|
|
The UN awarded Eritrea to Ethiopia in 1952 as part of a federation. Ethiopia's annexation of Eritrea as a province 10 years later sparked a 30-year struggle for independence that ended in 1991 with Eritrean rebels defeating governmental forces; independence was overwhelmingly approved in a 1993 referendum. A two-and-a-half-year border war with Ethiopia that erupted in 1998 ended under UN auspices in December 2000. Eritrea hosted a UN peacekeeping operation that monitored a 25 km-wide Temporary Security Zone (TSZ) on the border with Ethiopia. Eritrea's denial of fuel to the mission caused the UN to withdraw the mission and terminate its mandate 31 July 2008. An international commission, organized to resolve the border dispute, posted its findings in 2002. However, both parties have been unable to reach agreement on implementing the decision. On 30 November 2007, the Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission remotely demarcated the border by coordinates and dissolved itself, leaving Ethiopia still occupying several tracts of disputed territory, including the town of Badme. Eritrea accepted the EEBC's "virtual demarcation" decision and called on Ethiopia to remove its troops from the TSZ that it states is Eritrean territory. Ethiopia has not accepted the virtual demarcation decision. In 2009 the UN imposed sanctions on Eritrea after accusing it of backing anti-Ethiopian Islamist insurgents in Somalia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
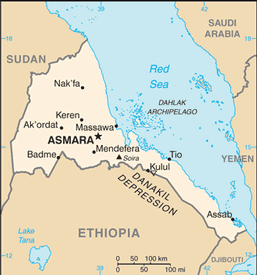
Eastern Africa, bordering the Red Sea, between Djibouti and Sudan
|
|
|
|
|
15 00 N, 39 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 117,600 sq km
country comparison to the world: 100
land:
101,000 sq km
water:
16,600 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Pennsylvania
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,626 km
border countries:
Djibouti 109 km, Ethiopia 912 km, Sudan 605 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,234 km (mainland on Red Sea 1,151 km, islands in Red Sea 1,083 km)
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dry desert strip along Red Sea coast; cooler and wetter in the central highlands (up to 61 cm of rainfall annually, heaviest June to September); semiarid in western hills and lowlands
|
|
|
|
|
dominated by extension of Ethiopian north-south trending highlands, descending on the east to a coastal desert plain, on the northwest to hilly terrain and on the southwest to flat-to-rolling plains
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: near Kulul within the Danakil Depression -75 m
highest point:
Soira 3,018 m
|
|
|
|
|
gold, potash, zinc, copper, salt, possibly oil and natural gas, fish
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 4.78%
permanent crops:
0.03%
other:
95.19% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
210 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
6.3 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.3 cu km/yr (3%/0%/97%)
per capita:
68 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
frequent droughts; locust swarms
volcanism:
Dubbi (elev. 1,625 m), which last erupted in 1861, is the country's only historically active volcano
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; desertification; soil erosion; overgrazing; loss of infrastructure from civil warfare
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic geopolitical position along world's busiest shipping lanes; Eritrea retained the entire coastline of Ethiopia along the Red Sea upon de jure independence from Ethiopia on 24 May 1993
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,939,484 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 42.1% (male 1,256,384/female 1,244,569)
15-64 years:
54.3% (male 1,580,535/female 1,641,911)
65 years and over:
3.6% (male 96,627/female 119,458) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18.7 years
male:
18.3 years
female:
19.1 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.472% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
32.8 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
8.08 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 22% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
5.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
ASMARA (capital) 649,000 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.82 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.33 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 63
male:
46.77 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
35.72 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 62.52 years
country comparison to the world: 179
male:
60.4 years
female:
64.69 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.48 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
0.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
25,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
1,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 74% of population
rural: 57% of population
total: 61% of population
unimproved:
urban: 26% of population
rural: 43% of population
total: 39% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 52% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 14% of population
unimproved:
urban: 48% of population
rural: 96% of population
total: 86% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Eritrean(s)
adjective:
Eritrean
|
|
|
|
|
nine recognized ethnic groups: Tigrinya 55%, Tigre 30%, Saho 4%, Kunama 2%, Rashaida 2%, Bilen 2%, other (Afar, Beni Amir, Nera) 5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim, Coptic Christian, Roman Catholic, Protestant
|
|
|
|
|
Tigrinya (official), Arabic (official), English (official), Tigre, Kunama, Afar, other Cushitic languages
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
58.6%
male:
69.9%
female:
47.6% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5 years
male:
6 years
female:
4 years (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: State of Eritrea
conventional short form:
Eritrea
local long form:
Hagere Ertra
local short form:
Ertra
former:
Eritrea Autonomous Region in Ethiopia
|
|
|
|
|
transitional government
note:
following a successful referendum on independence for the Autonomous Region of Eritrea on 23-25 April 1993, a National Assembly, composed entirely of the People's Front for Democracy and Justice or PFDJ, was established as a transitional legislature; a Constitutional Commission was also established to draft a constitution; ISAIAS Afworki was elected president by the transitional legislature; the constitution, ratified in May 1997, did not enter into effect, pending parliamentary and presidential elections; parliamentary elections were scheduled in December 2001 but were postponed indefinitely; currently the sole legal party is the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ)
