|
|
Montevideo, founded by the Spanish in 1726 as a military stronghold, soon took advantage of its natural harbor to become an important commercial center. Claimed by Argentina but annexed by Brazil in 1821, Uruguay declared its independence four years later and secured its freedom in 1828 after a three-year struggle. The administrations of President Jose BATLLE in the early 20th century established widespread political, social, and economic reforms that established a statist tradition. A violent Marxist urban guerrilla movement named the Tupamaros, launched in the late 1960s, led Uruguay's president to cede control of the government to the military in 1973. By yearend, the rebels had been crushed, but the military continued to expand its hold over the government. Civilian rule was not restored until 1985. In 2004, the left-of-center Frente Amplio Coalition won national elections that effectively ended 170 years of political control previously held by the Colorado and Blanco parties. Uruguay's political and labor conditions are among the freest on the continent.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Argentina and Brazil
|
|
|
|
|
33 00 S, 56 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 176,215 sq km
country comparison to the world: 90
land:
175,015 sq km
water:
1,200 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than the state of Washington
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,648 km
border countries:
Argentina 580 km, Brazil 1,068 km
|
|
|
|
|
660 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or edge of continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
warm temperate; freezing temperatures almost unknown
|
|
|
|
|
mostly rolling plains and low hills; fertile coastal lowland
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Cerro Catedral 514 m
|
|
|
|
|
arable land, hydropower, minor minerals, fish
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 7.77%
permanent crops:
0.24%
other:
91.99% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2,100 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
139 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.15 cu km/yr (2%/1%/96%)
per capita:
910 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
seasonally high winds (the pampero is a chilly and occasional violent wind that blows north from the Argentine pampas), droughts, floods; because of the absence of mountains, which act as weather barriers, all locations are particularly vulnerable to rapid changes from weather fronts
|
|
|
|
|
water pollution from meat packing/tannery industry; inadequate solid/hazardous waste disposal
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
second-smallest South American country (after Suriname); most of the low-lying landscape (three-quarters of the country) is grassland, ideal for cattle and sheep raising
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,510,386 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 22.1% (male 394,454/female 381,920)
15-64 years:
64.5% (male 1,125,912/female 1,137,904)
65 years and over:
13.4% (male 188,719/female 281,477) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 33.7 years
male:
32.3 years
female:
35.1 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.447% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
13.67 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
9.06 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
-0.14 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 92% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.4% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.037 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.67 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10.99 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 149
male:
12.37 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
9.57 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 76.55 years
country comparison to the world: 68
male:
73.3 years
female:
79.92 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.89 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
|
|
|
|
|
0.6% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Uruguayan(s)
adjective:
Uruguayan
|
|
|
|
|
white 88%, mestizo 8%, black 4%, Amerindian (practically nonexistent)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 47.1%, non-Catholic Christians 11.1%, nondenominational 23.2%, Jewish 0.3%, atheist or agnostic 17.2%, other 1.1% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish, Portunol, or Brazilero (Portuguese-Spanish mix on the Brazilian frontier)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
98%
male:
97.6%
female:
98.4% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
14 years
female:
16 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
2.9% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Oriental Republic of Uruguay
conventional short form:
Uruguay
local long form:
Republica Oriental del Uruguay
local short form:
Uruguay
former:
Banda Oriental, Cisplatine Province
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Montevideo
geographic coordinates:
34 53 S, 56 11 W
time difference:
UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins first Sunday in October; ends second Sunday in March
|
|
|
|
|
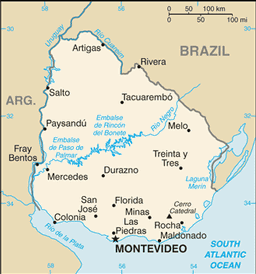
19 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Artigas, Canelones, Cerro Largo, Colonia, Durazno, Flores, Florida, Lavalleja, Maldonado, Montevideo, Paysandu, Rio Negro, Rivera, Rocha, Salto, San Jose, Soriano, Tacuarembo, Treinta y Tres
