|
|
The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C., and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty with the overthrow of the British-backed monarchy in 1952. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to meet the demands of Egypt's growing population through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Libya and the Gaza Strip, and the Red Sea north of Sudan, and includes the Asian Sinai Peninsula
|
|
|
|
|
27 00 N, 30 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,001,450 sq km
country comparison to the world: 30
land:
995,450 sq km
water:
6,000 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than three times the size of New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,665 km
border countries:
Gaza Strip 11 km, Israel 266 km, Libya 1,115 km, Sudan 1,273 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,450 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|
|
desert; hot, dry summers with moderate winters
|
|
|
|
|
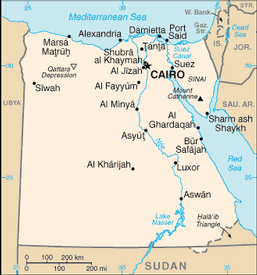
vast desert plateau interrupted by Nile valley and delta
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Qattara Depression -133 m
highest point:
Mount Catherine 2,629 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, manganese, limestone, gypsum, talc, asbestos, lead, rare earth elements, zinc
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 2.92%
permanent crops:
0.5%
other:
96.58% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
35,300 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
86.8 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 68.3 cu km/yr (8%/6%/86%)
per capita:
923 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
periodic droughts; frequent earthquakes; flash floods; landslides; hot, driving windstorm called khamsin occurs in spring; dust storms; sandstorms
|
|
|
|
|
agricultural land being lost to urbanization and windblown sands; increasing soil salination below Aswan High Dam; desertification; oil pollution threatening coral reefs, beaches, and marine habitats; other water pollution from agricultural pesticides, raw sewage, and industrial effluents; limited natural freshwater resources away from the Nile, which is the only perennial water source; rapid growth in population overstraining the Nile and natural resources
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
controls Sinai Peninsula, only land bridge between Africa and remainder of Eastern Hemisphere; controls Suez Canal, a sea link between Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea; size, and juxtaposition to Israel, establish its major role in Middle Eastern geopolitics; dependence on upstream neighbors; dominance of Nile basin issues; prone to influxes of refugees from Sudan and the Palestinian territories
|
|
|
|
|
|
82,079,636 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 32.7% (male 13,725,282/female 13,112,157)
15-64 years:
62.8% (male 26,187,921/female 25,353,947)
65 years and over:
4.5% (male 1,669,313/female 2,031,016) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24.3 years
male:
24 years
female:
24.6 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.96% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
24.63 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
4.82 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
|
|
|
|
|
-0.21 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 43.4% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
2.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
CAIRO (capital) 10.902 million; Alexandria 4.387 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.83 male(s)/female
total population:
1.03 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25.2 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 81
male:
26.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
23.52 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 72.66 years
country comparison to the world: 123
male:
70.07 years
female:
75.38 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.97 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
11,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
Rift Valley fever
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 98% of population
total: 99% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 1% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 97% of population
rural: 92% of population
total: 94% of population
unimproved:
urban: 3% of population
rural: 8% of population
total: 6% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Egyptian(s)
adjective:
Egyptian
|
|
|
|
|
Egyptian 99.6%, other 0.4% (2006 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (mostly Sunni) 90%, Coptic 9%, other Christian 1%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic (official), English and French widely understood by educated classes
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
71.4%
male:
83%
female:
59.4% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11 years
male:
11 years
female:
11 years (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
3.8% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Arab Republic of Egypt
conventional short form:
Egypt
local long form:
Jumhuriyat Misr al-Arabiyah
local short form:
Misr
former:
United Arab Republic (with Syria)
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Cairo
geographic coordinates:
30 03 N, 31 15 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
