| Introduction ::Czech Republic |
|
|
At the close of World War I, the Czechs and Slovaks of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire merged to form Czechoslovakia. During the interwar years, having rejected a federal system, the new country's leaders were frequently preoccupied with meeting the demands of other ethnic minorities within the republic, most notably the Sudeten Germans and the Ruthenians (Ukrainians). On the eve of World War II, the Czech part of the country was forcibly annexed to the Third Reich, and the Slovaks declared independence as a fascist ally of Nazi Germany. After the war, a reunited but truncated Czechoslovakia (less Ruthenia) fell within the Soviet sphere of influence. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalize Communist Party rule and create "socialism with a human face." Anti-Soviet demonstrations the following year ushered in a period of harsh repression known as "normalization." With the collapse of Soviet-backed authority in 1989, Czechoslovakia regained its freedom through a peaceful "Velvet Revolution." On 1 January 1993, the country underwent a "velvet divorce" into its two national components, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004.
|
|
|
|
| Geography ::Czech Republic |
|
|
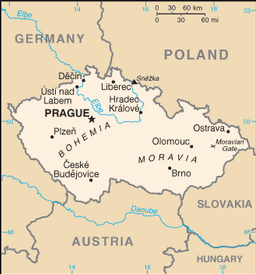
Central Europe, between Germany, Poland, Slovakia, and Austria
|
|
|
|
|
49 45 N, 15 30 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 78,867 sq km
country comparison to the world: 115
land:
77,247 sq km
water:
1,620 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than South Carolina
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,989 km
border countries:
Austria 362 km, Germany 815 km, Poland 615 km, Slovakia 197 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
|
|
|
|
|
Bohemia in the west consists of rolling plains, hills, and plateaus surrounded by low mountains; Moravia in the east consists of very hilly country
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Elbe River 115 m
highest point:
Snezka 1,602 m
|
|
|
|
|
hard coal, soft coal, kaolin, clay, graphite, timber
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 38.82%
permanent crops:
3%
other:
58.18% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
390 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
16 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.91 cu km/yr (41%/57%/2%)
per capita:
187 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding
|
|
|
|
|
air and water pollution in areas of northwest Bohemia and in northern Moravia around Ostrava present health risks; acid rain damaging forests; efforts to bring industry up to EU code should improve domestic pollution
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; strategically located astride some of oldest and most significant land routes in Europe; Moravian Gate is a traditional military corridor between the North European Plain and the Danube in central Europe
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,190,213 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 13.5% (male 704,495/female 666,191)
15-64 years:
70.2% (male 3,599,774/female 3,554,158)
65 years and over:
16.3% (male 663,982/female 1,001,613) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 40.8 years
male:
39.2 years
female:
42.5 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.12% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
|
|
|
|
|
8.7 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
|
|
|
|
|
10.86 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
0.97 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 74% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
PRAGUE (capital) 1.162 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.059 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.66 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.73 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 205
male:
4.06 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.38 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 77.19 years
country comparison to the world: 63
male:
73.93 years
female:
80.66 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.26 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 99% of population
rural: 97% of population
total: 98% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1% of population
rural: 3% of population
total: 2% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Czech(s)
adjective:
Czech
|
|
|
|
|
Czech 90.4%, Moravian 3.7%, Slovak 1.9%, other 4% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 26.8%, Protestant 2.1%, other 3.3%, unspecified 8.8%, unaffiliated 59% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Czech 94.9%, Slovak 2%, other 2.3%, unidentified 0.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: NA
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
15 years
female:
16 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
4.2% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Czech Republic |
|
|
conventional long form: Czech Republic
conventional short form:
Czech Republic
local long form:
Ceska Republika
local short form:
Cesko
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Prague
geographic coordinates:
50 05 N, 14 28 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
13 regions (kraje, singular - kraj) and 1 capital city* (hlavni mesto); Jihocesky (South Bohemia), Jihomoravsky (South Moravia), Karlovarsky, Kralovehradecky, Liberecky, Moravskoslezsky (Moravia-Silesia), Olomoucky, Pardubicky, Plzensky (Pilsen), Praha (Prague)*, Stredocesky (Central Bohemia), Ustecky, Vysocina, Zlinsky
|
|
|
|
|
1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia); note - although 1 January is the day the Czech Republic came into being, the Czechs generally consider 28 October 1918, the day the former Czechoslovakia declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, as their independence day
