|
|
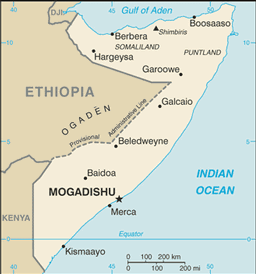
Britain withdrew from British Somaliland in 1960 to allow its protectorate to join with Italian Somaliland and form the new nation of Somalia. In 1969, a coup headed by Mohamed SIAD Barre ushered in an authoritarian socialist rule that managed to impose a degree of stability in the country for more than two decades. After the regime's collapse early in 1991, Somalia descended into turmoil, factional fighting, and anarchy. In May 1991, northern clans declared an independent Republic of Somaliland that now includes the administrative regions of Awdal, Woqooyi Galbeed, Togdheer, Sanaag, and Sool. Although not recognized by any government, this entity has maintained a stable existence and continues efforts to establish a constitutional democracy, including holding municipal, parliamentary, and presidential elections. The regions of Bari, Nugaal, and northern Mudug comprise a neighboring semi-autonomous state of Puntland, which has been self-governing since 1998 but does not aim at independence; it has also made strides toward reconstructing a legitimate, representative government but has suffered some civil strife. Puntland disputes its border with Somaliland as it also claims portions of eastern Sool and Sanaag. Beginning in 1993, a two-year UN humanitarian effort (primarily in the south) was able to alleviate famine conditions, but when the UN withdrew in 1995, having suffered significant casualties, order still had not been restored. A two-year peace process, led by the Government of Kenya under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), concluded in October 2004 with the election of Abdullahi YUSUF Ahmed as President of the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of Somalia and the formation of an interim government, known as the Somalia Transitional Federal Institutions (TFIs). The TFIs included a 275-member parliamentary body, known as the Transitional Federal Assembly (TFA). President YUSUF resigned late in 2008 while United Nations-sponsored talks between the TFG and the opposition Alliance for the Re-Liberation of Somalia (ARS) were underway in Djibouti. In January 2009, following the creation of a TFG-ARS unity government, Ethiopian military forces, which had entered Somalia in December 2006 to support the TFG in the face of advances by the opposition Islamic Courts Union (ICU), withdrew from the country. The TFA was increased to 550 seats with the addition of 200 ARS and 75 civil society members of parliament. The expanded parliament elected Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed, the former CIC and ARS chairman as president on 31 January 2009, in Djibouti. Subsequently, President SHARIF appointed Omar Abdirashid ali SHARMARKE, son of a former president of Somalia, as prime minister on 13 February 2009. The TFIs are based on the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC), which outlines a five-year mandate leading to the establishment of a new Somali constitution and a transition to a representative government following national elections. However, in January 2009 the TFA amended the TFC to extend TFG's mandate until 2011. While its institutions remain weak, the TFG continues to reach out to Somali stakeholders and to work with international donors to help build the governance capacity of the TFIs and to work toward national elections in 2011.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, east of Ethiopia
|
|
|
|
|
10 00 N, 49 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 637,657 sq km
country comparison to the world: 43
land:
627,337 sq km
water:
10,320 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Texas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,340 km
border countries:
Djibouti 58 km, Ethiopia 1,600 km, Kenya 682 km
|
|
|
|
|
3,025 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
principally desert; northeast monsoon (December to February), moderate temperatures in north and hot in south; southwest monsoon (May to October), torrid in the north and hot in the south, irregular rainfall, hot and humid periods (tangambili) between monsoons
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat to undulating plateau rising to hills in north
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Shimbiris 2,416 m
|
|
|
|
|
uranium and largely unexploited reserves of iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt, natural gas, likely oil reserves
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 1.64%
permanent crops:
0.04%
other:
98.32% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
15.7 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.29 cu km/yr (0%/0%/100%)
per capita:
400 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
recurring droughts; frequent dust storms over eastern plains in summer; floods during rainy season
|
|
|
|
|
famine; use of contaminated water contributes to human health problems; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on Horn of Africa along southern approaches to Bab el Mandeb and route through Red Sea and Suez Canal
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,112,453
country comparison to the world: 82
note:
this estimate was derived from an official census taken in 1975 by the Somali Government; population counting in Somalia is complicated by the large number of nomads and by refugee movements in response to famine and clan warfare (July 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 45% (male 2,282,325/female 2,271,707)
15-64 years:
52.5% (male 2,659,151/female 2,650,330)
65 years and over:
2.5% (male 102,941/female 145,999) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.6 years
male:
17.4 years
female:
17.7 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.809% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
43.33 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
15.24 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 37% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
4.2% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.7 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 107.42 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 5
male:
116.47 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
