|
|
Singapore was founded as a British trading colony in 1819. It joined the Malaysian Federation in 1963 but separated two years later and became independent. Singapore subsequently became one of the world's most prosperous countries with strong international trading links (its port is one of the world's busiest in terms of tonnage handled) and with per capita GDP equal to that of the leading nations of Western Europe.
|
|
|
|
|
|
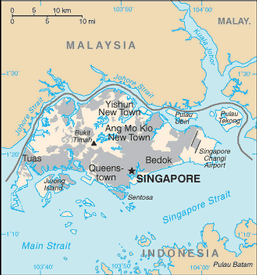
Southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia
|
|
|
|
|
1 22 N, 103 48 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 697 sq km
country comparison to the world: 192
land:
687 sq km
water:
10 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than 3.5 times the size of Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|
|
193 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 3 nm
exclusive fishing zone:
within and beyond territorial sea, as defined in treaties and practice
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
tropical; hot, humid, rainy; two distinct monsoon seasons - Northeastern monsoon (December to March) and Southwestern monsoon (June to September); inter-monsoon - frequent afternoon and early evening thunderstorms
|
|
|
|
|
lowland; gently undulating central plateau contains water catchment area and nature preserve
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Singapore Strait 0 m
highest point:
Bukit Timah 166 m
|
|
|
|
|
fish, deepwater ports
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 1.47%
permanent crops:
1.47%
other:
97.06% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 cu km (1975)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.19 cu km/yr (45%/51%/4%)
per capita:
44 cu m/yr (1975)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
industrial pollution; limited natural fresh water resources; limited land availability presents waste disposal problems; seasonal smoke/haze resulting from forest fires in Indonesia
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
focal point for Southeast Asian sea routes
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,701,069 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 14.1% (male 343,424/female 319,277)
15-64 years:
76.9% (male 1,758,670/female 1,856,862)
65 years and over:
9% (male 188,667/female 234,169) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 39.6 years
male:
39.1 years
female:
40 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.863% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
8.65 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 216
|
|
|
|
|
4.8 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
|
|
|
|
|
4.79 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 100% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
1.2% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.077 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.08 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.81 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.32 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 223
male:
2.52 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
2.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 82.06 years
country comparison to the world: 6
male:
79.45 years
female:
84.87 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 221
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
4,200 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Singaporean(s)
adjective:
Singapore
|
|
|
|
|
Chinese 76.8%, Malay 13.9%, Indian 7.9%, other 1.4% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Buddhist 42.5%, Muslim 14.9%, Taoist 8.5%, Hindu 4%, Catholic 4.8%, other Christian 9.8%, other 0.7%, none 14.8% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Mandarin 35%, English 23%, Malay 14.1%, Hokkien 11.4%, Cantonese 5.7%, Teochew 4.9%, Tamil 3.2%, other Chinese dialects 1.8%, other 0.9% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
92.5%
male:
96.6%
female:
88.6% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
3.7% of GDP (2001)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Singapore
conventional short form:
Singapore
local long form:
Republic of Singapore
local short form:
Singapore
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Singapore
geographic coordinates:
1 17 N, 103 51 E
time difference:
UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
9 August 1965 (from Malaysian Federation)
|
|
|
|
|
National Day, 9 August (1965)
|
|
|
|
|
3 June 1959; amended 1965 (based on pre-independence State of Singapore Constitution)