|
|
|
|
|
name: Asmara (Asmera)
geographic coordinates:
15 20 N, 38 56 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
6 regions (zobatat, singular - zoba); Anseba, Debub (South), Debubawi K'eyih Bahri (Southern Red Sea), Gash Barka, Ma'akel (Central), Semenawi Keyih Bahri (Northern Red Sea)
|
|
|
|
|
24 May 1993 (from Ethiopia)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 24 May (1993)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 23 May 1997, but has not yet been fully implemented
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system of civil, customary, and Islamic religious law
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President ISAIAS Afworki (since 8 June 1993); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government and is head of the State Council and National Assembly
head of government:
President ISAIAS Afworki (since 8 June 1993)
cabinet:
State Council the collective is executive authority; members appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); the most recent and only election was held on 8 June 1993 (next election date uncertain as the National Assembly did not hold a presidential election in December 2001 as anticipated)
election results:
ISAIAS Afworki elected president; percent of National Assembly vote - ISAIAS Afworki 95%, other 5%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly (150 seats; members elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
in May 1997, following the adoption of the new constitution, 75 members of the PFDJ Central Committee (the old Central Committee of the EPLF), 60 members of the 527-member Constituent Assembly, which had been established in 1997 to discuss and ratify the new constitution, and 15 representatives of Eritreans living abroad were formed into a Transitional National Assembly to serve as the country's legislative body until countrywide elections to a National Assembly were held; although only 75 of 150 members of the Transitional National Assembly were elected, the constitution stipulates that once past the transition stage, all members of the National Assembly will be elected by secret ballot of all eligible voters; National Assembly elections scheduled for December 2001 were postponed indefinitely
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court; Regional, subregional, and village courts
|
|
|
|
|
People's Front for Democracy and Justice or PFDJ [ISAIAS Afworki] (the only party recognized by the government); note - a National Assembly committee drafted a law on political parties in January 2001, but the full National Assembly has yet to debate or vote on it
|
|
|
|
|
Eritrean Democratic Party (EDP) [HAGOS, Mesfin]; Eritrean Islamic Jihad or EIJ (includes Eritrean Islamic Jihad Movement or EIJM also known as the Abu Sihel Movement); Eritrean Islamic Salvation or EIS (also known as the Arafa Movement); Eritrean Liberation Front or ELF [ABDULLAH Muhammed]; Eritrean National Alliance or ENA (a coalition including EIJ, EIS, ELF, and a number of ELF factions) [HERUY Tedla Biru]; Eritrean Public Forum or EPF [ARADOM Iyob]
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS (observer), ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO (subscriber), ITU, ITUC, LAS (observer), MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Berhane Gebrehiwet SOLOMON
chancery:
1708 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 319-1991
FAX:
[1] (202) 319-1304
consulate(s) general:
Oakland (California)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Joel REIFMAN
embassy:
179 Ala Street, Asmara
mailing address:
P. O. Box 211, Asmara
telephone:
[291] (1) 120004
FAX:
[291] (1) 127584
|
|
|
|
|
red isosceles triangle (based on the hoist side) dividing the flag into two right triangles; the upper triangle is green, the lower one is blue; a gold wreath encircling a gold olive branch is centered on the hoist side of the red triangle; green stands for the country's agriculture economy, red signifies the blood shed in the fight for freedom, and blue symbolizes the bounty of the sea; the wreath-olive branch symbol is similar to that on the first flag of Eritrea from 1952; the shape of the red triangle broadly mimics the shape of the country
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Ertra, Ertra, Ertra" (Eritrea, Eritrea, Eritrea)
lyrics/music:
SOLOMON Tsehaye Beraki/Isaac Abraham MEHAREZGI and ARON Tekle Tesfatsion
note:
adopted 1993; upon independence from Ethiopia in 1993, Eritrea adopted its own national anthem
|
|
|
|
|
|
Since independence from Ethiopia in 1993, Eritrea has faced the economic problems of a small, desperately poor country, accentuated by the recent implementation of restrictive economic policies. Eritrea has a command economy under the control of the sole political party, the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ). Like the economies of many African nations, a large share of the population - nearly 80% - is engaged in subsistence agriculture, but they produce only a small share of total output. Since the conclusion of the Ethiopian-Eritrea war in 2000, the government has maintained a firm grip on the economy, expanding the use of the military and party-owned businesses to complete Eritrea's development agenda. The government strictly controls the use of foreign currency by limiting access and availability. Few private enterprises remain in Eritrea. Eritrea's economy depends heavily on taxes paid by members of the diaspora. Erratic rainfall and the delayed demobilization of agriculturalists from the military continue to interfere with agricultural production, and Eritrea's recent harvests have been unable to meet the food needs of the country. The Government continues to place its hope for additional revenue on the development of several international mining projects. Despite difficulties for international companies in working with the Eritrean Government, a Canadian mining company signed a contract with the government in 2007 and began mineral extraction in 2010. Eritrea's economic future depends upon its ability to master social problems such as illiteracy, unemployment, and low skills, and more importantly, on the government's willingness to support a true market economy.