98.11 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 50 years
country comparison to the world: 213
male:
48.12 years
female:
51.94 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.44 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
0.5% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
24,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
1,600 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever, malaria, and Rift Valley fever
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Somali(s)
adjective:
Somali
|
|
|
|
|
Somali 85%, Bantu and other non-Somali 15% (including Arabs 30,000)
|
|
|
|
|
Sunni Muslim
|
|
|
|
|
Somali (official), Arabic, Italian, English
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
37.8%
male:
49.7%
female:
25.8% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Somalia
local long form:
Jamhuuriyada Demuqraadiga Soomaaliyeed
local short form:
Soomaaliya
former:
Somali Republic, Somali Democratic Republic
|
|
|
|
|
no permanent national government; transitional, parliamentary federal government
|
|
|
|
|
name: Mogadishu
geographic coordinates:
2 04 N, 45 22 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
18 regions (plural - NA, singular - gobolka); Awdal, Bakool, Banaadir, Bari, Bay, Galguduud, Gedo, Hiiraan, Jubbada Dhexe (Middle Jubba), Jubbada Hoose (Lower Jubba), Mudug, Nugaal, Sanaag, Shabeellaha Dhexe (Middle Shabelle), Shabeellaha Hoose (Lower Shabelle), Sool, Togdheer, Woqooyi Galbeed
|
|
|
|
|
1 July 1960 (from a merger of British Somaliland that became independent from the UK on 26 June 1960 and Italian Somaliland that became independent from the Italian-administered UN trusteeship on 1 July 1960 to form the Somali Republic)
|
|
|
|
|
Foundation of the Somali Republic, 1 July (1960); note - 26 June (1960) in Somaliland
|
|
|
|
|
25 August 1979, presidential approval 23 September 1979
note:
the formation of transitional governing institutions, known as the Transitional Federal Government, is currently ongoing
|
|
|
|
|
no national system; a mixture of English common law, Italian law, Islamic sharia, and Somali customary law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Transitional Federal President Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed (since 31 January 2009); note - a transitional governing entity with a five-year mandate, known as the Transitional Federal Institutions (TFIs), was established in October 2004; the TFIs relocated to Somalia in June 2004; in 2009, the TFI's were given a two-year extension to October 2011
head of government:
Prime Minister Omar Abdirashid Ali SHARMARKE (since 13 February 2009)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the prime minister and approved by the Transitional Federal Assembly
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
election results:
Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed elected president by the expanded Transitional Federal Assembly in Djibouti
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly
note:
unicameral Transitional Federal Assembly (TFA) (550 seats; 475 members appointed according to the 4.5 clan formula, with the remaining 75 seats reserved for civil society and business persons)
|
|
|
|
|
following the breakdown of the central government, most regions have reverted to local forms of conflict resolution, either secular, traditional Somali customary law, or sharia (Islamic) law with a provision for appeal of all sentences
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
other: numerous clan and sub-clan factions exist both in support and in opposition to the transitional government
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, CAEU, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAS, NAM, OIC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
|
|
|
|
|
Somalia does not have an embassy in the US (ceased operations on 8 May 1991); note - the Transitional Federal Government is represented in the United States through its Permanent Mission to the United Nations
|
|
|
|
|
the US does not have an embassy in Somalia; US interests are represented by the US Embassy in Nairobi, Kenya at United Nations Avenue, Nairobi; mailing address: Unit 64100, Nairobi; APO AE 09831; telephone: [254] (20) 363-6000; FAX [254] (20) 363-6157
|
|
|
|
|
light blue with a large white five-pointed star in the center; blue field influenced by the flag of the UN
|
|
|
|
|
although an interim government was created in 2004, other regional and local governing bodies continue to exist and control various regions of the country, including the self-declared Republic of Somaliland in northwestern Somalia and the semi-autonomous State of Puntland in northeastern Somalia
|
|
|
|
|
|
Despite the lack of effective national governance, Somalia has maintained a healthy informal economy, largely based on livestock, remittance/money transfer companies, and telecommunications. Agriculture is the most important sector with livestock normally accounting for about 40% of GDP and more than 50% of export earnings. Nomads and semi-pastoralists, who are dependent upon livestock for their livelihood, make up a large portion of the population. Livestock, hides, fish, charcoal, and bananas are Somalia's principal exports, while sugar, sorghum, corn, qat, and machined goods are the principal imports. Somalia's small industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, has largely been looted and the machinery sold as scrap metal. Somalia's service sector also has grown. Telecommunication firms provide wireless services in most major cities and offer the lowest international call rates on the continent. In the absence of a formal banking sector, money transfer/remittance services have sprouted throughout the country, handling up to $1.6 billion in remittances annually. Mogadishu's main market offers a variety of goods from food to the newest electronic gadgets. Hotels continue to operate and are supported with private-security militias. Due to armed attacks on and threats to humanitarian aid workers, the World Food Programme partially suspended its operations in southern Somalia in early January 2010 pending improvement in the security situation. Somalia's arrears to the IMF have continued to grow.
