| Introduction ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
Popes in their secular role ruled portions of the Italian peninsula for more than a thousand years until the mid 19th century, when many of the Papal States were seized by the newly united Kingdom of Italy. In 1870, the pope's holdings were further circumscribed when Rome itself was annexed. Disputes between a series of "prisoner" popes and Italy were resolved in 1929 by three Lateran Treaties, which established the independent state of Vatican City and granted Roman Catholicism special status in Italy. In 1984, a concordat between the Holy See and Italy modified certain of the earlier treaty provisions, including the primacy of Roman Catholicism as the Italian state religion. Present concerns of the Holy See include religious freedom, international development, the environment, the Middle East, China, the decline of religion in Europe, terrorism, interreligious dialogue and reconciliation, and the application of church doctrine in an era of rapid change and globalization. About one billion people worldwide profess the Catholic faith.
|
|
|
|
| Geography ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
Southern Europe, an enclave of Rome (Italy)
|
|
|
|
|
41 54 N, 12 27 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.44 sq km
country comparison to the world: 249
land:
0.44 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
about 0.7 times the size of The National Mall in Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.2 km
border countries:
Italy 3.2 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
temperate; mild, rainy winters (September to May) with hot, dry summers (May to September)
|
|
|
|
|
urban; low hill
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: unnamed location 19 m
highest point:
unnamed location 75 m
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0%
permanent crops:
0%
other:
100% (urban area) (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution, Environmental Modification
|
|
|
|
|
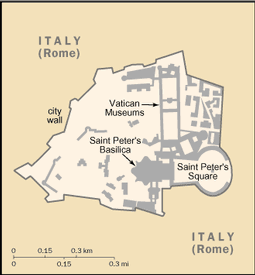
landlocked; enclave in Rome, Italy; world's smallest state; beyond the territorial boundary of Vatican City, the Lateran Treaty of 1929 grants the Holy See extraterritorial authority over 23 sites in Rome and five outside of Rome, including the Pontifical Palace at Castel Gandolfo (the Pope's summer residence)
|
|
|
|
| People ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
829 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 235
|
|
|
|
|
0.004% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 100% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.1% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: none
adjective:
none
|
|
|
|
|
Italians, Swiss, other
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic
|
|
|
|
|
Italian, Latin, French, various other languages
|
|
|
|
|
definition: NA
total population:
100%
male:
100%
female:
100%
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
conventional long form: The Holy See (State of the Vatican City)
conventional short form:
Holy See (Vatican City)
local long form:
Santa Sede (Stato della Citta del Vaticano)
local short form:
Santa Sede (Citta del Vaticano)
|
|
|
|
|
ecclesiastical
|
|
|
|
|
name: Vatican City
geographic coordinates:
41 54 N, 12 27 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
11 February 1929 (from Italy); note - the three treaties signed with Italy on 11 February 1929 acknowledged, among other things, the full sovereignty of the Vatican and established its territorial extent; however, the origin of the Papal States, which over the years have varied considerably in extent, may be traced back to the 8th century
|
|
|
|
|
Election Day of Pope BENEDICT XVI, 19 April (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
Fundamental Law promulgated by Pope JOHN PAUL II on 26 November 2000, effective 22 February 2001 (replaced the first Fundamental Law of 1929)
|
|
|
|
|
based on Code of Canon Law and revisions to it
|
|
|
|
|
limited to cardinals less than 80 years old
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Pope BENEDICT XVI (since 19 April 2005)
head of government:
Secretary of State Cardinal Tarcisio BERTONE (since 15 September 2006)
cabinet:
Pontifical Commission for the State of Vatican City appointed by the pope
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
pope elected for life by the College of Cardinals; election last held on 19 April 2005 (next to be held after the death of the current pope); secretary of state appointed by the pope
election results:
Joseph RATZINGER elected Pope BENEDICT XVI
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State
|
|
|
|
|
there are three tribunals responsible for civil and criminal matters within Vatican City; three other tribunals rule on issues pertaining to the Holy See
note:
judicial duties were established by the Motu Proprio, papal directive, of Pope PIUS XII on 1 May 1946
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
none (exclusive of influence exercised by church officers)
|
|
|
|
|
CE (observer), IAEA, Interpol, IOM (observer), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, OAS (observer), OPCW, OSCE, Schengen Convention (de facto member), UN (observer), UNCTAD, UNHCR, Union Latina (observer), UNWTO (observer), UPU, WFTU, WIPO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Apostolic Nuncio Archbishop Pietro SAMBI
chancery:
3339 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 333-7121
FAX:
[1] (202) 337-4036
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Miguel Humberto DIAZ
embassy:
Villa Domiziana, Via delle Terme Deciane 26, 00153 Rome
mailing address:
PSC 833, Box 66, APO AE 09624
telephone:
[39] (06) 4674-3428
FAX:
[39] (06) 575-3411
|
|
|
|
|
two vertical bands of yellow (hoist side) and white with the arms of the Holy See, consisting of the crossed keys of Saint Peter surmounted by the three-tiered papal tiara, centered in the white band; the yellow color represents the pope's spiritual power, the white his worldly power
|
|
|
|
| Economy ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
The Holy See is supported financially by a variety of sources, including investments, real estate income, and donations from Catholic individuals, dioceses, and institutions; these help fund the Roman Curia (Vatican bureaucracy), diplomatic missions, and media outlets. The separate Vatican City State budget includes the Vatican museums and post office and is supported financially by the sale of stamps, coins, medals, and tourist mementos; by fees for admission to museums; and by publications sales. Moreover, an annual collection taken up in dioceses and direct donations go to a non-budgetary fund known as Peter's Pence, which is used directly by the Pope for charity, disaster relief, and aid to churches in developing nations. The incomes and living standards of lay workers are comparable to those of counterparts who work in the city of Rome.
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
note: essentially services with a small amount of industry; nearly all dignitaries, priests, nuns, guards, and the approximately 3,000 lay workers live outside the Vatican
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $355.5 million
expenditures:
$356.8 million (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
printing; production of coins, medals, postage stamps; mosaics and staff uniforms; worldwide banking and financial activities
|
|
|
|
|
NA kWh
|
|
|
|
|
NA kWh
|
|
|
|
|
NA kWh; note - electricity supplied by Italy; a small portion of electricity is self-produced from solar panels
|
|
|
|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar - 0.7338 (2009), 0.6827 (2008), 0.7345 (2007), 0.7964 (2006), 0.8041 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
5,120 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 212
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: automatic digital exchange
domestic:
connected via fiber optic cable to Telecom Italia network
international:
country code - 39; uses Italian system
|
|
|
|
|
AM 5, FM 3, shortwave 5 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.va
|
|
|
|
|
63 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
| Military ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|
|
Pontifical Swiss Guard Corps (Corpo della Guardia Svizzera Pontificia) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
defense is the responsibility of Italy; ceremonial and limited security duties performed by Pontifical Swiss Guard
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Holy See (Vatican City) |
|