|
|
|
|
|
25 August 1825 (from Brazil)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 25 August (1825)
|
|
|
|
|
27 November 1966; effective 15 February 1967; suspended 27 June 1973; revised 26 November 1989 and 7 January 1997
|
|
|
|
|
based on Spanish civil law system; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Jose "Pepe" MUJICA Cordano (since 1 March 2010); Vice President Danilo ASTORI Saragoza (since 1 March 2010); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Jose "Pepe" MUJICA Cordano (since 1 March 2010); Vice President Danilo ASTORI Saragoza (since 1 March 2010)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president with parliamentary approval
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for five-year terms (may not serve consecutive terms); election last held on 29 November 2009 (next to be held in October 2014)
election results:
Jose "Pepe" MUJICA elected president; percent of vote - Jose "Pepe" MUJICA 54.8%, Luis Alberto LACALLE 45.2%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral General Assembly or Asamblea General consists of Chamber of Senators or Camara de Senadores (30 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms; vice president has one vote in the Senate) and Chamber of Representatives or Camara de Representantes (99 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
Chamber of Senators - last held on 25 October 2009 (next to be held in October 2014); Chamber of Representatives - last held on 25 October 2009 (next to be held in October 2014)
election results:
Chamber of Senators - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Frente Amplio 16, Blanco 9, Colorado Party 5; Chamber of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Frente Amplio 50, Blanco 30, Colorado Party 17, Independent Party 2
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (judges are nominated by the president and elected for 10-year terms by the General Assembly)
|
|
|
|
|
Broad Front (Frente Amplio) - formerly known as the Progressive Encounter/Broad Front Coalition or EP-FA [Jorge BROVETTO] (a broad governing coalition that includes Movement of the Popular Participation or MPP, New Space Party (Nuevo Espacio) [Rafael MICHELINI], Progressive Alliance (Alianza Progresista) [Rodolfo NIN NOVOA], Socialist Party [Eduardo FERNANDEZ], Communist Party [Marina ARISMENDI], Uruguayan Assembly (Asamblea Uruguay) [Danilo ASTORI], and Vertiente Artiguista [Mariano ARANA]); Colorado Party (Foro Batllista) [Julio Maria SANGUINETTI]; National Party or Blanco [Luis Alberto LACALLE and Jorge LARRANAGA]
|
|
|
|
|
Architect's Society of Uruguay (professional organization); Chamber of Uruguayan Industries (manufacturer's association); Chemist and Pharmaceutical Association (professional organization); PIT/CNT (powerful federation of Uruguayan Unions - umbrella labor organization); Rural Association of Uruguay (rancher's association); Uruguayan Construction League; Uruguayan Network of Political Women
other:
Catholic Church; students
|
|
|
|
|
CAN (associate), FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUC, NAM (observer), OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, RG, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Carlos Alberto GIANELLI Derois
chancery:
1913 I Street NW, Washington, DC 20006
telephone:
[1] (202) 331-1313 through 1316
FAX:
[1] (202) 331-8142
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, Miami, New York
consulate(s):
San Juan (Puerto Rico)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador David NELSON
embassy:
Lauro Muller 1776, Montevideo 11200
mailing address:
APO AA 34035
telephone:
[598] (2) 418-7777
FAX:
[598] (2) 418-8611
|
|
|
|
|
nine equal horizontal stripes of white (top and bottom) alternating with blue; a white square in the upper hoist-side corner with a yellow sun bearing a human face known as the Sun of May with 16 rays that alternate between triangular and wavy
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uruguay's economy is characterized by an export-oriented agricultural sector, a well-educated work force, and high levels of social spending. After averaging growth of 5% annually during 1996-98, in 1999-2002 the economy suffered a major downturn, stemming largely from the spillover effects of the economic problems of its large neighbors, Argentina and Brazil. In 2001-02, Argentine citizens made massive withdrawals of dollars deposited in Uruguayan banks after bank deposits in Argentina were frozen, which led to a plunge in the Uruguayan peso, a banking crisis, and a sharp economic contraction. Real GDP fell in four years by nearly 20%, with 2002 the worst year. The unemployment rate rose, inflation surged, and the burden of external debt doubled. Financial assistance from the IMF helped stem the damage. Uruguay restructured its external debt in 2003 without asking creditors to accept a reduction on the principal. Economic growth for Uruguay resumed, and averaged 8% annually during the period 2004-08. The 2008-09 global financial crisis put a brake on Uruguay's vigorous growth, which decelerated to 1.7% in 2009. Nevertheless, the country managed to avoid a recession and keep positive growth rates, mainly through higher public expenditure and investment.
|
|
|
|
|
$44.52 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
$43.77 billion (2008 est.)