|
|
|
|
|
$5.731 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$5.589 billion (2008 est.)
$5.45 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$2.763 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
2.6% (2008 est.)
2.6% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$600 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 224
$600 (2008 est.)
$600 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 65%
industry:
10%
services:
25% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.447 million (few skilled laborers) (2007)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 71%
industry and services:
29% (1975)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $NA
expenditures:
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
note:
businesses print their own money, so inflation rates cannot be easily determined
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
bananas, sorghum, corn, coconuts, rice, sugarcane, mangoes, sesame seeds, beans; cattle, sheep, goats; fish
|
|
|
|
|
a few light industries, including sugar refining, textiles, wireless communication
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
280 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
260.4 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
5,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
|
|
|
|
|
1,475 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
6,387 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
5.663 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
$300 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
livestock, bananas, hides, fish, charcoal, scrap metal
|
|
|
|
|
UAE 56.8%, Yemen 21.2%, Saudi Arabia 3.7% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$798 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 176
|
|
|
|
|
manufactures, petroleum products, foodstuffs, construction materials, qat
|
|
|
|
|
Djibouti 30.3%, Kenya 7.9%, India 7.7%, US 6.2%, Oman 5.8%, UAE 5.7%, Yemen 4.9% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$3 billion (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
Somali shillings (SOS) per US dollar - NA (2007-08), 1,438.3 (2006) official rate; the unofficial black market rate was about 23,000 shillings per dollar as of February 2007
note:
the Republic of Somaliland, a self-declared independent country not recognized by any foreign government, issues its own currency, the Somaliland shilling
|
|
|
|
|
|
100,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 144
|
|
|
|
|
627,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: the public telecommunications system was almost completely destroyed or dismantled during the civil war; private companies offer limited local fixed-line service and private wireless companies offer service in most major cities while charging the lowest international rates on the continent
domestic:
local cellular telephone systems have been established in Mogadishu and in several other population centers
international:
country code - 252; international connections are available from Mogadishu by satellite (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 11 (also 1 station each in Puntland and Somaliland), shortwave 1 (in Mogadishu) (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
4 (2 in Mogadishu and 2 in Hargeisa) (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
.so
|
|
|
|
|
0 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 232
|
|
|
|
|
102,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7
over 3,047 m:
4
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 52
2,438 to 3,047 m:
4
1,524 to 2,437 m:
19
914 to 1,523 m:
23
under 914 m:
6 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22,100 km
country comparison to the world: 106
paved:
2,608 km
unpaved:
19,492 km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
country comparison to the world: 157
by type:
cargo 1
foreign-owned:
1 (UAE 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Berbera, Kismaayo
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean are high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous vessels, including commercial shipping and pleasure craft, have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; crew, passengers, and cargo are held for ransom; the presence of several naval task forces in the Gulf of Aden and additional anti-piracy measures on the part of ship operators have reduced the piracy incidents; in response local pirates shifted operations farther south along the east coast of Somalia and eastward along the coast of Oman
|
|
|
|
|
|
Somali National Forces: Somali Army (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,261,704
females age 16-49:
2,217,584 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,328,567
females age 16-49:
1,386,971 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 99,919
female:
99,771 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.9% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Somalia |
|
|
Ethiopian forces invaded southern Somalia and routed Islamist Courts from Mogadishu in January 2007; "Somaliland" secessionists provide port facilities in Berbera to landlocked Ethiopia and have established commercial ties with other regional states; "Puntland" and "Somaliland" "governments" seek international support in their secessionist aspirations and overlapping border claims; the undemarcated former British administrative line has little meaning as a political separation to rival clans within Ethiopia's Ogaden and southern Somalia's Oromo region; Kenya works hard to prevent the clan and militia fighting in Somalia from spreading south across the border, which has long been open to nomadic pastoralists
|
|
|
|
|
IDPs: 1.1 million (civil war since 1988, clan-based competition for resources) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|