|
|
|
|
|
based on English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
21 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President S R NATHAN (since 1 September 1999)
note:
uses S R NATHAN but his full name and the one used in formal communications is Sellapan RAMANATHAN
head of government:
Prime Minister LEE Hsien Loong (since 12 August 2004); Senior Minister GOH Chok Tong (since 12 August 2004); Senior Minister Shunmugam JAYAKUMAR (since 1 April 2009); Minister Mentor LEE Kuan Yew (since 12 August 2004); Deputy Prime Minister TEO Chee Huan (since 1 April 2009) and Deputy Prime Minister WONG Kan Seng (since 1 September 2005)
cabinet:
appointed by president, responsible to parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for six-year term; appointed on 17 August 2005 (next election to be held by August 2011); following legislative elections, leader of majority party or leader of majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by president; deputy prime ministers appointed by president
election results:
Sellapan Rama (S R) NATHAN was appointed president in August 2005 after Presidential Elections Committee disqualified three other would-be candidates; scheduled election not held
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Parliament (84 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms); note - in addition, there are up to 9 nominated members; up to three losing opposition candidates who came closest to winning seats may be appointed as "nonconstituency" members
elections:
last held on 6 May 2006 (next to be held by 2011)
election results:
percent of vote by party - PAP 66.6%, WP 16.3%, SDA 13%, SDP 4.1%; seats by party - PAP 82, WP 1, SDA 1
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (chief justice is appointed by the president with the advice of the prime minister, other judges are appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice); Court of Appeals
|
|
|
|
|
People's Action Party or PAP [LEE Hsien Loong]; Reform Party [NG Teck Siong]; Singapore Democratic Alliance or SDA [CHIAM See Tong]; Singapore Democratic Party or SDP [CHEE Soon Juan]; Workers' Party or WP [Sylvia LIM Swee Lian]
note:
SDA includes Singapore Justice Party or SJP, Singapore National Malay Organization or PKMS, Singapore People's Party or SPP
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, AOSIS, APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, C, CP, EAS, FATF, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNMIT, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador CHAN Heng Chee
chancery:
3501 International Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 537-3100
FAX:
[1] (202) 537-0876
consulate(s) general:
San Francisco
consulate(s):
New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador David ADELMAN
embassy:
27 Napier Road, Singapore 258508
mailing address:
FPO AP 96507-0001
telephone:
[65] 6476-9100
FAX:
[65] 6476-9340
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white; near the hoist side of the red band, there is a vertical, white crescent (closed portion is toward the hoist side) partially enclosing five white five-pointed stars arranged in a circle
|
|
|
|
|
|
Singapore has a highly developed and successful free-market economy. It enjoys a remarkably open and corruption-free environment, stable prices, and a per capita GDP higher than that of most developed countries. The economy depends heavily on exports, particularly in consumer electronics, information technology products, pharmaceuticals, and on a growing financial services sector. Real GDP growth averaged 6.8% between 2004 and 2008, but contracted 2.1% in 2009 as a result of the global financial crisis. The economy has begun to rebound in 2010 and the government predicts growth of 3-5% for the year. Over the longer term, the government hopes to establish a new growth path that focuses on raising productivity growth, which has sunk to 1% per year in the last decade. Singapore has attracted major investments in pharmaceuticals and medical technology production and will continue efforts to establish Singapore as Southeast Asia's financial and high-tech hub.
|
|
|
|
|
$235.7 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$240.7 billion (2008 est.)
$238.1 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$165 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-2.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
1.1% (2008 est.)
7.8% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$50,300 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$52,200 (2008 est.)