|
|
|
|
|
$3.625 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
$3.548 billion (2009 est.)
$3.415 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$2.117 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
3.9% (2009 est.)
-9.8% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$600 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 223
$600 (2009 est.)
$600 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 11.8%
industry:
20.4%
services:
67.7% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.935 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 80%
industry and services:
20% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
50% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
10.3% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $463.4 million
expenditures:
$920.1 million (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
20% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
20% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$1.382 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
$1.007 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.872 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
$2.171 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.919 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
$2.206 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
sorghum, lentils, vegetables, corn, cotton, tobacco, sisal; livestock, goats; fish
|
|
|
|
|
food processing, beverages, clothing and textiles, light manufacturing, salt, cement
|
|
|
|
|
8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
271 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
228 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
4,790 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
$-212 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
$-188 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$25 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
$20 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
livestock, sorghum, textiles, food, small manufactures
|
|
|
|
|
India 25.3%, Italy 20.7%, Sudan 14.1%, China 12.9%, France 5.5%, Saudi Arabia 5.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$738 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
$682 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, petroleum products, food, manufactured goods
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia 20.7%, India 13.6%, Italy 12.6%, China 9.9%, US 5.1%, Germany 4.6% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$104 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
$88 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2010 est.)
$961.9 million (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
nakfa (ERN) per US dollar -
15.375 (2010)
15.375 (2009)
15.38 (2008)
15.5 (2007)
15.4 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
48,500 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
141,100 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: inadequate; most telephones are in Asmara; government is seeking international tenders to improve the system (2002)
domestic:
combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular subscribership is only about 3 per 100 persons (2009)
international:
country code - 291; note - international connections exist
|
|
|
|
|
government controls broadcast media with private ownership prohibited; 1 state-owned TV station; state-owned radio operates 2 networks; purchases of satellite dishes and subscriptions to international broadcast media are permitted (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.er
|
|
|
|
|
1,241 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
200,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
914 to 1,523 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 306 km
country comparison to the world: 119
narrow gauge:
306 km 0.950-m gauge (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,010 km
country comparison to the world: 157
paved:
874 km
unpaved:
3,136 km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
country comparison to the world: 132
by type:
cargo 2, petroleum tanker 1, roll on/roll off 1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Assab, Massawa
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eritrean Armed Forces: Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18-40 years of age for male and female voluntary and compulsory military service; 16-month conscript service obligation (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,350,446
females age 16-49:
1,362,575 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 896,096
females age 16-49:
953,757 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 66,829
female:
66,731 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.3% of GDP (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Eritrea |
|
|
Eritrea and Ethiopia agreed to abide by 2002 Ethiopia-Eritrea Boundary Commission's (EEBC) delimitation decision but, neither party responded to the revised line detailed in the November 2006 EEBC Demarcation Statement; Sudan accuses Eritrea of supporting eastern Sudanese rebel groups; in 2008 Eritrean troops move across the border on Ras Doumera peninsula and occupy Doumera Island with undefined sovereignty in the Red Sea
|
|
|
|
|
IDPs: 32,000 (border war with Ethiopia from 1998-2000; most IDPs are near the central border region) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Eritrea is a source country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation; each year, large numbers of migrant workers depart Eritrea in search of work, particularly in the Gulf States, where some likely become victims of forced labor, including in domestic servitude, or commercial sexual exploitation; thousands of Eritreans flee the country illegally, mostly to Sudan, Ethiopia, and Kenya where their illegal status makes them vulnerable to situations of human trafficking; the government remains complicit in conscripting children into military service
tier rating:
Tier 3 - the Government of Eritrea does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the Eritrean government does not operate with transparency and published neither data nor statistics regarding its efforts to combat human trafficking; it did not respond to requests to provide information for this report; the government made no known progress in prosecuting and punishing trafficking crimes over the reporting period and did not appear to provide any significant assistance to victims of trafficking during the reporting period (2009)
|
|
|
|
|