29 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazat); Ad Daqahliyah, Al Bahr al Ahmar (Red Sea), Al Buhayrah (El Beheira), Al Fayyum (El Faiyum), Al Gharbiyah, Al Iskandariyah (Alexandria), Al Isma'iliyah (Ismailia), Al Jizah (Giza), Al Minufiyah (El Monofia), Al Minya, Al Qahirah (Cairo), Al Qalyubiyah, Al Uqsur (Luxor), Al Wadi al Jadid (New Valley), As Suways (Suez), Ash Sharqiyah, Aswan, Asyut, Bani Suwayf (Beni Suef), Bur Sa'id (Port Said), Dumyat (Damietta), Helwan, Janub Sina' (South Sinai), Kafr ash Shaykh, Matruh (Western Desert), Qina (Qena), Shamal Sina' (North Sinai), Sittah Uktubar, Suhaj (Sohag)
|
|
|
|
|
28 February 1922 (from UK protectorate status; the revolution that began on 23 July 1952 led to a republic being declared on 18 June 1953 and all British troops withdrawn on 18 June 1956); note - it was ca. 3200 B.C. that the Two Lands of Upper (southern) and Lower (northern) Egypt were first united politically
|
|
|
|
|
Revolution Day, 23 July (1952)
|
|
|
|
|
11 September 1971; amended 22 May 1980, 25 May 2005, and 26 March 2007; note - constitution dissolved by the military caretaker government 13 February 2011
|
|
|
|
|
mixed legal system based on Napoleonic civil law and Islamic religious law; judicial review by Supreme Court and Council of State (oversees validity of administrative decisions)
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President (vacant); Vice President (vacant); note - following the resignation of President Mohamed Hosni MUBARAK in February 2011, the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces, headed by Defense Minister Muhammad Hussein TANTAWI, assumed control of the government
head of government:
Prime Minister Essam Abdel Aziz SHARAF (since 4 March 2011); Deputy Prime Minister Yehia El-GAMAL (since 24 February 2011)
cabinet:
a new cabinet was sworn in on 7 March 2011
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a six-year term (no term limits)
election results:
Hosni MUBARAK reelected president; percent of vote - Hosni MUBARAK 88.6%, Ayman NOUR 7.6%, Noman GOMAA 2.9%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral system consists of the Advisory Council or Majlis al-Shura (Shura Council) that traditionally functions mostly in a consultative role (264 seats; 176 members elected by popular vote, 88 appointed by the president; members serve six-year terms; mid-term elections for half of the elected members) and the People's Assembly or Majlis al-Sha'b (518 seats; 508 members elected by popular vote, 64 seats reserved for women, 10 appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms)
elections:
Advisory Council - last held in June 2010 (next to be held in 2013); People's Assembly - last held in November-December 2010 in one round of voting and one run-off election (next to be held in 2015); note - on 13 February 2011 the ruling military council dissolved the parliament
election results:
Advisory Council - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NDP 80, Al-Geel 1, Nasserist 1, NWP 1, Tagammu 1, Tomorrow Party 1, independents 3; People's Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NDP 419, NWP 6, Tagammu 5, Democratic Peace Party 1, Social Justice Party 1, Tomorrow Party 1, independents 71, seats undecided 4, seats appointed by president 10
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Constitutional Court
|
|
|
|
|
Al-Geel; Democratic Peace Party; Nasserist Party [Ahmed HASSAN]; National Democratic Party or NDP (governing party) [Mohamed Hosni MUBARAK]; National Progressive Unionist Grouping or Tagammu [Rifaat EL-SAID]; New Wafd Party or NWP [Sayed EL-BEDAWY]; Social Justice Party [Mohamed Abdel Al HASAN]; Tomorrow Party [Ayman NOUR]
note:
formation of political parties must be approved by the government; only parties with representation in elected bodies are listed
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim Brotherhood (technically illegal)
note:
despite a constitutional ban against religious-based parties and political activity, the technically illegal Muslim Brotherhood constitutes Egypt's most potentially significant political opposition; President MUBARAK has alternated between tolerating limited political activity by the Brotherhood and blocking its influence (its members compete as independents in elections but do not currently hold any seats in the legislature); civic society groups are sanctioned, but constrained in practical terms; only trade unions and professional associations affiliated with the government are officially sanctioned; Internet social networking groups and bloggers
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, BSEC (observer), CAEU, CICA, COMESA, D-8, EBRD, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, OIF, OSCE (partner), PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Sameh Hassan SHOUKRY
chancery:
3521 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 895-5400
FAX:
[1] (202) 244-4319
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Houston, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Margaret SCOBEY
embassy:
8 Kamal El Din Salah St., Garden City, Cairo
mailing address:
Unit 64900, Box 15, APO AE 09839-4900; 5 Tawfik Diab Street, Garden City, Cairo
telephone:
[20] (2) 2797-3300
FAX:
[20] (2) 2797-3200
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black; the national emblem (a gold Eagle of Saladin facing the hoist side with a shield superimposed on its chest above a scroll bearing the name of the country in Arabic) centered in the white band; the band colors derive from the Arab Liberation flag and represent oppression (black), overcome through bloody struggle (red), to be replaced by a bright future (white)