|
|
|
|
|
Czechoslovak Founding Day, 28 October (1918)
|
|
|
|
|
ratified 16 December 1992, effective 1 January 1993; amended several times
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on former Austro-Hungarian civil codes and socialist theory; note - legislation is actively modernizing the legal system
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Vaclav KLAUS (since 7 March 2003)
head of government:
Prime Minister Petr NECAS (since 28 June 2010); First Deputy Prime Minister Karel SCHWARZENBERG (since 13 July 2010), Deputy Prime Minister Radek JOHN (since 13 July 2010)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by Parliament for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); last successful election held on 15 February 2008 (after earlier elections held 8 and 9 February 2008 were inconclusive; next election to be held in 2013); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Vaclav KLAUS reelected president on 15 February 2008; Vaclav KLAUS 141 votes, Jan SVEJNAR 111 votes (third round; combined votes of both chambers of parliament)
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Parliament or Parlament consists of the Senate or Senat (81 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve six-year terms; one-third elected every two years) and the Chamber of Deputies or Poslanecka Snemovna (200 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last held in two rounds on 15-16 and 22-23 October 2010 (next to be held by October 2012); Chamber of Deputies - last held on 28-29 May 2010 (next to be held by 2014)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CSSD 41, ODS 25, KDU-CSL 6, TOP 09 5, others 4; Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party - CSSD 22.1%, ODS 20.2%, TOP 09 16.7%, KSCM 11.3%, VV 10.9%; seats by party - CSSD 56, ODS 53, TOP 09 41, KSCM 26, VV 24
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court; judges are appointed by the president for an unlimited term; Constitutional Court; 15 judges are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate for a ten-year term; Supreme Administrative Court; chairman and deputy chairmen are appointed by the president for a 10-year term; judges are appointed by the president for an unlimited term
|
|
|
|
|
Association of Independent Candidates-European Democrats or SNK-ED [Zdenka MARKOVA]; Christian Democratic Union-Czechoslovak People's Party or KDU-CSL [Pavel BELOBRADEK]; Civic Democratic Party or ODS [Petr NECAS]; Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia or KSCM [Vojtech FILIP]; Czech Social Democratic Party or CSSD [Bohuslav SOBOTKA (acting)]; Green Party [Ondrej LISKA]; Public Affairs or VV [Radek JOHN]; Tradice Odpovednost Prosperita 09 or TOP 09 [Karel SCHWARZENBERG]; Union of Freedom-Democratic Union or US-DEU [Jan CERNY]
|
|
|
|
|
Czech-Moravian Confederation of Trade Unions or CMKOS [Jaroslav ZAVADIL]
|
|
|
|
|
Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, ESA, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUSCO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Norman EISEN
chancery:
3900 Spring of Freedom Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 274-9100
FAX:
[1] (202) 966-8540
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Norman EISEN
embassy:
Trziste 15, 118 01 Prague 1
mailing address:
use embassy street address
telephone:
[420] 257 022 000
FAX:
[420] 257 022 809
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red with a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side
note:
is identical to the flag of the former Czechoslovakia
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Kde domov muj?" (Where is My Home?)
lyrics/music:
Josef Kajetan TYL/Frantisek Jan SKROUP
note:
adopted 1993; the anthem is a verse from the former Czechoslovak anthem originally written as part of the opera "Fidlovacka"
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Czech Republic is a stable and prosperous market economy, which harmonized its laws and regulations with those of the EU prior to its EU accession in 2004. While the conservative, inward looking Czech financial system has remained relative healthy, the small, open, export-driven Czech economy remains very sensitive to changes in the economic performance of its main export markets, especially Germany. When Western Europe and Germany fell into recession in late 2008, demand for Czech goods plunged, leading to double digit drops in industrial production and exports. As a result, real GDP fell 4.1% in 2009, with most of the decline occurring during the first quarter. Real GDP, however, has slowly recovered with positive quarter-on-quarter growth starting in the second half of 2009 and continuing throughout 2010. The auto industry remains the largest single industry and, together with its suppliers, accounts for as much as 20% of Czech manufacturing. The Czech Republic produced more than a million cars for the first time in 2010, over 80% of which were exported. Foreign and domestic businesses alike voice concerns about corruption, especially in public procurement. Other long term challenges include dealing with a rapidly aging population, funding an unsustainable pension and health care system, and diversifying away from manufacturing and toward a more high-tech, services-based, knowledge economy.
|
|
|
|
|
$261.3 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
$255.4 billion (2009 est.)
$266.4 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$192.2 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
-4.1% (2009 est.)
2.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$25,600 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$25,000 (2009 est.)