$40.2 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$31.98 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
8.9% (2008 est.)
7.4% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$12,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$12,600 (2008 est.)
$11,600 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 9.5%
industry:
22.5%
services:
68% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.636 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 9%
industry:
15%
services:
76% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.9% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
7.6% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
27.4% of households (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.7%
highest 10%:
34.8% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
45.2 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 41
44.8 (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
15.5% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $8.841 billion
expenditures:
$9.666 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
58.7% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
59.8% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
7.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 42
10% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
12.45% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 124
7.25% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.247 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 78
$2.145 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.409 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 59
$7.919 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.096 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 79
$6.396 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 109
$159 million (31 December 2007)
$125.1 million (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, wheat, soybeans, barley; livestock, beef; fish; forestry
|
|
|
|
|
food processing, electrical machinery, transportation equipment, petroleum products, textiles, chemicals, beverages
|
|
|
|
|
-0.9% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
9.265 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
7.14 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
996 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
789 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
946 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
41,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
7,100 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
52,730 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
70 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
70 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
-$76 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
-$1.484 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.32 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
$7.084 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
meat, rice, leather products, wool, fish, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
Brazil 18.7%, China 8.5%, Argentina 7.3%, Germany 6.5%, Mexico 4.9%, Netherlands 4.5%, Russia 4.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.576 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
$8.799 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude petroleum and petroleum products, machinery, chemicals, road vehicles, paper, plastics
|
|
|
|
|
Argentina 19.6%, Brazil 17.9%, China 11%, US 9.7%, Paraguay 6.5%, Nigeria 4.5% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$7.907 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
$6.36 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$12.61 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
$10.73 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2009)
$4.19 billion (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$156 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
Uruguayan pesos (UYU) per US dollar - 23.017 (2009), 20.936 (2008), 23.947 (2007), 24.048 (2006), 24.479 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
959,300 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
3.508 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: fully digitalized
domestic:
most modern facilities concentrated in Montevideo; new nationwide microwave radio relay network; overall fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is 130 telephones per 100 persons
international:
country code - 598; the UNISOR submarine cable system provides direct connectivity to Brazil and Argentina; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 93, FM 191, shortwave 7 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
62 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
.uy
|
|
|
|
|
498,232 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
1.34 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9
over 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 48
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
20
under 914 m:
25 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 226 km; oil 155 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,641 km (1,200 km operational)
country comparison to the world: 79
standard gauge:
1,641 km 1.435-m gauge (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 77,732 km
country comparison to the world: 62
paved:
7,743 km
unpaved:
69,989 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
1,600 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17
country comparison to the world: 102
by type:
cargo 3, chemical tanker 2, passenger/cargo 9, petroleum tanker 2, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
10 (Argentina 3, Greece 1, Spain 6)
registered in other countries:
3 (Liberia 3) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Montevideo
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uruguayan Armed Forces: Uruguayan National Army (Ejercito Nacional Uruguaya, ENU), National Navy (Armada Nacional; includes naval air arm, Naval Rifle Corps (Cuerpo de Fusileros Navales, Fusna), Maritime Prefecture in wartime), Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Uruguaya, FAU) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; up to 40 years of age for specialists; enlistment is voluntary in peacetime, but the government has the authority to conscript in emergencies; minimum 6-year education (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 849,358
females age 16-49:
832,774 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 713,223
females age 16-49:
697,197 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 27,631
female:
26,703 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.6% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Uruguay |
|
|
in Jan 2007, ICJ provisionally ruled Uruguay may begin construction of two paper mills on the Uruguay River, which forms the border with Argentina, while the court examines further whether Argentina has the legal right to stop such construction with potential environmental implications to both countries; two uncontested boundary disputes with Brazil over Isla Brasilera at the tripoint with Argentina at the confluence of the Quarai/Cuareim and Uruguay rivers, and, in the 235 square kilometer Invernada River region, over which tributary represents the legitimate source of the Quarai/Cuareim River
|
|
|
|
|
small-scale transit country for drugs mainly bound for Europe, often through sea-borne containers; law enforcement corruption; money laundering because of strict banking secrecy laws; weak border control along Brazilian frontier; increasing consumption of cocaine base and synthetic drugs
|
|
|
|
|