note:
similar to the flag of Syria, which has two green stars in the white band, Iraq, which has an Arabic inscription centered in the white band, and Yemen, which has a plain white band
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Bilady, Bilady, Bilady" (My Homeland, My Homeland, My Homeland)
lyrics/music:
Younis-al QADI/Sayed DARWISH
note:
adopted 1979; after the signing of the 1979 peace with Israel, Egypt sought to create an anthem less militaristic than its previous one; Sayed DARWISH, commonly considered the father of modern Egyptian music, composed the anthem
|
|
|
|
|
|
Occupying the northeast corner of the African continent, Egypt is bisected by the highly fertile Nile valley, where most economic activity takes place. Egypt's economy was highly centralized during the rule of former President Gamal Abdel NASSER but opened up considerably under former Presidents Anwar EL-SADAT and Mohamed Hosni MUBARAK. Cairo from 2004 to 2008 aggressively pursued economic reforms to attract foreign investment and facilitate GDP growth. The global financial crisis slowed the reform efforts. The budget deficit climbed to over 8% of GDP and Egypt's GDP growth slowed to 4.6% in 2009, predominately due to reduced growth in export-oriented sectors, including manufacturing and tourism, and Suez Canal revenues. In 2010, the government spent more on infrastructure and public projects, and exports drove GDP growth to more than 5%, but GDP growth in 2011 is unlikely to bounce back to pre-global financial recession levels, when it stood at 7%. Despite the relatively high levels of economic growth over the past few years, living conditions for the average Egyptian remain poor.
|
|
|
|
|
$497.8 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$473.4 billion (2009 est.)
$452.3 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$218.5 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.1% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
4.7% (2009 est.)
7.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6,200 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
$6,000 (2009 est.)
$5,900 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 13.5%
industry:
37.9%
services:
48.6% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
26.1 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 32%
industry:
17%
services:
51% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
9.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
9.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
20% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.9%
highest 10%:
27.6% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
34.4 (2001)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
18.4% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $46.82 billion
expenditures:
$64.19 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
80.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
80.9% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
11.9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.5% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 34
11.5% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
11.98% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
12.33% (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$37.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$33.42 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$166.2 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$146.7 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$145.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$131.5 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$89.95 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 43
$85.89 billion (31 December 2008)
$139.3 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
cotton, rice, corn, wheat, beans, fruits, vegetables; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats
|
|
|
|
|
textiles, food processing, tourism, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, hydrocarbons, construction, cement, metals, light manufactures
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
118.4 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
104.1 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
814 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
251 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
680,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
683,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
89,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
48,450 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 billion bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
62.7 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
42.5 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
8.55 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
|
|
|
|
|
1.656 trillion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
$270 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$-3.195 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$25.34 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$23.09 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil and petroleum products, cotton, textiles, metal products, chemicals, processed food
|
|
|
|
|