$26,100 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2.2%
industry:
38.3%
services:
59.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.37 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.1%
industry:
38.6%
services:
58.3% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
7.1% (November 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
8% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.5%
highest 10%:
NA (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
26 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 130
25.4 (1996)
|
|
|
|
|
22.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $77.9 billion
expenditures:
$87.87 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
40% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
32.5% of GDP (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
1% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.25% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 133
1% (31 December 2009)
note:
the two-week repo rate was 0.75% on 31 December 2010; this is the main rate CNB uses
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
4.5% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$96.82 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$92.95 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$138.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$139 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$119.5 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$118.8 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$73.1 billion (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 45
$70.26 billion (31 December 2009)
$57.8 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, potatoes, sugar beets, hops, fruit; pigs, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
motor vehicles, metallurgy, machinery and equipment, glass, armaments
|
|
|
|
|
15.9% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
82.25 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
53.42 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
22.23 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.58 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10,970 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
207,600 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
29,670 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
219,900 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
15 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
178 million cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
8.164 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
1.111 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
9.683 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
3.072 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
|
$-5.956 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
$-2.146 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$116.5 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$112.6 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, raw materials and fuel, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 31.7%, Slovakia 8.7%, Poland 6.2%, France 5.5%, UK 4.9%, Austria 4.7%, Italy 4.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$109.2 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$103.1 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, raw materials and fuels, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 25.6%, China 11.9%, Poland 6.5%, Russia 5.4%, Slovakia 5.2% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$42.34 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$41.61 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$86.79 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
$86.55 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$130.4 billion (30 September 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$121.9 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$14.67 billion (30 September 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$14.35 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
koruny (CZK) per US dollar -
19.111 (2010)
19.063 (2009)
17.064 (2008)
20.53 (2007)
22.596 (2006)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Czech Republic |
|
|
2.092 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
14.258 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: privatization and modernization of the Czech telecommunication system got a late start but is advancing steadily; virtually all exchanges now digital; existing copper subscriber systems enhanced with Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) equipment to accommodate Internet and other digital signals; trunk systems include fiber-optic cable and microwave radio relay
domestic:
access to the fixed-line telephone network expanded throughout the 1990s but the number of fixed line connections has been dropping since then; mobile telephone usage increased sharply beginning in the mid-1990s and the number of cellular telephone subscriptions now greatly exceeds the population
international:
country code - 420; satellite earth stations - 6 (2 Intersputnik - Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions, 1 Intelsat, 1 Eutelsat, 1 Inmarsat, 1 Globalstar) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
roughly 130 television broadcasters operating some 350 television channels with 4 publicly operated and the remainder in private hands; 13 television stations have national coverage with 4 being publicly operated; cable and satellite TV subscription services are available; about 70 radio broadcasters are registered operating roughly 85 radio stations with 15 stations publicly operated; 16 radio stations provide national coverage with the remainder local or regional (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.cz
|
|
|
|
|
3.494 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
6.681 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Czech Republic |
|
|
122 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
total: 44
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
9
1,524 to 2,437 m:
12
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
18 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 78
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
27
under 914 m:
50 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 7,010 km; oil 547 km; refined products 94 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9,632 km
country comparison to the world: 22
standard gauge:
9,530 km 1.435-m gauge (3,165 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
102 km 0.750-m gauge (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 127,719 km
country comparison to the world: 36
paved:
127,719 km (includes 729 km of expressways) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
664 km (principally on Elbe, Vltava, Oder, and other navigable rivers, lakes, and canals) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
registered in other countries: 1 (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
Decin, Prague, Usti nad Labem
|
|
|
|
| Military ::Czech Republic |
|
|
Army of the Czech Republic (ACR): Joint Forces Command (includes Land Forces and Air Forces), Support and Training Forces Command (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18-28 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; no conscription (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,506,826
females age 16-49:
2,407,634 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,072,267
females age 16-49:
1,988,839 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 49,999
female:
47,501 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.46% of GDP (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Czech Republic |
|
|
while threats of international legal action never materialized in 2007, 915,220 Austrians, with the support of the popular Freedom Party, signed a petition in January 2008, demanding that Austria block the Czech Republic's accession to the EU unless Prague closes its controversial Soviet-style nuclear plant in Temelin, bordering Austria
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and minor transit point for Latin American cocaine to Western Europe; producer of synthetic drugs for local and regional markets; susceptible to money laundering related to drug trafficking, organized crime; significant consumer of ecstasy (2008)
|
|
|
|
|