, driving inflation and debt to perilously high levels. In early 2010, the junta collapsed and was replaced by a Transition Government, which ceded power in December 2010 to the country's first-ever democratically elected president, Alpha CONDE. International assistance and investment are expected to return to Guinea, but the levels will depend upon the ability of the new government to combat corruption and reform its banking system. IMF and World Bank programs will be especially critical as Guinea attempts to gain debt relief. Since the 2009 global economic downturn, the price and value of bauxite and alumina exports has steadily risen. Export levels will likely continue to grow as investor confidence returns. International investors have expressed keen interest in Guinea's vast iron ore reserves, which could further propel the country's growth.
|
|
|
|
|
$10.81 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
$10.6 billion (2009 est.)
$10.63 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$4.633 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
-0.3% (2009 est.)
4.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1,000 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
$1,100 (2009 est.)
$1,100 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 25.8%
industry:
45.7%
services:
28.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.392 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 76%
industry and services:
24% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
47% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%:
41% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
38.1 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 71
40.3 (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
14.6% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $574.1 million
expenditures:
$875.4 million (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
15% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 218
9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
country comparison to the world: 7
22.25% (31 December 2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$496.2 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
$459.7 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$830 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
$761.9 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$734.4 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
$674.2 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
rice, coffee, pineapples, palm kernels, cassava (tapioca), bananas, sweet potatoes; cattle, sheep, goats; timber
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, gold, diamonds, iron; alumina refining; light manufacturing, and agricultural processing
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
850 million kWh
country comparison to the world: 148
note:
excludes electricity generated at interior mining sites (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
790.5 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
9,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
8,674 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
$-434 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
$-538 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.468 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
$1.18 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, alumina, gold, diamonds, coffee, fish, agricultural products
|
|
|
|
|
India 19.68%, Spain 13.18%, Russia 7.24%, Germany 6.86%, Ireland 5.87%, US 5.71%, Ukraine 5.6% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.551 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
$1.236 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum products, metals, machinery, transport equipment, textiles, grain and other foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
China 8.67%, Netherlands 6.67%, France 4.33%, UK 4.22% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2010 est.)
$51 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.072 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
$3.222 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Guinean francs (GNF) per US dollar -
6,100 (2010)
5,500 (2009)
5,500 (2008)
4,122.8 (2007)
5,350 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
22,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
5.607 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: inadequate system of open-wire lines, small radiotelephone communication stations, and new microwave radio relay system
domestic:
Conakry reasonably well served; coverage elsewhere remains inadequate and large companies tend to rely on their own systems for nationwide links; fixed-line teledensity less than 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular subscribership is expanding and exceeded 50 per 100 persons in 2009
international:
country code - 224; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
|
|
|
|
|
government maintains marginal control over broadcast media; single state-run TV station; state-run radio broadcast station also operates several stations in rural areas; a steadily increasing number of privately-owned radio stations, nearly all in Conakry, and about a dozen community radio stations; foreign television programming available via satellite and cable subscription services (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
.gn
|
|
|
|
|
14 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 220
|
|
|
|
|
95,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
over 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12
1,524 to 2,437 m:
7
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,185 km
country comparison to the world: 86
standard gauge:
238 km 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge:
947 km 1.000-m gauge (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 44,348 km
country comparison to the world: 83
paved:
4,342 km
unpaved:
40,006 km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
1,300 km (navigable by shallow-draft native craft in the northern part of the Niger system) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
Conakry, Kamsar
|
|
|
|
|
|
National Armed Forces: Army, Navy (Armee de Mer or Marine Guineenne, includes Marines), Guinean Air Force (Force Aerienne de Guinee) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
18-25 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; 18-month conscript service obligation (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,359,203
females age 16-49:
2,329,784 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,493,991
females age 16-49:
1,535,418 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 118,443
female:
115,901 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.1% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Guinea |
|
|
conflicts among rebel groups, warlords, and youth gangs in neighboring states have spilled over into Guinea resulting in domestic instability; Sierra Leone considers Guinea's definition of the flood plain limits to define the left bank boundary of the Makona and Moa rivers excessive and protests Guinea's continued occupation of these lands, including the hamlet of Yenga, occupied since 1998
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 21,856 (Liberia); 5,259 (Sierra Leone); 3,900 (Cote d'Ivoire)
IDPs:
19,000 (cross-border incursions from Cote d'Ivoire, Liberia, Sierra Leone) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Guinea is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and sexual exploitation; the majority of victims are children, and internal trafficking is more prevalent than transnational trafficking; within the country, girls are trafficked primarily for domestic servitude and sexual exploitation, while boys are trafficked for forced agricultural labor, and as forced beggars, street vendors, shoe shiners, and laborers in gold and diamond mines; some Guinean men are also trafficked for agricultural labor within Guinea; transnationally, girls are trafficked into Guinea for domestic servitude and likely also for sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - Guinea is on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to eliminate trafficking over 2006; Guinea demonstrated minimal law enforcement efforts for a second year in a row, while protection efforts diminished over efforts in 2006; the government did not report any trafficking convictions in 2007; due to a lack of resources, the government does not provide shelter services for trafficking victims; the government took no measures to reduce the demand for commercial sexual exploitation (2008)
|
|
|
|
|