US 7.95%, Italy 7.26%, Spain 6.78%, India 6.69%, Saudi Arabia 5.53%, Syria 5.3%, France 4.39%, South Korea 4.27% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$46.52 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$45.56 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, chemicals, wood products, fuels
|
|
|
|
|
US 9.92%, China 9.63%, Germany 6.98%, Italy 6.88%, Turkey 4.94% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$35.72 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$33.93 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$30.61 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$29.66 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$72.41 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
$66.71 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
$4.272 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Egyptian pounds (EGP) per US dollar -
5.6124 (2010)
5.545 (2009)
5.4 (2008)
5.67 (2007)
5.725 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.313 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
55.352 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: underwent extensive upgrading during 1990s; principal centers at Alexandria, Cairo, Al Mansurah, Ismailia, Suez, and Tanta are connected by coaxial cable and microwave radio relay
domestic:
largest fixed-line system in the region; as of 2010 there were three mobile-cellular networks with a total of more than 55 million subscribers
international:
country code - 20; landing point for Aletar, the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cable networks, Link Around the Globe (FLAG) Falcon and FLAG FEA; satellite earth stations - 4 (2 Intelsat - Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean, 1 Arabsat, and 1 Inmarsat); tropospheric scatter to Sudan; microwave radio relay to Israel; a participant in Medarabtel (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
mix of state-run and private broadcast media; state-run TV operates 2 national and 6 regional terrestrial networks as well as a few satellite channels; about 20 private satellite channels and a large number of Arabic satellite channels are available via subscription; state-run radio operates about 70 stations belonging to 8 networks; 2 privately-owned radio stations operational (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.eg
|
|
|
|
|
187,197 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
20.136 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
|
86 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
total: 73
over 3,047 m:
15
2,438 to 3,047 m:
36
1,524 to 2,437 m:
15
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
5 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
5
under 914 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
6 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 320 km; condensate/gas 13 km; gas 6,628 km; liquid petroleum gas 956 km; oil 4,332 km; oil/gas/water 3 km; refined products 895 km; water 13 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,083 km
country comparison to the world: 34
standard gauge:
5,083 km 1.435-m gauge (62 km electrified) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 65,050 km
country comparison to the world: 70
paved:
47,500 km
unpaved:
17,550 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
3,500 km (includes the Nile River, Lake Nasser, Alexandria-Cairo Waterway, and numerous smaller canals in Nile Delta; the Suez Canal (193.5 km including approaches) is navigable by oceangoing vessels drawing up to 17.68 m) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
total: 66
country comparison to the world: 63
by type:
bulk carrier 11, cargo 24, container 3, passenger/cargo 7, petroleum tanker 12, roll on/roll off 9
foreign-owned:
13 (Denmark 1, France 1, Greece 8, Jordan 2, Lebanon 1)
registered in other countries:
52 (Cambodia 12, Cook Islands 1, Georgia 11, Honduras 2, Malta 1, Marshall Islands 1, Moldova 5, Panama 11, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 4, Saudi Arabia 1, Sierra Leone 2, unknown 1) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Ayn Sukhnah, Alexandria, Damietta, El Dekheila, Port Said, Sidi Kurayr, Suez
|
|
|
|
|
|
Army, Navy, Air Force, Air Defense Command
|
|
|
|
|
18-30 years of age for male conscript military service; service obligation 12-36 months, followed by a 9-year reserve obligation (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 21,012,199
females age 16-49:
20,145,021 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 18,060,543
females age 16-49:
17,244,838 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 783,405
female:
748,647 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Egypt |
|
|
Sudan claims but Egypt de facto administers security and economic development of Halaib region north of the 22nd parallel boundary; Egypt no longer shows its administration of the Bir Tawil trapezoid in Sudan on its maps; Gazan breaches in the security wall with Egypt in January 2008 highlight difficulties in monitoring the Sinai border; Saudi Arabia claims Egyptian-administered islands of Tiran and Sanafir
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 60,000 - 80,000 (Iraq); 70,198 (Palestinian Territories); 12,157 (Sudan) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
transit point for cannabis, heroin, and opium moving to Europe, Israel, and North Africa; transit stop for Nigerian drug couriers; concern as money laundering site due to lax enforcement of financial regulations
|
|
|
|
|