$52,300 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0%
industry:
26.8%
services:
73.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.03 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0%
industry:
23.8%
services:
76.2% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
2.2% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 4.4%
highest 10%:
23.2% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
48.1 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
29.9% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $21.29 billion
expenditures:
$24.14 billion
note:
expenditures exclude public debt, financial transfers, and development estimates (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
117.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
99.2% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
6.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.38% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
5.38% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$52.57 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 22
$44.4 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$179 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 16
$162.2 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$143.6 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 36
$129.2 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$474.8 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 31
$268.6 billion (31 December 2008)
$353.5 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
orchids, vegetables; poultry, eggs; fish, ornamental fish
|
|
|
|
|
electronics, chemicals, financial services, oil drilling equipment, petroleum refining, rubber processing and rubber products, processed food and beverages, ship repair, offshore platform construction, life sciences, entrepot trade
|
|
|
|
|
-4.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
41.72 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
37.94 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8,553 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
934,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
1.289 million bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
2.109 million bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
8.27 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|
|
8.27 billion cu m
country comparison to the world: 26
note:
from Indonesia and Malaysia (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
$26.22 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
$26.9 billion (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$268.9 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
$342.7 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment (including electronics), consumer goods, pharmaceuticals and other chemicals, mineral fuels
|
|
|
|
|
Hong Kong 11.6%, Malaysia 11.5%, US 11.2%, Indonesia 9.7%, China 9.7%, Japan 4.6% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$245 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$318.7 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, mineral fuels, chemicals, foodstuffs, consumer goods
|
|
|
|
|
US 14.7%, Malaysia 11.6%, China 10.5%, Japan 7.6%, Indonesia 5.8%, South Korea 5.7% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$187.8 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
$174.2 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$19.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
$25.52 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$264.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$250.2 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$177.9 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$202.7 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Singapore dollars (SGD) per US dollar - 1.4545 (2009), 1.415 (2008), 1.507 (2007), 1.5889 (2006), 1.6644 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Singapore |
|
|
1.857 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
6.375 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: excellent service
domestic:
excellent domestic facilities; launched 3G wireless service in February 2005; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is nearly 175 telephones per 100 persons
international:
country code - 65; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations -4; supplemented by VSAT coverage (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 19, shortwave 1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (broadcasting on 8 channels); additional reception of numerous UHF and VHF signals originating in Malaysia and Indonesia (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.sg
|
|
|
|
|
864,943 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
3.37 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Singapore |
|
|
8 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 106 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,325 km
country comparison to the world: 163
paved:
3,325 km (includes 161 km of expressways) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,292
country comparison to the world: 5
by type:
bulk carrier 167, cargo 87, carrier 5, chemical tanker 209, container 273, liquefied gas 96, petroleum tanker 386, refrigerated cargo 5, roll on/roll off 4, specialized tanker 7, vehicle carrier 53
foreign-owned:
774 (Australia 12, Bangladesh 2, Belgium 8, Chile 6, China 14, Cyprus 1, Denmark 87, France 1, Germany 24, Greece 15, Hong Kong 47, India 13, Indonesia 66, Italy 5, Japan 131, South Korea 3, Malaysia 27, Norway 143, Slovenia 1, Sweden 20, Switzerland 2, Taiwan 72, Thailand 23, UAE 12, UK 17, US 22)
registered in other countries:
331 (Australia 1, Bahamas 17, Belize 2, Bolivia 1, Cambodia 4, Cayman Islands 10, Comoros 1, Cyprus 3, Dominica 7, France 2, Honduras 12, Hong Kong 18, Indonesia 27, Isle of Man 1, Kiribati 4, Liberia 32, Malaysia 16, Marshall Islands 18, Mongolia 9, Norway 1, Panama 100, Philippines 1, Saint Kitts and Nevis 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 4, Thailand 2, Tuvalu 23, US 12, unknown 2) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Singapore
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous commercial vessels have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia; crews have been murdered or cast adrift
|
|
|
|
|
|
Singapore Armed Forces: Army, Navy, Air Force (includes Air Defense) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-21 years of age for male compulsory military service; 16 years of age for volunteers; 2-year conscript service obligation, with a reserve obligation to age 40 (enlisted) or age 50 (officers) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,266,426 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,027,701
females age 16-49:
1,097,762 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 27,430
female:
25,918 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.9% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Singapore |
|
|
disputes persist with Malaysia over deliveries of fresh water to Singapore, Singapore's extensive land reclamation works, bridge construction, and maritime boundaries in the Johor and Singapore Straits; in 2008, ICJ awards sovereignty of Pedra Branca (Pulau Batu Puteh/Horsburgh Island) to Singapore, and Middle Rocks to Malaysia, but does not rule on maritime regimes, boundaries, or disposition of South Ledge; Indonesia and Singapore continue to work on finalization of their 1973 maritime boundary agreement by defining unresolved areas north of Indonesia's Batam Island; piracy remains a problem in the Malacca Strait
|
|
|
|
|
drug abuse limited because of aggressive law enforcement efforts; as a transportation and financial services hub, Singapore is vulnerable, despite strict laws and enforcement, as a venue for money laundering
|
|
|
|
|